請於注射完成之後啟動綠色安全保護裝置 ( 滑動超過針頭 ) 單次使用型預充針筒上的灰色針頭套含有乾燥天然橡膠成分 ( 一種乳膠衍生物 ); 對乳膠過敏者不可碰觸此針頭套 步驟 1: 移除灰色針頭套 移除針頭套. 步驟 2: 進行注射 插入針頭並將所有液體注入體內 切勿將灰色針頭套套回針頭 步驟 3:
|
|
|
- 暑 裴
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TM 保骼麗注射液 Prolia (denosumab) 衛署菌疫輸字第 號 1 適應症 治療有骨折高風險性之停經後婦女骨質疏鬆症 說明 : 有骨折高風險性之停經後婦女骨質疏鬆症, 包含下列任一狀況 : 有骨質疏鬆症骨折病史 具有多項骨折危險因子 先前接受其他骨質疏鬆症療法失敗或無法耐受其他骨質疏鬆症療法之病患 對患有骨質疏鬆症之停經後婦女,Prolia 可降低脊椎 非脊椎和髖骨骨折的發生率 2 劑量與用法 本藥限由醫師使用 2.1 建議劑量 施打 Prolia 應由健康照護專業人員來進行 Prolia 的建議劑量為每 6 個月一次皮下注射單劑 60 毫克 請以皮下注射的方式將 Prolia 施打於上臂 大腿或腹部 所有的患者都應每天補充 1000 毫克的鈣質與至少 400 IU 的維生素 D [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.1)] 如果漏打一劑 Prolia, 應於患者方便時儘快施打 之後再從最後一次注射的日期算起, 排定每 6 個月一次的注射時間 2.2 準備與施打 在注射 Prolia 之前, 應目視檢查溶液是否有微粒異物或變色的現象 Prolia 為無色至淡黃色的澄清溶液, 並可能含有微量的透明至白色的蛋白質微粒 如果溶液有變色或混濁的現象, 或溶液中含有許多顆粒或微粒異物, 請不要使用 乳膠過敏 : 對乳膠過敏者不可碰觸單次使用型預充針筒上的灰色針頭套, 因為此針頭套含有乾燥天然橡膠成分 ( 一種乳膠衍生物 ) 在施打之前, 可先將 Prolia 自冰箱中取出, 然後讓其在原始包裝盒中的情況下自然回溫 ( 最高不超過 25 C/77 F) 此過程通常需要 15 至 30 分鐘 切勿以任何其他方式將 Prolia 加溫 [ 參見包裝規格 / 貯存與操作 (14)] 附有針頭安全保護裝置之預充針筒的使用指示 重要注意事項 : 為盡可能避免意外針頭刺傷,Prolia 單次使用型預充針筒附有一個綠色的安全保護裝置 ; 注射完成之後即可手動啟動此安全保護裝置 切勿在進行注射之前將綠色安全保護裝置向前滑動超過針頭 ; 它會鎖住並阻礙注射 推桿 安全保護裝置 ( 綠色塑膠製 ) 視窗 針頭套 ( 灰色橡膠製 ) 手指握把 ( 透明塑膠製 )
2 請於注射完成之後啟動綠色安全保護裝置 ( 滑動超過針頭 ) 單次使用型預充針筒上的灰色針頭套含有乾燥天然橡膠成分 ( 一種乳膠衍生物 ); 對乳膠過敏者不可碰觸此針頭套 步驟 1: 移除灰色針頭套 移除針頭套. 步驟 2: 進行注射 插入針頭並將所有液體注入體內 切勿將灰色針頭套套回針頭 步驟 3: 立即將綠色安全保護裝置滑動超過針頭 將針頭指向離開您的方向 用一隻手握住預充針筒上的透明塑膠製手指握把 然後用另一隻手握住綠色安全保護裝置的底部, 並輕輕將其向著針頭的方向滑動, 直到綠色安全保護裝置牢固地鎖定在位置上並 ( 或 ) 聽到 卡嗒 的聲音為止 切勿將綠色安全保護裝置抓得太緊 您只要輕輕地握住並滑動, 它就會很容易移動 握住透明的手指握把 輕輕地將綠色安全保護裝置滑動超過針頭並牢固地鎖定在位置上 將綠色安全保護裝置滑動超過針頭時, 切勿抓得太緊 立即將針筒與針頭套棄入旁邊的尖銳廢棄物收集容器中 切勿將針頭套套回使用過的針筒 3 劑型與劑量規格 1 毫升裝的單次使用型預充針筒, 每支預充針筒裝有 60 毫克 / 毫升的溶液
3 4 禁忌 4.1 低血鈣症 在開始使用 Prolia 治療之前, 必須先矯治既有的低血鈣症 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.1)] 5 警語和注意事項 5.1 低血鈣症與礦物質代謝 低血鈣症可能會因使用 Prolia 而惡化 在開始使用 Prolia 治療之前, 必須先矯治既有的低血鈣症 對容易發生低血鈣症與礦物質代謝障礙的患者 ( 例如有副甲狀腺功能低下病史 曾接受甲狀腺手術 副甲狀腺手術 患有營養吸收障礙症候群 小腸已切除 嚴重腎功能受損 [ 肌酸酐廓清率 <30 毫升 / 分鐘 ] 或正在接受透析治療 ), 強烈建議針對血鈣與礦物質濃度 ( 磷和鎂 ) 進行臨床監視 對嚴重腎功能受損 [ 肌酸酐廓清率 <30 毫升 / 分鐘 ] 或正在接受透析治療的患者, 施打 Prolia 後發生低血鈣症是一個相當重大的風險 請告知嚴重腎功能受損的患者 ( 包括正在接受透析治療的患者 ) 低血鈣症的症狀, 以及適量補充鈣質與維生素 D 以維持血鈣濃度的重要性 所有患者都應適量補充鈣質與維生素 D [ 參見劑量與用法 (2.1) 禁忌 (4.1) 不良反應 (6.1) 以及病患諮詢須知 (15.1)] 5.2 嚴重感染 在一項針對超過 7800 位患有停經後骨質疏鬆症之婦女所進行的臨床試驗中,Prolia 組因發生嚴重感染而住院治療的通報頻率要高於安慰劑組 [ 參見不良反應 (6.1)] 嚴重皮膚感染以及腹部 泌尿道及耳朵的感染都是在使用 Prolia 治療的患者中較為常見 心內膜炎在接受 Prolia 治療之受試者中的通報頻率也較高 在伺機性感染的發生率方面, 安慰劑組與 Prolia 組大致相當, 各治療組中的整體感染發生率也很類似 請告知患者, 如果他們出現嚴重感染 ( 包括蜂窩性組織炎 ) 的徵兆或症狀, 應立即就醫診治 併用免疫抑制劑或免疫系統受損的患者發生嚴重感染的風險可能會升高 對此類患者, 在開始使用 Prolia 之前應先衡量效益 - 風險狀況 對在使用 Prolia 期間發生嚴重感染的患者, 處方醫師應評估繼續使用 Prolia 治療的必要性 5.3 皮膚不良反應 在一項針對超過 7800 位患有停經後骨質疏鬆症之婦女所進行的大型臨床試驗中, 表皮與皮膚方面的不良事件, 如皮膚炎 濕疹與皮疹, 在 Prolia 組中的發生率明顯高於安慰劑組 這些事件大部份並非僅發生於注射部位 [ 參見不良反應 (6.1)] 如果出現嚴重的症狀, 應考慮停用 Prolia 5.4 顎骨壞死 顎骨壞死 (ONJ) 會自然發生, 且通常和拔牙及 ( 或 ) 局部感染後癒合延遲有關 在接受 denosumab 治療的患者中曾有發生 ONJ 的報告 [ 參見不良反應 (6.1)] 在開始使用 Prolia 治療之前, 應由處方醫師進行常規的口腔檢查 對併有發生 ONJ 之危險因子的患者, 在開始使用 Prolia 治療之前, 應考慮進行牙科檢查並採取適當的口腔預防措施, 這些危險因子包括侵入性的牙科處置 ( 如拔牙 植牙 口腔手術 ) 確診的癌症 合併其他治療 ( 如化學療法 皮質類固醇 ) 口腔衛生不良 以及合併症 ( 如牙周病及 ( 或 ) 其它既有的牙科疾病 貧血 凝血病變 感染 假牙密合不良 ) 使用 Prolia 治療期間應維持良好的口腔衛生習慣 對須進行侵入性牙科處置的患者, 治療醫師及 ( 或 ) 口腔外科醫師在進行臨床判斷時依據個人的效益 - 風險評估結果來擬訂個別病患的處置計劃 疑似有 ONJ 現象或在使用 Prolia 期間發生 ONJ 的患者應接受牙醫師或口腔外科醫師的照護 對此類患者, 以大範圍的牙科手術來治療 ONJ 可能會使病情更加惡化 應依據個人的效益 - 風險評估結果來考慮是否要停止使用 Prolia 治療 5.5 對骨代謝的抑制作用 在針對患有停經後骨質疏鬆症之婦女所進行的臨床試驗中, 骨代謝指標與骨骼組織形態學的評估結果顯示, 使用 Prolia 治療會使骨再塑作用受到明顯的抑制 [ 參見臨床藥理學 (11.2) 臨床研究 (13.1)] 目前並不確知這些發現的意義與長期使用 Prolia 治療的影響 使用 Prolia 時所觀察到的骨再塑抑制程度若長
4 期維持不輟, 可能會引發不良的結果, 如顎骨壞死 非典型骨折 以及骨折癒合延遲 請監視患者是否出現這些結果 6 不良反應 下列嚴重不良反應除了在下文中會論及之外, 在本仿單的其他段落中也有詳細的說明 : 低血鈣症 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.1)] 嚴重感染 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.2)] 皮膚不良反應 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.3)] 顎骨壞死 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.4)] 使用 Prolia 時最常通報的不良反應為背痛 四肢疼痛 肌肉骨骼疼痛 高膽固醇血症 以及膀胱炎 最常導致停用 Prolia 的不良反應為乳癌 背痛及便秘 GSK 與 Amgen 現行有一套全面的全球藥物安全監測計畫, 目的在於蒐集所需的資訊, 協助進一步評估全球風險管理計畫 (RMP) 中提到的風險並界定其特徵 GSK 台灣分公司將追蹤安全性監測重點的所有安全疑慮, 並於獲得安全性問題時, 立即向當地主管機關通報任何安全方面的問題 當地通報的安全性事件將傳送至全球資料庫內, 並且定期檢視當地文獻, 查看是否有與 denosumab 使用相關不良反應的報告 此外, 利用國際資料庫, 產生所需的基礎資訊, 及早找出並評估任何安全性問題的訊號並進行偵測 針對此類安全性數據進行的分析與訊號偵測將納入定期安全性更新報告 (PSUR) 中 目前透過 Prolia 上市後主動安全性監視計劃向處方醫師收集特定不良事件方面的資訊 若需更多此計劃的相關資訊, 請參見網站 或撥打電話 (02) 詢問 6.1 臨床試驗的經驗 由於臨床研究的進行條件差異極大, 因此, 在一種藥物的臨床研究中所觀察到的不良反應發生率, 不可直接和另一種藥物之臨床研究中的發生率進行比較, 也可能無法反映臨床實務中所觀察到的發生率 治療患有骨質疏鬆症的停經後婦女 有一項針對 7808 位 60 至 91 歲之停經後婦女所進行的 3 年 隨機 雙盲 安慰劑對照性跨國研究曾評估過使用 Prolia 治療停經後骨質疏鬆症的安全性 共有 3876 位婦女使用安慰劑, 另有 3886 位婦女每 6 個月一次皮下注射單劑 60 毫克的 Prolia 所有婦女都被要求每天補充至少 1000 毫克鈣質與 400 IU 維生素 D 在安慰劑組中, 所有導因之死亡的發生率為 2.3% (n=90), 在 Prolia 組中則為 1.8% (n=70) 在安慰劑組中, 非致命性嚴重不良事件的發生率為 24.2%, 在 Prolia 組中則為 25.0% 在安慰劑組和 Prolia 組中, 因發生不良事件而退出研究的病患比例分別為 2.1% 與 2.4% 在患有骨質疏鬆症之停經後婦女中的通報率 2%, 且在接受 Prolia 治療之婦女中的發生頻率高於接受安慰劑治療之婦女的不良反應如下表所示 系統器官類別選用名詞 血液與淋巴系統疾患 表 1. 在骨質疏鬆症患者中之發生率 2%, 且發生頻率高於接受安慰劑治療之患者的不良反應 Prolia (N=3886) n (%) 安慰劑 (N=3876) n (%) 貧血 129 (3.3) 107 (2.8) 心臟疾患
5 心絞痛 101 (2.6) 87 (2.2) 心房纖維顫動 79 (2.0) 77 (2.0) 耳朵與內耳迷路疾患暈眩 195 (5.0) 187 (4.8) 胃腸道疾患上腹痛 129 (3.3) 111 (2.9) 脹氣 84 (2.2) 53 (1.4) 胃食道逆流 80 (2.1) 66 (1.7) 全身性疾患與投藥部位症狀周邊水腫 189 (4.9) 155 (4.0) 無力 90 (2.3) 73 (1.9) 感染與寄生蟲感染膀胱炎 228 (5.9) 225 (5.8) 上呼吸道感染 190 (4.9) 167 (4.3) 肺炎 152 (3.9) 150 (3.9) 咽炎 91 (2.3) 78 (2.0) 帶狀皰疹 79 (2.0) 72 (1.9) 代謝與營養疾患高膽固醇血症 280 (7.2) 236 (6.1) 肌肉骨骼與結締組織疾患背痛 1347 (34.7) 1340 (34.6) 四肢疼痛 453 (11.7) 430 (11.1) 肌肉骨骼疼痛 297 (7.6) 291 (7.5) 骨骼疼痛 142 (3.7) 117 (3.0) 肌痛 114 (2.9) 94 (2.4) 脊椎骨關節炎 82 (2.1) 64 (1.7) 神經系統疾患坐骨神經痛 178 (4.6) 149 (3.8) 精神疾患失眠 126 (3.2) 122 (3.1) 皮膚與皮下組織疾患皮疹 96 (2.5) 79 (2.0) 搔癢 87 (2.2) 82 (2.1) 低血鈣症 在第 1 個月回診時, 安慰劑組有 0.4% 之婦女的血鈣濃度下降至低於 8.5 mg/dl 的程度,Prolia 組則有
6 1.7% 在腎功能正常的受試者中, 血鈣濃度的最低值大約會出現於投予 Prolia 後的第 10 天 在臨床研究中, 和腎功能正常的受試者相比較, 腎功能受損的受試者較容易發生較大程度的血鈣濃度降低現象 在一項針對 55 位腎功能程度各異之患者所進行的研究中, 有 5 位受試者出現血鈣濃度 <7.5 mg/dl 的現象或是發生症狀性低血鈣症 在這項研究的受試者中, 並無任何受試者屬於腎功能正常組, 有 10% 的受試者屬於 CrCL 50 至 80 毫升 / 分鐘組, 有 29% 的受試者屬於 CrCL<30 毫升 / 分鐘組, 並有 29% 的受試者屬於血液透析組 這些受試者皆未補充鈣質與維生素 D 在一項針對 4,550 位患有骨質疏鬆症之停經後婦女所進行的研究中, 投予 Prolia 10 天之後, 肌酸酐廓清率 <30 毫升 / 分鐘之受試者中的血鈣濃度相較於基礎值的平均變化為 -5.5%, 在 CrCL>30 毫升 / 分鐘的受試者中則為 -3.1% 嚴重感染 細胞核因子 kappa-b 配體接受體活化因子 (RANKL) 會表現於活化的 T 與 B 淋巴球上及淋巴結中 因此, RANKL 抑制劑 ( 如 Prolia) 可能會升高感染的風險 在針對 7808 位患有骨質疏鬆症之停經後婦女所進行的臨床研究中, 因感染而導致死亡的發生率在安慰劑組與 Prolia 治療組中皆為 0.2% 不過, 在安慰劑組中, 非致命性嚴重感染的發生率為 3.3%, 在 Prolia 組中則為 4.0% 曾有因腹部 ( 安慰劑組 0.7%,Prolia 組 0.9%) 泌尿道 ( 安慰劑組 0.5%,Prolia 組 0.7%) 及耳朵 ( 安慰劑組 0.0%,Prolia 組 0.1%) 發生嚴重感染而住院治療的報告 在使用安慰劑的患者中並無任何發生心內膜炎的報告, 而接受 Prolia 治療的患者則有 3 位發生心內膜炎 須住院治療的皮膚感染, 包括丹毒與蜂窩性組織炎, 在使用 Prolia 治療之患者中的通報頻率較高 ( 安慰劑組 <0.1%,Prolia 組 0.4%) 在伺機性感染的通報率方面, 兩組相當 皮膚反應 在使用 Prolia 治療的患者中, 發生表皮與皮膚不良事件 ( 如皮膚炎 濕疹與皮疹 ) 的病例數明顯較多, 這些事件在安慰劑組中的通報率為 8.2%,Prolia 組則為 10.8% (p <0.0001) 這些事件大部份並非僅發生於注射部位 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.3)] 顎骨壞死 在骨質疏鬆症臨床試驗計劃中, 使用 Prolia 治療的患者曾有發生 ONJ 的報告 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.4)] 胰臟炎 在安慰劑組中有 4 位患者 (0.1%) 通報發生胰臟炎, 在 Prolia 組中則有 8 位 (0.2%) 在這些通報病例中, 安慰劑組有一位受試者屬於嚴重事件,Prolia 組則是 8 位受試者全部屬於嚴重事件, 其中並包括一個死亡病例 有數位患者有胰臟炎過往病史 從投予產品到事件發生所經過的時間各不相同 新發生的惡性腫瘤 在安慰劑組中, 新惡性腫瘤的整體發生率為 4.3%,Prolia 組則為 4.8% 曾有發生和乳房 ( 安慰劑組 0.7%, Prolia 組 0.9%) 生殖系統 ( 安慰劑組 0.2%,Prolia 組 0.5%) 及胃腸系統 ( 安慰劑組 0.6%,Prolia 組 0.9%) 相關之新惡性腫瘤的報告 其與使用藥物之間的因果關係尚未確立 免疫生成性 Denosumab 是一種人類單株抗體 和所有的治療用蛋白質製劑一樣, 本品也可能具有免疫生成性 利用一種電化學發光橋接免疫分析法 (electrochemiluminescent bridging immunoassay) 進行檢測之後, 在使用 Prolia 治療長達 5 年的患者中, 結合性抗體檢測結果呈陽性反應 ( 包括原先即有抗體 短暫出現抗體 以及生成抗體 ) 的比例不到 1% (8113 位患者中有 55 例 ) 再利用一種以化學發光細胞為基礎的體外生物分析法進行評估, 結果並無任何患者的中和性抗體檢測結果呈陽性反應 並無任何證據顯示生成結合性抗體會使藥物動力學概況 毒性概況或臨床反應發生改變 生成抗體的發生率極為倚賴分析方法的敏感度與特異性 此外, 所觀察到的陽性抗體 ( 包括中和性抗體 ) 檢測結果的發生率可能會受到多種因素的影響, 包括分析的方法 樣本的處理方式 採樣的時間
7 點 併用的藥物 以及基礎疾病 基於這些原因, 將 denosumab 引發抗體的情形和其他產品引發抗體的發生率進行比較可能會造成誤導 7 藥物交互作用 目前尚未針對 Prolia 進行過任何藥物 - 藥物交互作用研究 8 特殊族群之使用 8.1 懷孕 妊娠用藥分級 C 目前尚無任何適當且控制良好的對孕婦使用 Prolia 的研究 在利用基因移除法去除 RANK 配體 (RANKL) 的基因工程小鼠 ( 基因剔除小鼠 ) 中, 缺乏 RANKL (denosumab 的作用目標 ) 會導致胎兒淋巴結發育不良, 並會影響仔鼠出生後的齒列及骨骼生長 懷孕的 RANKL 基因剔除小鼠也會出現母體乳腺成熟作用改變, 繼而導致產後泌乳減少的現象 [ 參見特殊族群之使用 (8.3)] Prolia 僅核准用於停經後的婦女 只有在潛在效益超越胎兒可能面臨之風險的情況下, 才可於懷孕期間使用 Prolia 於使用 Prolia 治療期間懷孕的婦女最好能夠通報 GSK 台灣分公司納入懷孕監視計劃 此為例行的藥物安全監控措施, 所有在接受 denosumab 治療期間懷孕的婦女皆可撥打電話 進行通報 在一項胚胎胎兒發育研究中, 曾對食蟹猴於器官生成期間每週皮下注射一次劑量最高較人類建議劑量 ( 每 6 個月一次投予 60 毫克 ) 高出 13 倍的 denosumab ( 以體重 [ 毫克 / 公斤 ] 為比較基礎 ) 結果並未發現任何顯示發生母體毒性或造成胎兒傷害的證據 不過, 這項研究僅評估了相當於第一孕期階段的胎兒毒性, 且並未檢查胎兒的淋巴結 隨著懷孕的進展, 單株抗體會以線性模式通過胎盤, 並以第三孕期的通過量最大 目前尚未針對動物評估過投予藥物在第二與第三孕期間所可能造成的不良發育影響 [ 參見非臨床毒理學 (12.2)] 8.2 授乳母親 目前並不確知 Prolia 是否會分泌進入人類的乳汁 由於許多藥物都會分泌進入人類的乳汁, 且 Prolia 可能會使餵哺母乳的嬰兒發生嚴重的不良反應, 因此應考慮本藥對母親的重要性, 然後做出是否要停止餵哺母乳還是停用本藥的決定 針對缺乏 RANK/RANKL 傳訊通路 (signaling pathway) 之懷孕小鼠所進行的動物研究顯示, 母體乳腺成熟作用會發生改變, 繼而導致產後泌乳減少, 根據這些研究, 母體在懷孕期間接觸 Prolia 可能會影響乳腺發育及泌乳作用 [ 參見非臨床毒理學 (12.2)] 8.3 兒童之使用 Prolia 並不建議用於兒童病患 Prolia 在兒童病患中的安全性及有效性尚未確立 使用 Prolia 治療可能會影響生長板尚未閉合之兒童的骨骼生長, 也可能會抑制齒列生長 在初生大鼠中, 以一種由蝕骨細胞抑制因子 (osteoprotegerin) 與 Fc 結合而成的結構 (OPG-Fc) ( 在 10 毫克 / 公斤的劑量下 ) 抑制 RANKL (Prolia 的作用目標 ), 結果會伴隨發生骨骼生長及牙齒生長受到抑制的現象 在投予劑量較人類建議劑量 ( 每 6 個月一次投予 60 毫克 ) 高出 10 倍及 50 倍 (10 及 50 毫克 / 公斤 ) 之 denosumab ( 以體重 [ 毫克 / 公斤 ] 為比較基礎 ) 的青少年期靈長類動物中, 曾發現生長板異常的現象 [ 參見非臨床毒理學 (12.2)] 8.4 老年人之使用 在所有參與 Prolia 臨床研究的患者中, 有 9943 位患者 (76%) 65 歲, 並有 3576 位 (27%) 75 歲 在這些患者與較年輕的患者之間, 並未發現任何安全性或療效方面的整體性差異, 在其他見於報告的臨床經驗中也未發現較年長與較年輕的患者之間有治療反應方面的差異, 但不能排除某些較年長的患者較為敏感的可能性 8.5 腎功能損害 對腎功能受損的患者, 並不須調整劑量
8 臨床研究顯示, 嚴重腎功能受損 ( 肌酸酐廓清率 <30 毫升 / 分鐘 ) 或正在接受透析治療的患者發生低血鈣症的風險較高 對嚴重腎功能受損或正在接受透析治療的患者投予 Prolia 時, 應權衡其效益風險概況 強烈建議針對血鈣與礦物質濃度 ( 磷和鎂 ) 進行臨床監視 對嚴重腎功能受損或正在接受透析治療的患者, 適量補充鈣質與維生素 D 是極為重要的一環 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.1) 不良反應 (6.1) 及臨床藥理學 (11.3)] 8.6 肝功能損害 目前尚無任何臨床研究評估過肝功能損害對 Prolia 之藥物動力學的影響 9 過量 目前尚無任何 Prolia 使用過量的經驗 10 性狀說明 Prolia (denosumab) 是一種對人類 RANKL ( 細胞核因子 kappa-b 配體接受體活化因子 ) 具有親和力及專一性的人類 IgG2 單株抗體 Denosumab 的分子量約為 147 kda, 並且是透過基因工程技術在哺乳類動物 ( 中國倉鼠卵巢 ) 的細胞中製造而得 Prolia 為無菌 不含防腐劑 無色至淡黃色的澄清溶液 每 1 毫升單次使用型預充針筒裝的 Prolia 含有 60 毫克 denosumab (60 毫克 / 毫升溶液 ) 4.7% 山梨醇 17 mm 醋酸 0.01% 聚山梨醇 20 注射用水 (USP), 並以氫氧化鈉將 ph 值調整至 臨床藥理學 11.1 作用機制 Prolia 會與 RANKL 結合,RANKL 是一種對蝕骨細胞 ( 會產生骨蝕作用的細胞 ) 之形成 功能與存活極為重要的穿膜蛋白或可溶性蛋白 Prolia 可阻止 RANKL 活化其接受體, 亦即蝕骨細胞及其前驅物表面上的 RANK 遏阻 RANKL/RANK 間的交互作用可抑制蝕骨細胞的形成 功能與存活, 因此可降低骨蝕作用 (bone resorption), 並提高皮質骨及小樑骨的骨量與強度 11.2 藥效學 在臨床研究中, 使用 60 毫克的 Prolia 治療可使骨蝕作用指標血清第 1 型碳端胜肽 (C-telopeptides;CTX) 在 3 天內降低約 85%, 並於 1 個月內達到最大降低效果 在投予 Prolia 1-3 個月後, 有 39-68% 之受試者的 CTX 濃度低於分析定量測定的下限 (0.049 ng/ml) 在每次投藥間隔終了時, 由於 denosumab 的血清濃度下降,CTX 降低的效果會出現部份減弱的現象, 從最高的降低 87% 減弱至 45% ( 範圍為 45-80%), 這表示 Prolia 對骨再塑作用 (bone remodelling) 的影響具有可逆性 這些作用在持續治療期間會一直維持不輟 重新開始治療之後,CTX 被 Prolia 抑制的程度和在剛開始使用 Prolia 治療之患者中所見的情形大致相當 骨再塑過程中的骨生成作用 (bone formation) 與骨蝕作用在生理上是互相聯絡的 (physiological coupling), 因此, 骨生成作用的指標 ( 如骨鈣素 [osteocalcin] 與第 I 型前膠原蛋白氮端胜肽 [P1NP]) 在投予第一劑 Prolia 一個月後也會開始出現降低的現象 在停止使用 Prolia 治療之後, 骨蝕作用的指標會升高至較治療前的檢測值高出 40-60% 的程度, 但在 12 個月內便會回復至基礎值 11.3 藥物動力學 在一項針對健康男性及女性志願者 (n=73, 年齡範圍 :18 至 64 歲 ) 所進行的研究中, 於禁食 ( 至少 12 小時 ) 後皮下注射單劑 60 毫克的 Prolia 之後,denosumab 的平均最高濃度 (C max ) 為 6.75 mcg/ml ( 標準偏差 [SD]=1.89 mcg/ml) 達到 denosumab 最高濃度的中位時間 (T max ) 為 10 天 ( 範圍 :3 至 21 天 ) 達到 C max 之後, denosumab 的血清濃度在 4 至 5 個月期間會持續下降, 這段期間的平均半衰期為 25.4 天 (SD=8.5 天 ; n=46) Denosumab 的 16 週濃度經時曲線下面積 (AUC 0-16 weeks ) 的平均值為 316 mcg day/ml (SD=101 mcg day/ml) 以每 6 個月皮下注射一次 60 毫克的方式投予多重劑量之後,denosumab 的藥物動力學並未出現任何隨時間而蓄積或改變的現象
9 Prolia 的藥物動力學並不會因結合性抗體的生成而受到影響 曾在一項群體藥物動力學分析中評估人口統計學特性的影響 這項分析顯示, 藥物動力學並不會因年齡 ( 停經後婦女 ) 種族或體重 (36 至 140 公斤 ) 而出現明顯的差異 藥物交互作用 目前尚未針對 Prolia 進行過任何的藥物 - 藥物交互作用研究 特殊族群 性別 : 在一項針對 50 歲之健康男性所進行的研究中, 所觀察到的 denosumab 平均血清濃度經時變化曲線和一項針對停經後婦女使用相同劑量療程之研究中所觀察到的結果大致相似 年齡 : 在參與研究的所有族群中 ( 年齡範圍為 歲 ),denosumab 的藥物動力學並未因年齡而受到影響 種族 :Denosumab 的藥物動力學並不會因種族而受到影響 腎功能損害 : 在一項針對 55 位腎功能程度各異之患者 ( 包括接受透析治療的患者 ) 所進行的研究中, 腎功能受損的程度並未對 denosumab 的藥物動力學造成任何影響 ; 因此, 並不須因腎功能受損而調整劑量 肝功能損害 : 目前尚無任何臨床研究評估過肝功能損害對 denosumab 之藥物動力學的影響 12 非臨床毒理學 12.1 致癌性 致突變性 生育力損害 致癌性 長期動物研究中未評估過 denosumab 的致癌性 致突變性 denosumab 的基因毒性並未被評估 生育力損害 在較人類建議劑量 ( 每 6 個月一次投予 60 毫克 ) 高出 倍 ( 以體重 [ 毫克 / 公斤 ] 為比較基礎 ) 的劑量下, denosumab 並不會對母猴的生育力或公猴的生殖器官造成任何影響 12.2 動物毒理學及 ( 或 ) 藥理學 Prolia 是一種蝕骨細胞骨蝕作用抑制劑 ( 經由抑制 RANKL 功用 ) 對切除卵巢的母猴, 每月一次使用劑量較人類建議劑量 ( 每 6 個月一次投予 60 毫克 ) 高出 50 倍 ( 以體重 [ 毫克 / 公斤 ] 為比較基礎 ) 的 denosumab 治療, 可抑制骨代謝作用, 並提高海綿骨與皮質骨的骨密度 (BMD) 與強度 ; 骨骼組織都很正常, 並未發現任何礦化不足 類骨質蓄積或出現網狀骨的跡象 在使用劑量較人類建議劑量 ( 每 6 個月一次投予 60 毫克 ) 高出 10 倍 (10 及 50 毫克 / 公斤 ) 之 denosumab ( 以體重 [ 毫克 / 公斤 ] 為比較基礎 ) 治療的青少年期靈長類動物中, 曾發現生長板異常的現象, 一般認為這和 denosumab 的藥理作用相符合 [ 參見特殊族群之使用 (8.4)] 由於 denosumab 在動物中的生物活性僅可見於非人類的靈長類動物, 因此, 對基因工程 ( 基因剔除 ) 小鼠進行評估或使用其他的 RANK/RANKL 途徑生物抑制劑 ( 即 OPG-Fc), 應可提供額外的 denosumab 藥效學特性相關資訊 RANK/RANKL 基因剔除小鼠會出現缺少淋巴結生成, 並會因乳腺成熟 ( 懷孕期間的小葉乳泡腺發育 ) 受到抑制而出現泌乳不足的現象 初生的 RANK/RANKL 基因剔除小鼠會出現骨骼生長作用減弱及長牙不全的現象 一項針對 2 週大之大鼠投予 RANKL 抑制劑 OPG-Fc 的確證性研究也顯示有骨骼生長作用減弱 生長板改變 以及長牙不全的現象 在此模型中, 當停止投予 RANKL 抑制劑時, 這些變化都可部份回復 [ 參見特殊族群之使用 ( )]
10 13 臨床研究 13.1 患有骨質疏鬆症的停經後婦女 使用 Prolia 治療停經後骨質疏鬆症的療效與安全性已在一項為期 3 年的隨機 雙盲 安慰劑對照試驗中獲得證實 所收錄婦女的腰椎或全髖骨基礎 BMD T 分數皆介於 -2.5 與 -4.0 之間 這項研究排除了患有其他疾病 ( 如類風濕性關節炎 成骨不全症及 Paget 氏症 ) 或正在接受會對骨骼造成影響之治療的婦女 7808 位參與研究之婦女的年齡為 60 至 91 歲, 平均年齡為 72 歲 整體而言, 腰椎的平均基礎 BMD T 分數為 -2.8, 並有 23% 的婦女在進入研究前曾發生脊椎骨折 受試婦女經隨機分組後分別接受每 6 個月皮下注射一次安慰劑 (n=3906) 或 Prolia 60 毫克 (n=3902) 的治療 所有婦女都每天補充至少 1000 毫克的鈣質與 400 IU 的維生素 D 主要的療效評估變數為 3 年期間經形態學評估確定 ( 經放射診斷確定 ) 之新脊椎骨折的發生率 脊椎骨折的診斷依據為側面脊椎 X 光片 (T4-L4), 並採用半定量評分法進行評估 次要的療效評估變數包括髖骨骨折與非脊椎骨折的發生率, 評估的時間為 3 年 對脊椎骨折的影響 如表 2 所示,Prolia 可明顯降低第 年期間經形態學評估確定之新脊椎骨折的發生率 (p<0.0001) 在使用安慰劑治療的婦女中,3 年期間的新脊椎骨折發生率為 7.2%, 在使用 Prolia 治療的婦女中則為 2.3% 在 3 年期間發生經形態學評估確定之新脊椎骨折的絕對風險降低程度為 4.8%, 相對風險降低程度為 68% 表 2. Prolia 對新脊椎骨折之發生率的影響 發生骨折的婦女比例 (%) + 安慰劑 N=3691 (%) Prolia N=3702 (%) 絕對風險降低程度 (%)* (95% CI) 相對風險降低程度 (%)* (95% CI) 0-1 年 (0.8, 1.9) 61 (42, 74) 0-2 年 (2.7, 4.3) 71 (61, 79) 0-3 年 (3.9, 5.8) 68 (59, 74) * 絕對風險降低程度與相對風險降低程度的評估係以 Mantel-Haenszel 法為基礎, 並依據年齡群變數進行調整 + 事件發生率係以各個時間間隔中的粗發生率為基礎 不論年齡 基礎骨代謝速率 基礎 BMD 基礎骨折病史 以及先前使用骨質疏鬆症藥物的情形為何, Prolia 都可有效降低經形態學評估確定之新脊椎骨折的發生率 對髖骨骨折的影響 在使用安慰劑治療的婦女中,3 年期間的髖骨骨折發生率為 1.2%, 在使用 Prolia 治療的婦女中則為 0.7% 在 3 年期間, 依年齡調整後的臗骨骨折絕對風險降低程度為 0.3%, 相對風險降低程度為 40% (p=0.04) ( 圖 1)
11 圖 1. 3 年期間的髖骨骨折累計發生率 安慰劑組 Prolia 病人髖骨骨折發生率 (%) 研究月數 N = number 隨機分組後的受試者人數 of subjects randomized 對非脊椎骨折的影響 使用 Prolia 治療可使非脊椎骨折的發生率明顯降低 ( 表 3) 表 3. Prolia 對 3 年期間之非脊椎骨折發生率的影響 1 非脊椎骨折 發生骨折的婦女比例 (%) + 安慰劑 N=3906 (%) Prolia N=3902 (%) 絕對風險降低程度 (%) (95% CI) 相對風險降低程度 (%) (95% CI) (0.3, 2.7) 20 (5, 33)* * p 值 = 事件發生率係以 3 年期間的 Kaplan-Meier 法估算值為基礎 不含脊椎 ( 頸椎 胸椎及腰椎 ) 頭骨 顏面骨 下顎骨 掌骨 以及手指骨與腳趾骨 對骨密度 (BMD) 的影響 治療 3 年後,Prolia 可明顯升高進行檢測之所有解剖部位的 BMD 第 3 年時,BMD 方面的治療差異為腰椎 8.8% 全髖骨 6.4% 以及股骨頸 5.2% 不論基礎期的年齡 種族 體重 / 身體質量指數 (BMI) 基礎 BMD 及骨代謝程度為何, 其對腰椎 BMD 的影響都相當一致
12 在停用 Prolia 之後,BMD 會在 12 個月內回復到接近基礎值的程度 一項在日本針對 226 位患有停經後骨質疏鬆症婦女所進行的設有控制組之研究中, 使用第一年, 相較於安慰劑組腰椎 BMD 增加 0.5%( 與基礎值差異的 mean%), 三組使用不同劑量 denosumab ( 每六個月皮下注射 及 100 mg) 之受試者的腰椎 BMD 分別增加 5.7%,6.7% 及 7.5%, 所有組 p< 經過 denosumab 治療後的第 12 個月也會使全髖部及股骨頸的 BMD 增加顯著高於安慰劑組 (p<0.05) 患有骨質疏鬆症的停經後日本婦女, 在所有結構部位的 BMD 增加程度大致上相似於 甚或高於在患有骨質疏鬆症的停經後西方婦女所得到的觀察值 骨骼組織學與組織形態學 曾在 92 位患有骨質疏鬆症的停經後婦女中於第 24 個月及 ( 或 ) 第 36 個月取得總共 115 個穿腸骨棘骨骼切片樣本 (Prolia 組有 53 個樣本, 安慰劑組有 62 個樣本 ) 在所取得的切片樣本中, 有 115 個樣本 (100%) 適合進行定性組織學評估, 並有 7 個樣本 (6%) 適合進行完整定量組織形態學評估 定性組織學評估的結果顯示, 在使用 Prolia 治療的患者中, 骨骼的結構與性質都很正常, 且並未發現任何礦化不足 出現網狀骨或發生骨髓纖維化的跡象 切片樣本中若出現雙重四環素標記, 即意味骨再塑作用相當活躍, 若未出現四環素標記, 即表示骨生成作用受到抑制 在使用 Prolia 治療的受試者中, 有 35% 在第 24 個月的切片樣本中未出現任何四環素標記, 並有 38% 在第 36 個月的切片樣本中未出現任何四環素標記, 而使用安慰劑的患者則 100% 在兩個時間點都出現雙重標記 和安慰劑相比較, 使用 Prolia 治療可達到幾無活化頻率的效果, 並可明顯降低骨生成速率 不過, 目前並不確知這種程度之骨再塑抑制作用的長期影響 14 包裝規格 / 貯存與操作 Prolia 為附有安全保護裝置的單次使用型預充針筒裝 單次使用型預充針筒上的灰色針頭套含有乾燥天然橡膠成分 ( 一種乳膠衍生物 ) 60 毫克 /1 毫升單次使用型預充針筒裝每盒 1 支裝 NDC 請將 Prolia 連同原始包裝盒貯存於 2 C 至 8 C (36 F 至 46 F) 的冰箱中 切勿冷凍 在施打之前, 可先讓 Prolia 在保留於原始包裝盒中的情況下自然回溫 ( 最高不超過 25 C/77 F) 一但自冰箱中取出之後, 即不可讓 Prolia 暴露於超過 25 C/77 F 以上的溫度, 且必須於 14 天內使用 若未在 14 天內使用, 則應將 Prolia 拋棄 在印於標籤上的有效日期之後, 請勿使用 Prolia 請避免讓 Prolia 接觸直射光源與熱源 請避免用力振搖 Prolia 15 病患諮詢須知 參見病患用藥說明書 15.1 低血鈣症 請適當地為患者補充鈣質與維生素 D, 並告知他們在使用 Prolia 治療期間維持血鈣濃度的重要性 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.1) 與特殊族群之使用 (8.6)] 請告知患者, 如果他們出現低血鈣症的徵兆或症狀, 應立即就醫診治 15.2 嚴重感染 請告知患者, 如果他們出現感染 ( 包括蜂窩性組織炎 ) 的徵兆或症狀, 應立即就醫診治 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.2)] 15.3 皮膚反應
13 請告知患者, 如果他們出現皮膚反應 ( 皮膚炎 皮疹與濕疹 ) 的徵兆或症狀, 應立即就醫診治 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.3)] 15.4 顎骨壞死 請告知患者, 在使用 Prolia 治療期間應維持良好的口腔衛生, 並應於接受牙科處置之前告知牙醫師他們正在使用 Prolia 患者在接受牙科手術之後, 如果出現持續疼痛及 ( 或 ) 口腔或顎骨癒合緩慢的現象, 應告知他們的醫師或牙醫師 [ 參見警語和注意事項 (5.4)] 15.5 施打時程 如果漏打一劑 Prolia, 應於患者方便時儘快施打 之後再從最後一次注射的日期算起, 排定每 6 個月一次的注射時間 PROLIA 為 Amgen Inc. 的註冊商標, 並授權 GlaxoSmithKline 使用 2011 Amgen Inc. 保留所有權利 製造廠名廠址 : Amgen Manufacturing, Limited State Road 31, Kilometer 24.6, Juncos, Puerto Rico 藥商 : 荷商葛蘭素史克藥廠股份有限公司台灣分公司地址 : 台北市忠孝西路一段六十六號二十四樓
14 PROLIA TM Denosumab 1 INDICATIONS Treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture. USAGE: In any one of the follow situation: those patients with a history of osteoporotic fracture, or multiple risk factors for fracture; or those who have failed or are intolerant to other available osteoporosis therapy. In postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, Prolia reduces the incidence of vertebral, non-vertebral, and hip fractures. 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Prolia should be used under supervision of physician only 2.1 Recommended Dosage Prolia should be administered by a healthcare professional. The recommended dose of Prolia is 60 mg administered as a single subcutaneous injection once every 6 months. Administer Prolia via subcutaneous injection in the upper arm, the upper thigh, or the abdomen. All patients should receive calcium 1000 mg daily and at least 400 IU vitamin D daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. If a dose of Prolia is missed, administer the injection as soon as the patient is available. Thereafter, schedule injections every 6 months from the date of the last injection. 2.2 Preparation and Administration Visually inspect Prolia for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Prolia is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution that may contain trace amounts of translucent to white proteinaceous particles. Do not use if the solution is discolored or cloudy or if the solution contains many particles or foreign particulate matter. Latex Allergy: People sensitive to latex should not handle the grey needle cap on the single-use prefilled syringe, which contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex). Prior to administration, Prolia may be removed from the refrigerator and brought to room temperature (up to 25 C/77 F) by standing in the original container. This generally takes 15 to 30 minutes. Do not warm Prolia in any other way [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (14)]. Instructions for Prefilled Syringe with Needle Safety Guard IMPORTANT: In order to minimize accidental needlesticks, the Prolia single-use prefilled syringe will have a green safety guard; manually activate the safety guard after the injection is given. Page 1
15 DO NOT slide the green safety guard forward over the needle before administering the injection; it will lock in place and prevent injection. Activate the green safety guard (slide over the needle) after the injection. The grey needle cap on the single use prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex); people sensitive to latex should not handle the cap. Step 1: Remove Grey Needle Cap Remove needle cap. Step 2: Administer Injection Insert needle and inject all the liquid. DO NOT put grey needle cap back on needle. Step 3: Immediately Slide Green Safety Guard Over Needle With the needle pointing away from you Page 2
16 Hold the prefilled syringe by the clear plastic finger grip with one hand. Then, with the other hand, grasp the green safety guard by its base and gently slide it towards the needle until the green safety guard locks securely in place and/or you hear a click. DO NOT grip the green safety guard too firmly it will move easily if you hold and slide it gently. Hold clear finger grip. Gently slide green safety guard over needle and lock securely in place. Do not grip green safety guard too firmly when sliding over needle. Immediately dispose of the syringe and needle cap in the nearest sharps container. DO NOT put the needle cap back on the used syringe. 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 1 ml of a 60 mg/ml solution in a single-use prefilled syringe 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS 4.1 Hypocalcemia Pre-existing hypocalcemia must be corrected prior to initiating therapy with Prolia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 5.1 Hypocalcemia and Mineral Metabolism Hypocalcemia may be exacerbated by the use of Prolia. Pre-existing hypocalcemia must be corrected prior to initiating therapy with Prolia. In patients predisposed to hypocalcemia and disturbances of mineral metabolism (e.g. history of hypoparathyroidism, thyroid surgery, parathyroid surgery, malabsorption syndromes, excision of small intestine, severe renal impairment [creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min] or receiving dialysis), clinical monitoring of calcium and mineral levels (phosphorus and magnesium) is highly recommended. Page 3
17 Hypocalcemia following Prolia administration is a significant risk in patients with severe renal impairment [creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min], or receiving dialysis. Instruct all patients with severe renal impairment, including those receiving dialysis, about the symptoms of hypocalcemia and the importance of maintaining calcium levels with adequate calcium and vitamin D supplementation. Adequately supplement all patients with calcium and vitamin D [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Contraindications (4.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Patient Counseling Information (15.1)]. 5.2 Serious Infections In a clinical trial of over 7800 women with postmenopausal osteoporosis, serious infections leading to hospitalization were reported more frequently in the Prolia group than in the placebo group [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Serious skin infections, as well as infections of the abdomen, urinary tract, and ear, were more frequent in patients treated with Prolia. Endocarditis was also reported more frequently in Prolia-treated subjects. The incidence of opportunistic infections was balanced between placebo and Prolia groups, and the overall incidence of infections was similar between the treatment groups. Advise patients to seek prompt medical attention if they develop signs or symptoms of severe infection, including cellulitis. Patients on concomitant immunosuppressant agents or with impaired immune systems may be at increased risk for serious infections. Consider the benefit-risk profile in such patients before treating with Prolia. In patients who develop serious infections while on Prolia, prescribers should assess the need for continued Prolia therapy. 5.3 Dermatologic Adverse Reactions In a large clinical trial of over 7800 women with postmenopausal osteoporosis, epidermal and dermal adverse events such as dermatitis, eczema, and rashes occurred at a significantly higher rate in the Prolia group compared to the placebo group. Most of these events were not specific to the injection site [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Consider discontinuing Prolia if severe symptoms develop. 5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), which can occur spontaneously, is generally associated with tooth extraction and/or local infection with delayed healing. ONJ has been reported in patients receiving denosumab [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. A routine oral exam should be performed by the prescriber prior to initiation of Prolia treatment. A dental examination with appropriate preventive dentistry should be considered prior to treatment with Prolia in patients with risk factors for ONJ such as invasive dental procedures (e.g., tooth extraction, dental implants, oral surgery), diagnosis of cancer, concomitant therapies (e.g., chemotherapy, corticosteroids), poor oral hygiene, and co-morbid disorders (e.g., periodontal and/or other pre-existing dental disease, anemia, coagulopathy, infection, ill-fitting dentures). Good oral hygiene practices should be maintained during treatment with Prolia. For patients requiring invasive dental procedures, clinical judgment of the treating physician and/or oral surgeon should guide the management plan of each patient based on individual benefit-risk assessment. Patients who are suspected of having or who develop ONJ while on Prolia should receive care by a dentist or an oral surgeon. In these patients, extensive dental surgery to treat ONJ may exacerbate the condition. Discontinuation of Prolia therapy should be considered based on individual benefit-risk assessment. Page 4
18 5.5 Suppression of Bone Turnover In clinical trials in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis, treatment with Prolia resulted in significant suppression of bone remodeling as evidenced by markers of bone turnover and bone histomorphometry [see Clinical Pharmacology (11.2), Clinical Studies (13.1)]. The significance of these findings and the effect of long-term treatment with Prolia are unknown. The long-term consequences of the degree of suppression of bone remodeling observed with Prolia may contribute to adverse outcomes such as osteonecrosis of the jaw, atypical fractures, and delayed fracture healing. Monitor patients for these consequences. 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS The following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and also elsewhere in the labeling: Hypocalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Dermatologic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] Osteonecrosis of the Jaw [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] The most common adverse reactions reported with Prolia are back pain, pain in extremity, musculoskeletal pain, hypercholesterolemia, and cystitis. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of Prolia are breast cancer, back pain, and constipation. Amgen & GSK proposes a comprehensive global pharmacovigilance plan to gather the necessary information that will aid further assessment and characterization of the risks detailed in the global Risk Management Plan (RMP). GSK Taiwan will follow up all safety concerns targeted for review and safety surveillance and report any safety issues to the local regulatory authority as soon as GSK Taiwan receives the safety information. Local safety events reported will be forwarded to the global data base. Routine local literature will be reviewed for reports of adverse reactions associated with the use of denosumab. In addition, international databases will be utilized to generate necessary background information for the identification and evaluation of signals and detection of any safety issue early. Analysis of these safety data and signal detection will provided in the Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSUR). The Prolia Postmarketing Active Safety Surveillance Program is available to collect information from prescribers on specific adverse events. Please see call (02) for more information about this program Clinical Trials Experience Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice. Treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis The safety of Prolia in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in a 3-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational study of 7808 postmenopausal women aged 60 to 91 years. A total of 3876 women were exposed to placebo and 3886 women were exposed to Prolia Page 5
19 administered subcutaneously once every 6 months as a single 60 mg dose. All women were instructed to take at least 1000 mg of calcium and 400 IU of vitamin D supplementation per day. The incidence of all-cause mortality was 2.3% (n = 90) in the placebo group and 1.8% (n = 70) in the Prolia group. The incidence of nonfatal serious adverse events was 24.2% in the placebo group and 25.0% in the Prolia group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 2.1% and 2.4% for the placebo and Prolia groups, respectively. Adverse reactions reported in 2% of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis and more frequently in the Prolia-treated women than in the placebo-treated women are shown in the table below. Table 1. Adverse Reactions Occurring in 2% of Patients with Osteoporosis and More Frequently than in Placebo-treated Patients SYSTEM ORGAN CLASS Preferred Term Prolia (N = 3886) n (%) Placebo (N = 3876) n (%) BLOOD AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEM DISORDERS Anemia 129 (3.3) 107 (2.8) CARDIAC DISORDERS Angina pectoris 101 (2.6) 87 (2.2) Atrial fibrillation 79 (2.0) 77 (2.0) EAR AND LABYRINTH DISORDERS Vertigo 195 (5.0) 187 (4.8) GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS Abdominal pain upper 129 (3.3) 111 (2.9) Flatulence 84 (2.2) 53 (1.4) Gastroesophageal reflux disease 80 (2.1) 66 (1.7) GENERAL DISORDERS AND ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITIONS Edema peripheral 189 (4.9) 155 (4.0) Asthenia 90 (2.3) 73 (1.9) INFECTIONS AND INFESTATIONS Cystitis 228 (5.9) 225 (5.8) Upper respiratory tract infection 190 (4.9) 167 (4.3) Pneumonia 152 (3.9) 150 (3.9) Pharyngitis 91 (2.3) 78 (2.0) Herpes zoster 79 (2.0) 72 (1.9) METABOLISM AND NUTRITION DISORDERS Hypercholesterolemia 280 (7.2) 236 (6.1) Page 6
20 Prolia (N = 3886) n (%) Placebo (N = 3876) n (%) SYSTEM ORGAN CLASS Preferred Term MUSCULOSKELETAL AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISORDERS Back pain 1347 (34.7) 1340 (34.6) Pain in extremity 453 (11.7) 430 (11.1) Musculoskeletal pain 297 (7.6) 291 (7.5) Bone pain 142 (3.7) 117 (3.0) Myalgia 114 (2.9) 94 (2.4) Spinal osteoarthritis 82 (2.1) 64 (1.7) NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS Sciatica 178 (4.6) 149 (3.8) PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Insomnia 126 (3.2) 122 (3.1) SKIN AND SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE DISORDERS Rash 96 (2.5) 79 (2.0) Pruritus 87 (2.2) 82 (2.1) Hypocalcemia Decreases in serum calcium levels to less than 8.5 mg/dl were reported in 0.4% women in the placebo group and 1.7% women in the Prolia group at the month 1 visit. The nadir in serum calcium level occurs at approximately day 10 after Prolia dosing in subjects with normal renal function. In clinical studies, subjects with impaired renal function were more likely to have greater reductions in serum calcium levels compared to subjects with normal renal function. In a study of 55 patients with varying degrees of renal function, serum calcium levels < 7.5 mg/dl or symptomatic hypocalcemia were observed in 5 subjects. These included no subjects in the normal renal function group, 10% of subjects in the CrCL 50 to 80 ml/min group, 29% of subjects in the CrCL < 30 ml/min group, and 29% of subjects in the hemodialysis group. These subjects did not receive calcium and vitamin D supplementation. In a study of 4,550 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, the mean change from baseline in serum calcium level 10 days after Prolia dosing was -5.5% in subjects with creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min vs. -3.1% in subjects with CrCL 30 ml/min. Serious Infections Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-b ligand (RANKL) is expressed on activated T and B lymphocytes and in lymph nodes. Therefore, a RANKL inhibitor such as Prolia may increase the risk of infection. In the clinical study of 7808 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, the incidence of infections resulting in death was 0.2% in both placebo and Prolia treatment groups. However, the incidence of nonfatal serious infections was 3.3% in the placebo group and 4.0% in the Prolia group. Hospitalizations due to serious infections in the abdomen (0.7% placebo vs. 0.9% Prolia), urinary tract (0.5% placebo vs. 0.7% Prolia), and ear (0.0% placebo vs. 0.1% Prolia) were reported. Endocarditis was reported in no placebo patients and 3 patients receiving Prolia. Page 7
21 Skin infections, including erysipelas and cellulitis, leading to hospitalization were reported more frequently in patients treated with Prolia (< 0.1% placebo vs. 0.4% Prolia). There was no imbalance in the reporting of opportunistic infections. Dermatologic Reactions A significantly higher number of patients treated with Prolia developed epidermal and dermal adverse events (such as dermatitis, eczema, and rashes), with these events reported in 8.2% of placebo and 10.8% of Prolia group (p < ). Most of these events were not specific to the injection site [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw ONJ has been reported in the osteoporosis clinical trial program in patients treated with Prolia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Pancreatitis Pancreatitis was reported in 4 patients (0.1%) in the placebo and 8 patients (0.2%) in the Prolia groups. Of these reports, one subject in the placebo group and all 8 subjects in the Prolia group had serious events including one death in the Prolia group. Several patients had a prior history of pancreatitis. The time from product administration to event occurrence was variable. New Malignancies The overall incidence of new malignancies was 4.3% in the placebo and 4.8% in the Prolia groups. New malignancies related to breast (0.7% placebo vs. 0.9% Prolia), reproductive (0.2% placebo vs. 0.5% Prolia), and gastrointestinal systems (0.6% placebo vs. 0.9% Prolia) were reported. A causal relationship to drug exposure has not been established. Immunogenicity Denosumab is a human monoclonal antibody. As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. Using an electrochemiluminescent bridging immunoassay, less than 1% (55 out of 8113) of patients treated with Prolia for up to 5 years tested positive for binding antibodies (including pre-existing, transient, and developing antibodies). None of the patients tested positive for neutralizing antibodies, as was assessed using a chemiluminescent cell-based in vitro biological assay. No evidence of altered pharmacokinetic profile, toxicity profile, or clinical response was associated with binding antibody development. The incidence of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of a positive antibody (including neutralizing antibody) test result may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of antibodies to denosumab with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading. 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS No drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with Prolia. 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy Page 8
22 Pregnancy Category C There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Prolia in pregnant women. In genetically engineered mice in which RANK ligand (RANKL) was turned off by gene removal (a knockout mouse ), absence of RANKL (the target of denosumab) caused fetal lymph node agenesis and led to postnatal impairment of dentition and bone growth. Pregnant RANKL knockout mice also showed altered maturation of the maternal mammary gland, leading to impaired lactation postpartum [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. Prolia is approved only for use in postmenopausal women. Prolia should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Women who become pregnant during Prolia treatment are encouraged toreport to GSK-Taiwan to be enrolled into the Pregnancy Surveillance Program which is a routine PV activities. Patients or their physicians should call to report. In an embryofetal developmental study, cynomolgus monkeys received subcutaneous denosumab weekly during organogenesis at doses up to 13-fold higher than the recommended human dose of 60 mg administered once every 6 months based on body weight (mg/kg). No evidence of maternal toxicity or fetal harm was observed. However, this study only assessed fetal toxicity during a period equivalent to the first trimester and fetal lymph nodes were not examined. Monoclonal antibodies are transported across the placenta in a linear fashion as pregnancy progresses, with the largest amount transferred during the third trimester. Potential adverse developmental effects resulting from exposures during the second and third trimesters have not been assessed in animals [see Nonclinical Toxicology (12.2)]. 8.2 Nursing Mothers It is not known whether Prolia is excreted into human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Prolia, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. Maternal exposure to Prolia during pregnancy may impair mammary gland development and lactation based on animal studies in pregnant mice lacking the RANK/RANKL signaling pathway that have shown altered maturation of the maternal mammary gland, leading to impaired lactation postpartum [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)]. 8.3 Pediatric Use Prolia is not recommended in pediatric patients. The safety and effectiveness of Prolia in pediatric patients have not been established. Treatment with Prolia may impair bone growth in children with open growth plates and may inhibit eruption of dentition. In neonatal rats, inhibition of RANKL (the target of Prolia therapy) with a construct of osteoprotegerin bound to Fc (OPG-Fc) at doses 10 mg/kg was associated with inhibition of bone growth and tooth eruption. Adolescent primates dosed with denosumab at 10 and 50 times (10 and 50 mg/kg dose) higher than the recommended human dose of 60 mg administered once every 6 months, based on body weight (mg/kg), had abnormal growth plates [see Nonclinical Toxicology (12.2)]. 8.4 Geriatric Use Of the total number of patients in clinical studies of Prolia, 9943 patients (76%) were 65 years old, while 3576 (27%) were 75 years old. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between these patients and younger patients and other reported clinical experience has not identified Page 9
23 differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. 8.5 Renal Impairment No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with renal impairment. In clinical studies, patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min) or receiving dialysis were at greater risk of developing hypocalcemia. Consider the benefit-risk profile when administering Prolia to patients with severe renal impairment or receiving dialysis. Clinical monitoring of calcium and mineral levels (phosphorus and magnesium) is highly recommended. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is important in patients with severe renal impairment or receiving dialysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (11.3)]. 8.6 Hepatic Impairment No clinical studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Prolia. 9 OVERDOSAGE There is no experience with overdosage with Prolia. 10 DESCRIPTION Prolia (denosumab) is a human IgG2 monoclonal antibody with affinity and specificity for human RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-b ligand). Denosumab has an approximate molecular weight of 147 kda and is produced in genetically engineered mammalian (Chinese hamster ovary) cells. Prolia is a sterile, preservative-free, clear, colorless to pale yellow solution. Each 1 ml single-use prefilled syringe of Prolia contains 60 mg denosumab (60mg/mL solution), 4.7% sorbitol, 17 mm acetate, 0.01% polysorbate 20, Water for Injection (USP), and sodium hydroxide to a ph of CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 11.1 Mechanism of Action Prolia binds to RANKL, a transmembrane or soluble protein essential for the formation, function, and survival of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. Prolia prevents RANKL from activating its receptor, RANK, on the surface of osteoclasts and their precursors. Prevention of the RANKL/RANK interaction inhibits osteoclast formation, function, and survival, thereby decreasing bone resorption and increasing bone mass and strength in both cortical and trabecular bone Pharmacodynamics In clinical studies, treatment with 60 mg of Prolia resulted in reduction in the bone resorption marker serum type 1 C-telopeptide (CTX) by approximately 85% by 3 days, with maximal reductions occurring by 1 month. CTX levels were below the limit of assay quantitation (0.049 ng/ml) in 39-68% of subjects Page 10
24 1-3 months after dosing of Prolia. At the end of each dosing interval, CTX reductions were partially attenuated from a maximal reduction of 87% to 45% (range: 45% to 80%), as serum denosumab levels diminished, reflecting the reversibility of the effects of Prolia on bone remodeling. These effects were sustained with continued treatment. Upon reinitiation, the degree of inhibition of CTX by Prolia was similar to that observed in patients initiating Prolia treatment. Consistent with the physiological coupling of bone formation and resorption in skeletal remodeling, subsequent reductions in bone formation markers (i.e., osteocalcin and procollagen type 1 N-terminal peptide [PlNP]) were observed starting 1 month after the first dose of Prolia. After discontinuation of Prolia therapy, markers of bone resorption increased to levels 40-60% above pretreatment values but returned to baseline levels within 12 months Pharmacokinetics In a study conducted in healthy male and female volunteers (n = 73, age range: 18 to 64 years) following a single subcutaneously administered Prolia dose of 60 mg after fasting (at least for 12 hours), the mean maximum denosumab concentration (C max ) was 6.75 mcg/ml (standard deviation [SD] = 1.89 mcg/ml). The median time to maximum denosumab concentration (T max ) was 10 days (range: 3 to 21 days). After C max, serum denosumab concentrations declined over a period of 4 to 5 months with a mean half-life of 25.4 days (SD = 8.5 days; n = 46). The mean area-under-the-concentration-time curve up to 16 weeks (AUC 0-16 weeks ) of denosumab was 316 mcg day/ml (SD = 101 mcg day/ml). No accumulation or change in denosumab pharmacokinetics with time was observed upon multiple dosing of 60 mg subcutaneously administered once every 6 months. Prolia pharmacokinetics were not affected by the formation of binding antibodies. A population pharmacokinetic analysis was performed to evaluate the effects of demographic characteristics. This analysis showed no notable differences in pharmacokinetics with age (in postmenopausal women), race, or body weight (36 to 140 kg). Drug Interactions No drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with Prolia. Specific Populations Gender: Mean serum denosumab concentration-time profiles observed in a study conducted in healthy men 50 years were similar to those observed in a study conducted in postmenopausal women using the same dose regimen. Age: The pharmacokinetics of denosumab was not affected by age across all populations studied whose ages ranged from years. Race: The pharmacokinetics of denosumab was not affected by race. Renal Impairment: In a study of 55 patients with varying degrees of renal function, including patients on dialysis, the degree of renal impairment had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of denosumab; thus, dose adjustment for renal impairment is not necessary. Hepatic Impairment: No clinical studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of denosumab. Page 11
25 12 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 12.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Carcinogenicity The carcinogenic potential of denosumab has not been evaluated in long-term animal studies. Mutagenicity The genotoxic potential of denosumab has not been evaluated. Impairment of Fertility Denosumab had no effect on female fertility or male reproductive organs in monkeys at doses that were 13- to 50-fold higher than the recommended human dose of 60 mg administered once every 6 months, based on body weight (mg/kg) Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology Prolia is an inhibitor of osteoclastic bone resorption via inhibition of RANKL. In ovariectomized monkeys, once-monthly treatment with denosumab suppressed bone turnover and increased bone mineral density (BMD) and strength of cancellous and cortical bone at doses 50-fold higher than the recommended human dose of 60 mg administered once every 6 months, based on body weight (mg/kg). Bone tissue was normal with no evidence of mineralization defects, accumulation of osteoid, or woven bone. Adolescent primates treated with denosumab at doses > 10 times (10 and 50 mg/kg dose) higher than the recommended human dose of 60 mg administered once every 6 months, based on mg/kg, had abnormal growth plates, considered to be consistent with the pharmacological activity of denosumab [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Because the biological activity of denosumab in animals is specific to nonhuman primates, evaluation of genetically engineered ( knockout ) mice or use of other biological inhibitors of the RANK/RANKL pathway, namely OPG-Fc, provided additional information on the pharmacodynamic properties of denosumab. RANK/RANKL knockout mice exhibited absence of lymph node formation, as well as an absence of lactation due to inhibition of mammary gland maturation (lobulo-alveolar gland development during pregnancy). Neonatal RANK/RANKL knockout mice exhibited reduced bone growth and lack of tooth eruption. A corroborative study in 2-week-old rats given the RANKL inhibitor OPG-Fc also showed reduced bone growth, altered growth plates, and impaired tooth eruption. These changes were partially reversible in this model when dosing with the RANKL inhibitors was discontinued [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.4)]. 13 CLINICAL STUDIES 13.1 Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis The efficacy and safety of Prolia in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was demonstrated in a 3-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Enrolled women had a baseline BMD T-score between -2.5 and -4.0 at either the lumbar spine or total hip. Women with other diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteogenesis imperfecta, and Paget s disease) or on therapies that affect bone were excluded from this study. The 7808 enrolled women were aged 60 to 91 years with a mean age of 72 years. Overall, the mean baseline lumbar spine BMD T-score was -2.8 and 23% of women had a Page 12
26 vertebral fracture at baseline. Women were randomized to receive SC injections of either placebo (N = 3906) or Prolia 60 mg (N = 3902) once every 6 months. All women received at least 1000 mg calcium and 400 IU vitamin D supplementation daily. The primary efficacy variable was the incidence of new morphometric (radiologically-diagnosed) vertebral fractures at 3 years. Vertebral fractures were diagnosed based on lateral spine radiographs (T4-L4) using a semiquantitative scoring method. Secondary efficacy variables included the incidence of hip fracture and nonvertebral fracture, assessed at 3 years. Effect on Vertebral Fractures Prolia significantly reduced the incidence of new morphometric vertebral fractures at 1, 2, and 3 years (p < ), as shown in Table 2. The incidence of new vertebral fractures at year 3 was 7.2% in the placebo-treated women compared to 2.3% for the Prolia-treated women. The absolute risk reduction was 4.8% and relative risk reduction was 68% for new morphometric vertebral fractures at year 3. Table 2. The Effect of Prolia on the Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures Proportion of Women Absolute Risk With Fracture (%) + Reduction Placebo (%)* N = 3691 (95% CI) Prolia N = 3702 (%) Relative Risk Reduction (%)* (95% CI) (%) 0-1 Year (0.8, 1.9) 61 (42, 74) 0-2 Years (2.7, 4.3) 71 (61, 79) 0-3 Years (3.9, 5.8) 68 (59, 74) * Absolute risk reduction and relative risk reduction based on Mantel-Haenszel method adjusting for age + group variable. Event rates based on crude rates in each interval. Prolia was effective in reducing the risk for new morphometric vertebral fractures regardless of age, baseline rate of bone turnover, baseline BMD, baseline history of fracture, or prior use of a drug for osteoporosis. Effect on Hip Fractures The incidence of hip fracture was 1.2% for placebo-treated women compared to 0.7% for Prolia-treated women at year 3. The age-adjusted absolute risk reduction of hip fractures was 0.3% with a relative risk reduction of 40% at 3 years (p = 0.04) (Figure 1). Page 13
27 Figure 1. Cumulative Incidence of Hip Fractures Over 3 Years N = number of subjects randomized Effect on Nonvertebral Fractures Treatment with Prolia resulted in a significant reduction in the incidence of nonvertebral fractures (Table 3). Table 3. The Effect of Prolia on the Incidence of Nonvertebral Fractures at Year 3 Proportion of Women With Fracture (%) + Absolute Risk Relative Risk Placebo N = 3906 (%) Prolia N = 3902 (%) Reduction (%) (95% CI) Reduction (%) (95% CI) Nonvertebral fracture (0.3, 2.7) 20 (5, 33) * * + 1 p-value = Event rates based on Kaplan-Meier estimates at 3 years. Excluding those of the vertebrae (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar), skull, facial, mandible, metacarpus, and finger and toe phalanges. Effect on Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Treatment with Prolia significantly increased BMD at all anatomic sites measured at 3 years. The treatment differences in BMD at 3 years were 8.8% at the lumbar spine, 6.4% at the total hip, and 5.2% at the femoral neck. Consistent effects on BMD were observed at the lumbar spine, regardless of baseline age, race, weight/body mass index (BMI), baseline BMD, and level of bone turnover. Page 14
28 In a placebo-controlled study in 266 Japanese women with postmenopausal osteoporosis, denosumab significantly increased 5.7%,, 6.7% and 7.5% (mean % change from baseline) of BMD at 1 year at the lumbar spine across 3 dose groups (14, 60 and 100 mg subcutaneous once every 6 months) for the 3 denosumab groups as compared to 0.5% for the placebo group, all p < Also, all 3 denosumab dose cohorts had significantly greater increases in BMD of the total hip, and femoral neck at month 12 compared with the placebo cohort (p < 0.05). The extent of increase in BMD at each anatomical site in Japanese women with postmenopausal osteoporosis was generally similar to, or somewhat higher than, that observed in Western women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bone Histology and Histomorphometry A total of 115 transiliac crest bone biopsy specimens were obtained from 92 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at either month 24 and/or month 36 (53 specimens in Prolia group, 62 specimens in placebo group). Of the biopsies obtained, 115 (100%) were adequate for qualitative histology and 7 (6%) were adequate for full quantitative histomorphometry assessment. Qualitative histology assessments showed normal architecture and quality with no evidence of mineralization defects, woven bone, or marrow fibrosis in patients treated with Prolia. The presence of double tetracycline labeling in a biopsy specimen provides an indication of active bone remodeling, while the absence of tetracycline label suggests suppressed bone formation. In subjects treated with Prolia, 35% had no tetracycline label present at the month 24 biopsy and 38% had no tetracycline label present at the month 36 biopsy, while 100% of placebo-treated patients had double label present at both time points. When compared to placebo, treatment with Prolia resulted in virtually absent activation frequency and markedly reduced bone formation rates. However, the long-term consequences of this degree of suppression of bone remodeling are unknown. 14 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Prolia is supplied in a single-use prefilled syringe with a safety guard. The grey needle cap on the singleuse prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex). 60 mg/1 ml in a single-use prefilled syringe 1 per carton NDC Store Prolia in a refrigerator at 2 C to 8 C (36 F to 46 F) in the original carton. Do not freeze. Prior to administration, Prolia may be allowed to reach room temperature (up to 25 C/77 F) in the original container. Once removed from the refrigerator, Prolia must not be exposed to temperatures above 25 C/77 F and must be used within 14 days. If not used within the 14 days, Prolia should be discarded. Do not use Prolia after the expiry date printed on the label. Protect Prolia from direct light and heat. Avoid vigorous shaking of Prolia. 15 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION See Medication Guide Hypocalcemia Adequately supplement patients with calcium and vitamin D and instruct them on the importance of maintaining serum calcium levels while receiving Prolia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Page 15
29 Specific Populations (8.6)]. Advise patients to seek prompt medical attention if they develop signs or symptoms of hypocalcemia Serious Infections Advise patients to seek prompt medical attention if they develop signs or symptoms of infections, including cellulitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Dermatologic Reactions Advise patients to seek prompt medical attention if they develop signs or symptoms of dermatological reactions (dermatitis, rashes, and eczema) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Advise patients to maintain good oral hygiene during treatment with Prolia and to inform their dentist prior to dental procedures that they are receiving Prolia. Patients should inform their physician or dentist if they experience persistent pain and/or slow healing of the mouth or jaw after dental surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] Schedule of Administration If a dose of Prolia is missed, administer the injection as soon as convenient. Thereafter, schedule injections every 6 months from the date of the last injection. Manufactured by: Amgen Manufacturing Limited, a subsidiary of Amgen Inc. One Amgen Center Drive Thousand Oaks, California This product, its production, and/or its use may be covered by one or more US Patents, including US Patent Nos. 6,740,522; 7,097,834; 7,364,736; and 7,411,050, as well as other patents or patents pending. PROLIA is a registered trademark of Amgen Inc., and is being used under license by GlaxoSmithKline Amgen Inc. All rights reserved. version 1 Page 16
鼠 疫(Plague)
 鼠 疫 (Plague) 一 疾 病 概 述 (Disease description) 存 在 囓 齒 類 及 其 跳 蚤 的 一 種 人 畜 共 通 傳 染 病, 並 藉 跳 蚤 傳 染 給 各 種 動 物 及 人 類, 其 最 初 反 應 為 跳 蚤 咬 傷 部 位 臨 近 的 淋 巴 腺 發 炎, 這 就 是 腺 鼠 疫, 經 常 發 生 於 鼠 蹊 部, 少 發 生 於 腋 下 或 頸 部,
鼠 疫 (Plague) 一 疾 病 概 述 (Disease description) 存 在 囓 齒 類 及 其 跳 蚤 的 一 種 人 畜 共 通 傳 染 病, 並 藉 跳 蚤 傳 染 給 各 種 動 物 及 人 類, 其 最 初 反 應 為 跳 蚤 咬 傷 部 位 臨 近 的 淋 巴 腺 發 炎, 這 就 是 腺 鼠 疫, 經 常 發 生 於 鼠 蹊 部, 少 發 生 於 腋 下 或 頸 部,
864 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 6 期 2016 年 6 月 of apoptosis related factors, decrease the incidence of adverse reactions, which is of great
 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 6 期 2016 年 6 月 863 曲 妥 珠 单 抗 联 合 多 西 紫 杉 醇 治 疗 Her-2 阳 性 乳 腺 癌 的 临 床 研 究 * 周 永 安, 刘 训 碧 黄 石 市 中 心 医 院 ( 普 爱 院 区 ) 乳 腺 肿 瘤 外 科, 湖 北 黄 石 435000 摘 要 : 目 的 探 析 注 射 用 曲
现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 6 期 2016 年 6 月 863 曲 妥 珠 单 抗 联 合 多 西 紫 杉 醇 治 疗 Her-2 阳 性 乳 腺 癌 的 临 床 研 究 * 周 永 安, 刘 训 碧 黄 石 市 中 心 医 院 ( 普 爱 院 区 ) 乳 腺 肿 瘤 外 科, 湖 北 黄 石 435000 摘 要 : 目 的 探 析 注 射 用 曲
Microsoft Word - Prolia_US_3.25 To TFDA[CH]=TW ind+USPI+JP data.doc
![Microsoft Word - Prolia_US_3.25 To TFDA[CH]=TW ind+USPI+JP data.doc Microsoft Word - Prolia_US_3.25 To TFDA[CH]=TW ind+USPI+JP data.doc](/thumbs/50/26211992.jpg) TM 保骼麗注射液 Prolia (denosumab) 衛署菌疫輸字第 000918 號 適應症 治療有骨折高風險性之停經後婦女骨質疏鬆症 說明 : 含下列任一狀況 : 有骨質疏鬆症骨折病史 具有多項骨折危險因子 先前接受其他骨質疏鬆症療法失敗或無法耐受其他骨質疏鬆症療法之病患 對患有骨質疏鬆症之停經後婦女,Prolia 可降低脊椎 非脊椎和髖骨骨折的發生率 2 劑量與用法 本藥須由醫師處方使用
TM 保骼麗注射液 Prolia (denosumab) 衛署菌疫輸字第 000918 號 適應症 治療有骨折高風險性之停經後婦女骨質疏鬆症 說明 : 含下列任一狀況 : 有骨質疏鬆症骨折病史 具有多項骨折危險因子 先前接受其他骨質疏鬆症療法失敗或無法耐受其他骨質疏鬆症療法之病患 對患有骨質疏鬆症之停經後婦女,Prolia 可降低脊椎 非脊椎和髖骨骨折的發生率 2 劑量與用法 本藥須由醫師處方使用
 : 23 S00017242 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------3 -------------------------------------------------------------------7
: 23 S00017242 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------3 -------------------------------------------------------------------7
: ( ),,
 Case Discussion: ( ), RN, ScD, MPH : 24,,,,,,, ( ) ) ( ), : ( ),, randomized controlled trial (RCT). minimization program,,,, : : ; Apgar score > 7 ;, : ; ; ; ; (BT180/min; 2, 83,50 (60.2%).,
Case Discussion: ( ), RN, ScD, MPH : 24,,,,,,, ( ) ) ( ), : ( ),, randomized controlled trial (RCT). minimization program,,,, : : ; Apgar score > 7 ;, : ; ; ; ; (BT180/min; 2, 83,50 (60.2%).,
肉 毒 桿 菌 素 的 疑 問 : 問 : 請 問 什 是 肉 毒 桿 菌 素? 適 用 何 種 情 況? 答 : 在 此 我 們 來 介 紹 肉 毒 桿 菌 素 肉 毒 桿 菌 素 並 不 是 活 的 " 細 菌 ", 而 是 由 肉 毒 桿 菌 所 提 煉 出 來 的 一 種 " 菌 素 ",
 序 肉 毒 桿 菌 素, 英 文 名 稱 為 botulinum toxin, 這 個 名 詞 來 自 拉 丁 文, 意 思 是 sausage poison 香 腸 毒 素. 在 二 次 世 界 大 戰 中, 西 元 1795~1813 年 間, 在 德 國 司 徒 加 (Stutggart) 地 區 曾 經 發 生 過 嚴 重 的 食 物 中 毒 大 流 行 事 件, 隨 後 由 於 食 物 衛
序 肉 毒 桿 菌 素, 英 文 名 稱 為 botulinum toxin, 這 個 名 詞 來 自 拉 丁 文, 意 思 是 sausage poison 香 腸 毒 素. 在 二 次 世 界 大 戰 中, 西 元 1795~1813 年 間, 在 德 國 司 徒 加 (Stutggart) 地 區 曾 經 發 生 過 嚴 重 的 食 物 中 毒 大 流 行 事 件, 隨 後 由 於 食 物 衛
untitled
 R2 10315 20042008 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE THEORY & TREATMENT TO RELIEVE PAIN OF BREAST CANCER PATIENTS 2007 5 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
R2 10315 20042008 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE THEORY & TREATMENT TO RELIEVE PAIN OF BREAST CANCER PATIENTS 2007 5 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2005 5,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, , , 2174, 7014 %, % 4, 1961, ,30, 30,, 4,1976,627,,,,, 3 (1993,12 ),, 2
 3,,,,,, 1872,,,, 3 2004 ( 04BZS030),, 1 2005 5,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, 1928 716,1935 6 2682 1928 2 1935 6 1966, 2174, 7014 %, 94137 % 4, 1961, 59 1929,30, 30,, 4,1976,627,,,,, 3 (1993,12 ),, 2 , :,,,, :,,,,,,
3,,,,,, 1872,,,, 3 2004 ( 04BZS030),, 1 2005 5,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, 1928 716,1935 6 2682 1928 2 1935 6 1966, 2174, 7014 %, 94137 % 4, 1961, 59 1929,30, 30,, 4,1976,627,,,,, 3 (1993,12 ),, 2 , :,,,, :,,,,,,
ADR ADR ADR : 2
 8 2000 10 2001 5 ADR ADR 415 ADR44 ADR 10.6% 2661 ADR105 ADR 3.9% P
8 2000 10 2001 5 ADR ADR 415 ADR44 ADR 10.6% 2661 ADR105 ADR 3.9% P
®
 中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 45 卷 第 15 期 214 年 8 月 2277 稳 心 颗 粒 治 疗 心 律 失 常 的 Meta 分 析 * 何 颖, 刘 莹, 邹 爱 英 天 津 中 医 药 大 学 第 二 附 属 医 院, 天 津 15 摘 要 : 利 用 Meta 分 析 法 评 价 稳 心 颗 粒 治 疗 心 律 失 常 的
中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 45 卷 第 15 期 214 年 8 月 2277 稳 心 颗 粒 治 疗 心 律 失 常 的 Meta 分 析 * 何 颖, 刘 莹, 邹 爱 英 天 津 中 医 药 大 学 第 二 附 属 医 院, 天 津 15 摘 要 : 利 用 Meta 分 析 法 评 价 稳 心 颗 粒 治 疗 心 律 失 常 的
Microsoft Word - 7-針刺.doc
 針 刺 結 合 推 拿 治 療 單 純 性 肥 胖 症 ( 胃 腸 腑 熱 型 ) 臨 床 研 究 59 針 刺 結 合 推 拿 治 療 單 純 性 肥 胖 症 ( 胃 腸 腑 熱 型 ) 臨 床 研 究 彭 淑 珍 春 風 中 醫 診 所 前 言 當 前, 肥 胖 病 已 成 為 國 內 外 的 一 個 熱 門 問 題, 現 代 醫 學 已 經 揭 示 肥 胖 病 與 糖 尿 病 腦 血 管 疾
針 刺 結 合 推 拿 治 療 單 純 性 肥 胖 症 ( 胃 腸 腑 熱 型 ) 臨 床 研 究 59 針 刺 結 合 推 拿 治 療 單 純 性 肥 胖 症 ( 胃 腸 腑 熱 型 ) 臨 床 研 究 彭 淑 珍 春 風 中 醫 診 所 前 言 當 前, 肥 胖 病 已 成 為 國 內 外 的 一 個 熱 門 問 題, 現 代 醫 學 已 經 揭 示 肥 胖 病 與 糖 尿 病 腦 血 管 疾
 Abstract Due to the improving of living standards, people gradually seek lighting quality from capacityto quality. And color temperature is the important subject of it. According to the research from aboard,
Abstract Due to the improving of living standards, people gradually seek lighting quality from capacityto quality. And color temperature is the important subject of it. According to the research from aboard,
一位末期腎病
 . 弘 光 學 報 50 期. 一 位 末 期 腎 病 患 者 於 加 護 病 房 面 臨 血 液 透 析 衝 擊 之 護 理 經 驗 傅 淑 禎 1 林 麗 君 1 劉 波 兒 2 * 1 光 田 醫 院 大 甲 分 院 2 弘 光 科 技 大 學 護 理 系 收 到 日 期 :95.10.13 修 訂 日 期 :96.1.9 接 受 日 期 :96.2.6 摘 要 本 文 是 探 討 一 位 末
. 弘 光 學 報 50 期. 一 位 末 期 腎 病 患 者 於 加 護 病 房 面 臨 血 液 透 析 衝 擊 之 護 理 經 驗 傅 淑 禎 1 林 麗 君 1 劉 波 兒 2 * 1 光 田 醫 院 大 甲 分 院 2 弘 光 科 技 大 學 護 理 系 收 到 日 期 :95.10.13 修 訂 日 期 :96.1.9 接 受 日 期 :96.2.6 摘 要 本 文 是 探 討 一 位 末
University of Science and Technology of China A dissertation for master s degree Transdermal Delivery of Gut Hormone PYY3-36 for the treatment of Obes
 中 国 科 学 技 术 大 学 硕 士 学 位 论 文 肠 激 素 PYY3-36 透 皮 给 药 治 疗 肥 胖 症 的 研 究 作 者 姓 名 : 学 科 专 业 : 导 师 姓 名 : 完 成 时 间 : 陈 敏 细 胞 生 物 学 温 龙 平 教 授 二 一 年 八 月 三 十 一 日 University of Science and Technology of China A dissertation
中 国 科 学 技 术 大 学 硕 士 学 位 论 文 肠 激 素 PYY3-36 透 皮 给 药 治 疗 肥 胖 症 的 研 究 作 者 姓 名 : 学 科 专 业 : 导 师 姓 名 : 完 成 时 间 : 陈 敏 细 胞 生 物 学 温 龙 平 教 授 二 一 年 八 月 三 十 一 日 University of Science and Technology of China A dissertation
Denosumab mg D60-90 T ( SERM) tibolone calcitonin calcitriold 12 ng/ml 7, % 68% 40% 20% denosumab ( 660 mg
 Denosumab 治療骨鬆與腫瘤骨轉移 中山醫學大學附設醫院藥劑科藥師林政仁 中山醫學大學醫學系助理教授曾思文 摘要 2010 (U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA) denosumab Denosumab IgG2 RANKL RANKL RANK 2011 FDA denosumab denosumab osteoporosis skeletal-related
Denosumab 治療骨鬆與腫瘤骨轉移 中山醫學大學附設醫院藥劑科藥師林政仁 中山醫學大學醫學系助理教授曾思文 摘要 2010 (U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA) denosumab Denosumab IgG2 RANKL RANKL RANK 2011 FDA denosumab denosumab osteoporosis skeletal-related
Pneumonia - Traditional Chinese
 Pneumonia When you have pneumonia, the air sacs in the lungs fill with infection or mucus. Pneumonia is caused by a bacteria, virus or chemical. It is not often passed from one person to another. Signs
Pneumonia When you have pneumonia, the air sacs in the lungs fill with infection or mucus. Pneumonia is caused by a bacteria, virus or chemical. It is not often passed from one person to another. Signs
Case Challenge [
 Case Challenge 台 中 榮 民 總 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 黃 文 男 醫 師 Case Presentation Brief History A 65-year year-old male RF (+) rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed for 7 years with medication of prednisolone, Cox-2 NSAIDs,,
Case Challenge 台 中 榮 民 總 醫 院 過 敏 免 疫 風 濕 科 黃 文 男 醫 師 Case Presentation Brief History A 65-year year-old male RF (+) rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed for 7 years with medication of prednisolone, Cox-2 NSAIDs,,
<4D6963726F736F667420576F7264202D20ECFAD0C0D0C0C2DBCEC4CCE1BDBB6F7665722E646F63>
 硕 士 专 业 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗 方 法 比 较 的 分 析 研 究 研 究 生 姓 名 指 导 教 师 姓 名 禚 欣 欣 康 定 华 专 业 名 称 皮 肤 性 病 学 研 究 方 向 皮 肤 肿 瘤 与 皮 肤 病 理 论 文 提 交 日 期 2013 年 4 月 I 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗
硕 士 专 业 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗 方 法 比 较 的 分 析 研 究 研 究 生 姓 名 指 导 教 师 姓 名 禚 欣 欣 康 定 华 专 业 名 称 皮 肤 性 病 学 研 究 方 向 皮 肤 肿 瘤 与 皮 肤 病 理 论 文 提 交 日 期 2013 年 4 月 I 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗
Fitness+ Natto Essence
 Naturext Fitness+ Natto Essence English - ( 华 语 解 释 ) ( Clinical Papers/ 临 床 论 文 ) Natural Vitamin (K2 60mcg+ D3 400IU) Synergetic Vitamin Formulation : Contains 60 mcg of Vitamin K2 (MK7); High Bioavailability;
Naturext Fitness+ Natto Essence English - ( 华 语 解 释 ) ( Clinical Papers/ 临 床 论 文 ) Natural Vitamin (K2 60mcg+ D3 400IU) Synergetic Vitamin Formulation : Contains 60 mcg of Vitamin K2 (MK7); High Bioavailability;
Microsoft PowerPoint - Cancer Epidemiology.ppt [相容模式]
![Microsoft PowerPoint - Cancer Epidemiology.ppt [相容模式] Microsoft PowerPoint - Cancer Epidemiology.ppt [相容模式]](/thumbs/43/23133079.jpg) Cancer Epidemiology 癌 症 流 行 病 學 林 英 助 副 教 授 : 牙 醫 學 系 07-3229746 轉 12 [email protected] Objective Discover the etiology leads - study of the distribution of cancer - quantify the risk associated with different
Cancer Epidemiology 癌 症 流 行 病 學 林 英 助 副 教 授 : 牙 醫 學 系 07-3229746 轉 12 [email protected] Objective Discover the etiology leads - study of the distribution of cancer - quantify the risk associated with different
國家圖書館典藏電子全文
 i ii Abstract The most important task in human resource management is to encourage and help employees to develop their potential so that they can fully contribute to the organization s goals. The main
i ii Abstract The most important task in human resource management is to encourage and help employees to develop their potential so that they can fully contribute to the organization s goals. The main
既 設 建 築 物 汙 水 處 理 設 施 生 化 需 氧 量 三 O 化 學 需 氧 量 一 OO 流 量 大 於 二 五 O 立 方 公 尺 / 日 懸 浮 固 體 三 O 大 腸 桿 菌 群 二 OO OOO 生 化 需 氧 量 五 O 既 設 建 築 物 指 中 華 民 國 九 化 學 需
 台 灣 基 層 透 析 協 會 本 會 宗 旨 : 關 懷 透 析 病 患, 提 升 透 析 品 質, 維 護 透 析 診 所 與 病 患 的 權 益, 最 新 消 息 : 協 助 政 府 制 定 相 關 醫 療 政 策 及 推 行 健 康 保 險 制 度 105 年 6 月 1 日, 腎 臟 醫 學 會 林 元 灝 秘 書 長 和 基 層 透 析 協 會 顏 大 翔 秘 書 長 至 劉 建 國 立
台 灣 基 層 透 析 協 會 本 會 宗 旨 : 關 懷 透 析 病 患, 提 升 透 析 品 質, 維 護 透 析 診 所 與 病 患 的 權 益, 最 新 消 息 : 協 助 政 府 制 定 相 關 醫 療 政 策 及 推 行 健 康 保 險 制 度 105 年 6 月 1 日, 腎 臟 醫 學 會 林 元 灝 秘 書 長 和 基 層 透 析 協 會 顏 大 翔 秘 書 長 至 劉 建 國 立
1269 malondialdehyde (MDA) were significantly decreased, while oxygen partial pressure (PaO 2 ), ph value, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione
 1268 维 生 素 A 联 合 牛 肺 表 面 活 性 物 质 治 疗 新 生 儿 呼 吸 窘 迫 综 合 征 的 临 床 研 究 朱 琼 1, 陈 小 利 2, 叶 华 2 1. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 儿 科, 重 庆 401520 2. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 内 儿 科, 重 庆 401520
1268 维 生 素 A 联 合 牛 肺 表 面 活 性 物 质 治 疗 新 生 儿 呼 吸 窘 迫 综 合 征 的 临 床 研 究 朱 琼 1, 陈 小 利 2, 叶 华 2 1. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 儿 科, 重 庆 401520 2. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 内 儿 科, 重 庆 401520
by mild (22.7%). Inhaled corticosteroids, systemic corticosteroids, and antibiotics were applied to 94.8% (292 cases), 74.7% (230 cases), and 90.9% (2
 论 著 临 床 研 究 doi: 0.7499/j.issn.008-8830.204.2.007 郑 州 市 城 区 儿 童 哮 喘 的 流 行 病 学 调 查 及 发 病 相 关 因 素 分 析 赵 坤 宋 桂 华 古 华 倩 2 刘 爽 3 张 岩 郭 彦 荣 (. 河 南 中 医 学 院 第 一 附 属 医 院 儿 科 医 院, 河 南 郑 州 450000; 2. 杭 州 市 余 杭 区
论 著 临 床 研 究 doi: 0.7499/j.issn.008-8830.204.2.007 郑 州 市 城 区 儿 童 哮 喘 的 流 行 病 学 调 查 及 发 病 相 关 因 素 分 析 赵 坤 宋 桂 华 古 华 倩 2 刘 爽 3 张 岩 郭 彦 荣 (. 河 南 中 医 学 院 第 一 附 属 医 院 儿 科 医 院, 河 南 郑 州 450000; 2. 杭 州 市 余 杭 区
Microsoft Word - HC20138_2010.doc
 Page: 1 of 7 Date: April 26, 2010 WINMATE COMMUNICATION INC. 9 F, NO. 111-6, SHING-DE RD., SAN-CHUNG CITY, TAIPEI, TAIWAN, R.O.C. The following merchandise was submitted and identified by the vendor as:
Page: 1 of 7 Date: April 26, 2010 WINMATE COMMUNICATION INC. 9 F, NO. 111-6, SHING-DE RD., SAN-CHUNG CITY, TAIPEI, TAIWAN, R.O.C. The following merchandise was submitted and identified by the vendor as:
UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) - Traditional Chinese
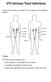 UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) Urinary tract infection, also called UTI, is an infection of the bladder or kidneys. Urethra Kidney Ureters Bladder Vagina Kidney Ureters Bladder Urethra Penis Causes UTI
UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) Urinary tract infection, also called UTI, is an infection of the bladder or kidneys. Urethra Kidney Ureters Bladder Vagina Kidney Ureters Bladder Urethra Penis Causes UTI
Microsoft PowerPoint - Jt HKBCF Ca breast SE Talk_Nov 13_2010[PDF]
![Microsoft PowerPoint - Jt HKBCF Ca breast SE Talk_Nov 13_2010[PDF] Microsoft PowerPoint - Jt HKBCF Ca breast SE Talk_Nov 13_2010[PDF]](/thumbs/42/23076200.jpg) 如 何 處 理 乳 癌 治 療 的 副 作 用 : 疲 勞 認 知 功 能 減 弱 性 功 能 障 礙 更 年 期 症 狀 等 曾 詠 恆 醫 生 香 港 大 學 臨 床 腫 瘤 學 系 助 理 教 授 香 港 大 學 內 科 學 系 榮 譽 助 理 教 授 二 零 一 零 年 十 一 月 十 三 日 專 題 內 容 乳 癌 確 診 類 型 乳 癌 的 發 展 及 趨 勢 治 療 發 展 治 療 引
如 何 處 理 乳 癌 治 療 的 副 作 用 : 疲 勞 認 知 功 能 減 弱 性 功 能 障 礙 更 年 期 症 狀 等 曾 詠 恆 醫 生 香 港 大 學 臨 床 腫 瘤 學 系 助 理 教 授 香 港 大 學 內 科 學 系 榮 譽 助 理 教 授 二 零 一 零 年 十 一 月 十 三 日 專 題 內 容 乳 癌 確 診 類 型 乳 癌 的 發 展 及 趨 勢 治 療 發 展 治 療 引
Clinical application of auriculotherpy 2006 nov 26
 Clinical application of Auriculotherapy and holographic therapy in postoperative pain and soft tissue injury Holographic therapy and auriculotherapy Aim The purpose of this report concerned with the activities
Clinical application of Auriculotherapy and holographic therapy in postoperative pain and soft tissue injury Holographic therapy and auriculotherapy Aim The purpose of this report concerned with the activities
臨 床 藥 物 治 療 學 Therapeutics of Clinical Drugs ( 5% 10%) 3 EGFRIs ( ) 4 (10-17%) TKI (5-9%) ( clindamycin 1%) doxycycline 100 mg minocycline 100 mg isot
 Therapeutics of Clinical Drugs 臨 床 藥 物 治 療 學 表 皮 生 長 因 子 抑 制 劑 皮 膚 併 發 症 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 藥 劑 科 藥 師 林 政 仁 吳 雀 維 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 醫 師 劉 親 穎 摘 要 (epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors EGFRIs)
Therapeutics of Clinical Drugs 臨 床 藥 物 治 療 學 表 皮 生 長 因 子 抑 制 劑 皮 膚 併 發 症 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 藥 劑 科 藥 師 林 政 仁 吳 雀 維 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 醫 師 劉 親 穎 摘 要 (epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors EGFRIs)
Male Circumcision - Traditional Chinese
 Male Circumcision Male circumcision is the removal of the foreskin around the end of the penis. If you decide on circumcision, your baby s doctor will do it in the hospital s nursery. If your baby is small
Male Circumcision Male circumcision is the removal of the foreskin around the end of the penis. If you decide on circumcision, your baby s doctor will do it in the hospital s nursery. If your baby is small
专 注 于 数 字 营 养 的 移 动 健 康 公 司 解 决 一 个 吃 的 健 康 的 问 题 中 粮 数 字 健 康 科 技 有 限 公 司 COFCO Digital Health Technology Co. Ltd By Hong Bill Xu COFCO Group Tel:86(1
 专 注 于 数 字 营 养 的 移 动 健 康 公 司 解 决 一 个 吃 的 健 康 的 问 题 中 粮 数 字 健 康 科 技 有 限 公 司 COFCO Digital Health Technology Co. Ltd By Hong Bill Xu COFCO Group Tel:86(10)8500-6419 Fax:86(10)8561-5955 Email:[email protected]
专 注 于 数 字 营 养 的 移 动 健 康 公 司 解 决 一 个 吃 的 健 康 的 问 题 中 粮 数 字 健 康 科 技 有 限 公 司 COFCO Digital Health Technology Co. Ltd By Hong Bill Xu COFCO Group Tel:86(10)8500-6419 Fax:86(10)8561-5955 Email:[email protected]
- MP <34 P<0.001 UA UA/MCA MCA P<0.05 UA UA/MCA UtA PI RI P<0.05 UtA 24 BP 24 MP III
 98017624 Changes of maternal and fetal hemodynamics in early-onset severe preeclampsia : : 98017624 : 98-6 : : : : : OO - MP 46 30 16 92
98017624 Changes of maternal and fetal hemodynamics in early-onset severe preeclampsia : : 98017624 : 98-6 : : : : : OO - MP 46 30 16 92
相 关 报 道 近 年 来 临 床 上 运 用 多 种 针 灸 疗 法 治 疗 肥 胖 及 其 引 起 的 并 发 症, 如 高 脂 血 症 糖 尿 病 高 血 压 及 痛 经 等, 均 获 得 满 意 疗 效. caused by sedentary lifestyle and genetic f
 在 线 投 稿 : http://www.baishideng.com/wcjd/ch/index.aspx 帮 助 平 台 : http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i5.815 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2016 年 2 月 18 日 ; 24(5): 815-820 ISSN 1009-3079 (print)
在 线 投 稿 : http://www.baishideng.com/wcjd/ch/index.aspx 帮 助 平 台 : http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i5.815 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2016 年 2 月 18 日 ; 24(5): 815-820 ISSN 1009-3079 (print)
<4D6963726F736F667420576F7264202D2078B1CFD2B5C2DBCEC4A3BAA1B6BDF0D8D1D2AAC2D4A1B7D0BAD0C4CCC0B7BDD6A4D1D0BEBF2E646F63>
 2003 级 硕 士 研 究 生 毕 业 论 文 金 匮 要 略 泻 心 汤 方 证 研 究 分 类 号 :R2 单 位 代 号 :10315 密 级 : 秘 密 学 科 代 码 :100800 2003 级 硕 士 研 究 生 毕 业 论 文 学 号 :20031023 金 匮 要 略 泻 心 汤 方 证 研 究 学 科 专 业 临 床 中 药 学 导 师 黄 煌 教 授 研 究 生 张 薛 光
2003 级 硕 士 研 究 生 毕 业 论 文 金 匮 要 略 泻 心 汤 方 证 研 究 分 类 号 :R2 单 位 代 号 :10315 密 级 : 秘 密 学 科 代 码 :100800 2003 级 硕 士 研 究 生 毕 业 论 文 学 号 :20031023 金 匮 要 略 泻 心 汤 方 证 研 究 学 科 专 业 临 床 中 药 学 导 师 黄 煌 教 授 研 究 生 张 薛 光
第一章 緒論
 (informed consent) 6 . (Informed 23 Consent) 24 (Informed Consent) informed consent 1. 2. 7 3. 4. 5. 6.. 26 1. 8 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.. Braddock 1993 59 65 1057 (discussion of the patient s role in decision making)
(informed consent) 6 . (Informed 23 Consent) 24 (Informed Consent) informed consent 1. 2. 7 3. 4. 5. 6.. 26 1. 8 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.. Braddock 1993 59 65 1057 (discussion of the patient s role in decision making)
5-25袁宏钧.indd
 第 24 卷 第 5 期 2015 年 5 月 碘 131 doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2015, 24(5):643 647. Chinese Journal of
第 24 卷 第 5 期 2015 年 5 月 碘 131 doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2015, 24(5):643 647. Chinese Journal of
HC50246_2009
 Page: 1 of 7 Date: June 2, 2009 WINMATE COMMUNICATION INC. 9 F, NO. 111-6, SHING-DE RD., SAN-CHUNG CITY, TAIPEI, TAIWAN, R.O.C. The following merchandise was submitted and identified by the vendor as:
Page: 1 of 7 Date: June 2, 2009 WINMATE COMMUNICATION INC. 9 F, NO. 111-6, SHING-DE RD., SAN-CHUNG CITY, TAIPEI, TAIWAN, R.O.C. The following merchandise was submitted and identified by the vendor as:
Microsoft Word - TIP006SCH Uni-edit Writing Tip - Presentperfecttenseandpasttenseinyourintroduction readytopublish
 我 难 度 : 高 级 对 们 现 不 在 知 仍 道 有 听 影 过 响 多 少 那 次 么 : 研 英 究 过 文 论 去 写 文 时 作 的 表 技 引 示 巧 言 事 : 部 情 引 分 发 言 该 生 使 在 中 用 过 去, 而 现 在 完 成 时 仅 表 示 事 情 发 生 在 过 去, 并 的 哪 现 种 在 时 完 态 成 呢 时? 和 难 过 道 去 不 时 相 关? 是 所 有
我 难 度 : 高 级 对 们 现 不 在 知 仍 道 有 听 影 过 响 多 少 那 次 么 : 研 英 究 过 文 论 去 写 文 时 作 的 表 技 引 示 巧 言 事 : 部 情 引 分 发 言 该 生 使 在 中 用 过 去, 而 现 在 完 成 时 仅 表 示 事 情 发 生 在 过 去, 并 的 哪 现 种 在 时 完 态 成 呢 时? 和 难 过 道 去 不 时 相 关? 是 所 有
聖馬爾定醫院正子中心健保開單診療指引(guideline)
 聖 馬 爾 定 醫 院 正 子 中 心 健 保 開 單 診 療 指 引 (guideline) 2011.10.27 全 身 癌 症 掃 描 檢 查 (2010 年 6 月 1 日 起 健 保 開 始 對 下 列 正 子 掃 描 之 適 應 症 給 付 ): 1. 乳 癌 淋 巴 癌 之 分 期 治 療 及 懷 疑 復 發 或 再 分 期 2. 大 腸 癌 直 腸 癌 食 道 癌 頭 頸 部 癌 (
聖 馬 爾 定 醫 院 正 子 中 心 健 保 開 單 診 療 指 引 (guideline) 2011.10.27 全 身 癌 症 掃 描 檢 查 (2010 年 6 月 1 日 起 健 保 開 始 對 下 列 正 子 掃 描 之 適 應 症 給 付 ): 1. 乳 癌 淋 巴 癌 之 分 期 治 療 及 懷 疑 復 發 或 再 分 期 2. 大 腸 癌 直 腸 癌 食 道 癌 頭 頸 部 癌 (
%
 38 1 2014 1 Vol. 38No. 1 January 2014 51 Population Research 2010 2010 2010 65 100028 Changing Lineal Families with Three Generations An Analysis of the 2010 Census Data Wang Yuesheng Abstract In contemporary
38 1 2014 1 Vol. 38No. 1 January 2014 51 Population Research 2010 2010 2010 65 100028 Changing Lineal Families with Three Generations An Analysis of the 2010 Census Data Wang Yuesheng Abstract In contemporary
HC20131_2010
 Page: 1 of 8 Date: April 14, 2010 WINMATE COMMUNICATION INC. 9 F, NO. 111-6, SHING-DE RD., SAN-CHUNG CITY, TAIPEI, TAIWAN, R.O.C. The following merchandise was submitted and identified by the vendor as:
Page: 1 of 8 Date: April 14, 2010 WINMATE COMMUNICATION INC. 9 F, NO. 111-6, SHING-DE RD., SAN-CHUNG CITY, TAIPEI, TAIWAN, R.O.C. The following merchandise was submitted and identified by the vendor as:
OA-253_H1~H4_OL.ai
 WARNINGS Note: Read ALL the following BEFORE using this product. Follow all Guidelines at all times while using this product. CAUTION This warning indicates possibility of personal injury and material
WARNINGS Note: Read ALL the following BEFORE using this product. Follow all Guidelines at all times while using this product. CAUTION This warning indicates possibility of personal injury and material
07 353-408
 編 號 :CCMP96-RD-006 以 德 菲 法 探 討 中 醫 臨 床 證 型 診 斷 基 準 - 六 淫 證 型 蘇 奕 彰 中 國 醫 藥 大 學 摘 要 德 菲 法 (Delphi Method) 是 廣 泛 被 使 用 的 研 究 方 法, 尤 其 適 用 於 新 的 研 究 領 域 (new research area) 及 探 索 性 研 究 (exploratory studies),
編 號 :CCMP96-RD-006 以 德 菲 法 探 討 中 醫 臨 床 證 型 診 斷 基 準 - 六 淫 證 型 蘇 奕 彰 中 國 醫 藥 大 學 摘 要 德 菲 法 (Delphi Method) 是 廣 泛 被 使 用 的 研 究 方 法, 尤 其 適 用 於 新 的 研 究 領 域 (new research area) 及 探 索 性 研 究 (exploratory studies),
600 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 5 期 2016 年 5 月 were significantly decreased, but the levels of IL-12 in two groups were significantly increa
 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 5 期 2016 年 5 月 599 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合 细 辛 脑 注 射 液 治 疗 小 儿 毛 细 支 气 管 炎 的 临 床 研 究 唐 辉 英, 佘 定 平, 马 颐 娇 深 圳 市 儿 童 医 院 呼 吸 科, 广 东 深 圳 518026 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合
现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 5 期 2016 年 5 月 599 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合 细 辛 脑 注 射 液 治 疗 小 儿 毛 细 支 气 管 炎 的 临 床 研 究 唐 辉 英, 佘 定 平, 马 颐 娇 深 圳 市 儿 童 医 院 呼 吸 科, 广 东 深 圳 518026 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合
<4D6963726F736F667420576F7264202D20A46AA4AFACECA7DEA46ABEC7B1D0AE76ACE3A873AD70B565A6A8AA47B3F8A769A4AFACE33938303637>
 大 仁 科 技 大 學 教 師 研 究 計 畫 成 果 報 告 長 期 照 護 中 心 之 室 內 空 氣 品 質 評 估 計 畫 編 號 : 仁 研 9867 執 行 期 限 :98 年 1 月 1 日 至 98 年 12 月 31 日 主 持 人 : 馮 靜 安 執 行 單 位 : 職 業 安 全 衛 生 系 ( 所 ) E-Mail:[email protected] 一 中 文
大 仁 科 技 大 學 教 師 研 究 計 畫 成 果 報 告 長 期 照 護 中 心 之 室 內 空 氣 品 質 評 估 計 畫 編 號 : 仁 研 9867 執 行 期 限 :98 年 1 月 1 日 至 98 年 12 月 31 日 主 持 人 : 馮 靜 安 執 行 單 位 : 職 業 安 全 衛 生 系 ( 所 ) E-Mail:[email protected] 一 中 文
要, 理 想 糾 紛 解 決 方 式 以 公 會 協 助 處 理 與 委 託 保 險 公 司 幫 忙 和 解 ; (2) 研 究 發 現 糾 紛 案 件 中,40-50 歲 之 男 性 以 針 灸 或 推 拿 為 主 要 治 療 方 式 碩 士 與 博 士 年 資 15-20 年 每 診 人 數 越
 編 號 :CCMP98-RD-022 中 醫 醫 療 糾 紛 與 醫 師 責 任 保 險 之 評 估 研 究 陳 俞 沛 台 灣 中 醫 診 斷 學 會 研 究 目 的 : 摘 要 近 年 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 的 中 醫 界, 醫 療 糾 紛 發 生 率 與 發 生 頻 率 也 逐 漸 提 高, 為 影 響 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 與 維 持 良 好 醫 療 品 質 的 一 大 隱 憂 醫 師
編 號 :CCMP98-RD-022 中 醫 醫 療 糾 紛 與 醫 師 責 任 保 險 之 評 估 研 究 陳 俞 沛 台 灣 中 醫 診 斷 學 會 研 究 目 的 : 摘 要 近 年 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 的 中 醫 界, 醫 療 糾 紛 發 生 率 與 發 生 頻 率 也 逐 漸 提 高, 為 影 響 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 與 維 持 良 好 醫 療 品 質 的 一 大 隱 憂 醫 師
Microsoft Word - 01李惠玲ok.doc
 康 寧 學 報 11:1-20(2009) 1 數 位 學 習 於 護 理 技 術 課 程 之 運 用 與 評 值 * 李 惠 玲 ** 高 清 華 *** 呂 莉 婷 摘 要 背 景 : 網 路 科 技 在 教 育 的 使 用 已 成 為 一 種 有 利 的 教 學 輔 助 工 具 網 路 教 學 的 特 性, 在 使 學 習 可 不 分 時 間 與 空 間 不 同 進 度 把 握 即 時 性 資
康 寧 學 報 11:1-20(2009) 1 數 位 學 習 於 護 理 技 術 課 程 之 運 用 與 評 值 * 李 惠 玲 ** 高 清 華 *** 呂 莉 婷 摘 要 背 景 : 網 路 科 技 在 教 育 的 使 用 已 成 為 一 種 有 利 的 教 學 輔 助 工 具 網 路 教 學 的 特 性, 在 使 學 習 可 不 分 時 間 與 空 間 不 同 進 度 把 握 即 時 性 資
现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 29 卷 第 9 期 2014 年 9 月 1045 and simulation of Tiapride Tablets, 3 times/d, 4 6 years old patients: 1 tablet/time; 7 11 y
 1044 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 29 卷 第 9 期 2014 年 9 月 菖 麻 熄 风 片 治 疗 小 儿 多 发 性 抽 动 症 肝 风 内 动 挟 痰 证 Ⅲ 期 临 床 研 究 胡 思 源 1, 马 融 1*, 田 恬 2, 钟 成 梁 1, 魏 小 维 1, 向 希 雄 3, 丁 樱 4, 吕 玉 霞 5, 王 雪 峰 6, 李 燕 宁 1. 天
1044 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 29 卷 第 9 期 2014 年 9 月 菖 麻 熄 风 片 治 疗 小 儿 多 发 性 抽 动 症 肝 风 内 动 挟 痰 证 Ⅲ 期 临 床 研 究 胡 思 源 1, 马 融 1*, 田 恬 2, 钟 成 梁 1, 魏 小 维 1, 向 希 雄 3, 丁 樱 4, 吕 玉 霞 5, 王 雪 峰 6, 李 燕 宁 1. 天
國家圖書館典藏電子全文
 1 2 3 Umbilical cord Blood Analysis for Women at First Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery OBJECTIVE: To analyze the gas values of the umbilical cord blood in the first vaginal delivered babies and to verify
1 2 3 Umbilical cord Blood Analysis for Women at First Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery OBJECTIVE: To analyze the gas values of the umbilical cord blood in the first vaginal delivered babies and to verify
标题
 医 药 导 报 2016 年 8 月 第 35 卷 第 8 期 803 特 约 稿 鱼 腥 草 制 剂 上 市 后 安 全 性 再 评 价 吴 健 鸿 1 ꎬ 杨 晓 燕 2 ꎬ 柳 强 妮 2 ꎬ 尹 平 2 2 ꎬ 曾 繁 典 (1. 武 汉 药 品 医 疗 器 械 检 验 所 ꎬ 武 汉 430075ꎻ2. 华 中 科 技 大 学 同 济 医 学 院 ꎬ 武 汉 430030) 摘 要 目 的
医 药 导 报 2016 年 8 月 第 35 卷 第 8 期 803 特 约 稿 鱼 腥 草 制 剂 上 市 后 安 全 性 再 评 价 吴 健 鸿 1 ꎬ 杨 晓 燕 2 ꎬ 柳 强 妮 2 ꎬ 尹 平 2 2 ꎬ 曾 繁 典 (1. 武 汉 药 品 医 疗 器 械 检 验 所 ꎬ 武 汉 430075ꎻ2. 华 中 科 技 大 学 同 济 医 学 院 ꎬ 武 汉 430030) 摘 要 目 的
广 州 市 花 都 区 公 务 员 培 训 需 求 分 析 的 研 究 A STUDY OF TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS ON CIVIL SERVANTS OF HUADU DISTRICT IN GUANGZHOU 作 者 姓 名 : 黄 宁 宁 领 域 ( 方 向 ): 公
 广 州 市 花 都 区 公 务 员 培 训 需 求 分 析 的 研 究 分 类 号 :C93 单 位 代 码 :10183 研 究 生 学 号 :201223A022 密 级 : 公 开 研 吉 林 大 学 硕 士 学 位 论 文 ( 专 业 学 位 ) 黄 宁 宁 广 州 市 花 都 区 公 务 员 培 训 需 求 分 析 的 研 究 A STUDY OF TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS
广 州 市 花 都 区 公 务 员 培 训 需 求 分 析 的 研 究 分 类 号 :C93 单 位 代 码 :10183 研 究 生 学 号 :201223A022 密 级 : 公 开 研 吉 林 大 学 硕 士 学 位 论 文 ( 专 业 学 位 ) 黄 宁 宁 广 州 市 花 都 区 公 务 员 培 训 需 求 分 析 的 研 究 A STUDY OF TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS
03施琅「棄留臺灣議」探索.doc
 38 93 43 59 43 44 1 2 1621 1645 1646 3 1647 1649 4 1 1996 12 121 2 1988 1 54---79 3 1990 2 39 4 1987 8 16 19 1649 27---28 45 1651 5 1656 1662 1664 1667 1668 6 1681 1683 7 13 1958 2 1651 2002 11 67 1961
38 93 43 59 43 44 1 2 1621 1645 1646 3 1647 1649 4 1 1996 12 121 2 1988 1 54---79 3 1990 2 39 4 1987 8 16 19 1649 27---28 45 1651 5 1656 1662 1664 1667 1668 6 1681 1683 7 13 1958 2 1651 2002 11 67 1961
- I -
 2005 Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage on the Intervertebral Disc in Vertebroplasty () 2005 4 - I - - II - Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage
2005 Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage on the Intervertebral Disc in Vertebroplasty () 2005 4 - I - - II - Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage
中 文 摘 要 : 胃 食 管 反 流 病 食 管 外 表 现 与 酸 反 流 关 系 的 研 究 研 究 生 : 赵 莉 导 师 : 刘 新 光 目 的 : 探 讨 反 流 性 食 管 炎 (RE) 常 见 的 食 管 外 表 现,24 小 时 食 管 ph 监 测 对 伴 有 食 管 外 表 现
 ( 医 学 部 ) 在 职 人 员 申 请 硕 士 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 胃 食 管 反 流 病 食 管 外 表 现 与 酸 反 流 关 系 的 研 究 学 院 ( 医 院 所 ): 北 京 大 学 第 一 医 院 学 科 专 业 : 消 化 内 科 申 请 人 姓 名 : 赵 莉 导 师 姓 名 职 称 : 刘 新 光 二 OO 七 年 五 月 1 中 文 摘 要 : 胃 食 管 反 流
( 医 学 部 ) 在 职 人 员 申 请 硕 士 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 胃 食 管 反 流 病 食 管 外 表 现 与 酸 反 流 关 系 的 研 究 学 院 ( 医 院 所 ): 北 京 大 学 第 一 医 院 学 科 专 业 : 消 化 内 科 申 请 人 姓 名 : 赵 莉 导 师 姓 名 职 称 : 刘 新 光 二 OO 七 年 五 月 1 中 文 摘 要 : 胃 食 管 反 流
Microsoft Word - D-2°w¶Ë¬ì¹ï¤U�Iµh®{¤âÀˬd¬yµ{_¬x°ö�×__P.329-335_.doc
 針 傷 科 對 下 背 痛 徒 手 檢 查 流 程 329 針 傷 科 對 下 背 痛 徒 手 檢 查 流 程 洪 培 修 1 張 晉 賢 2 張 世 良 3 1 嘉 義 基 督 教 醫 院 中 醫 科 系 2 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 中 醫 醫 院 基 隆 分 院 暨 長 庚 大 學 醫 學 院 3 中 國 醫 藥 大 學 中 醫 院 學 針 灸 研 究 所 摘 要 前 言 腰 痛 或 下 背 痛
針 傷 科 對 下 背 痛 徒 手 檢 查 流 程 329 針 傷 科 對 下 背 痛 徒 手 檢 查 流 程 洪 培 修 1 張 晉 賢 2 張 世 良 3 1 嘉 義 基 督 教 醫 院 中 醫 科 系 2 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 中 醫 醫 院 基 隆 分 院 暨 長 庚 大 學 醫 學 院 3 中 國 醫 藥 大 學 中 醫 院 學 針 灸 研 究 所 摘 要 前 言 腰 痛 或 下 背 痛
目 录 8.3 NOC 医 疗 服 务 声 明 执 业 注 册 申 请 表 医 疗 器 械 入 境 申 请 表 药 物 入 境 申 请 表 17
 目 录 1 概 述 1 2. 相 关 政 策 2 2.1 代 表 团 随 队 医 生 执 业 备 案 2 2.2 代 表 团 医 疗 专 业 人 员 保 险 2 2.3 代 表 团 药 物 和 医 疗 器 械 进 出 境 2 2.4 代 表 团 随 队 医 生 药 房 服 务 及 处 方 权 3 2.5 运 动 员 治 疗 用 药 豁 免 (TUE) 3 2.6 医 疗 费 用 政 策 4 2.7
目 录 1 概 述 1 2. 相 关 政 策 2 2.1 代 表 团 随 队 医 生 执 业 备 案 2 2.2 代 表 团 医 疗 专 业 人 员 保 险 2 2.3 代 表 团 药 物 和 医 疗 器 械 进 出 境 2 2.4 代 表 团 随 队 医 生 药 房 服 务 及 处 方 权 3 2.5 运 动 员 治 疗 用 药 豁 免 (TUE) 3 2.6 医 疗 费 用 政 策 4 2.7
10389144 2006 5 30 2006 5 30
 10389144 10389144 2006 5 30 2006 5 30 ED ED IIEFEFOF SDISOS ED 10 2 2 1 10 4 1 1 4 4 IIEF SD EFOFISOS EF 2 1 1 4 1 ED ED Study on the effect of Sex Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction Patients ABSTRACT Objective
10389144 10389144 2006 5 30 2006 5 30 ED ED IIEFEFOF SDISOS ED 10 2 2 1 10 4 1 1 4 4 IIEF SD EFOFISOS EF 2 1 1 4 1 ED ED Study on the effect of Sex Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction Patients ABSTRACT Objective
ºî½×2-p174-184
 174 美 國 感 染 症 醫 學 會 Methicillin 抗 藥 性 金 黃 色 葡 萄 球 菌 治 療 指 引 李 倩 瑜 1 鄭 舒 倖 2 行 政 院 衛 生 署 桃 園 醫 院 1 小 兒 科 2 感 染 科 (IDSA) 2011 methicillin (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MRSA) (practice guidelines)[1]
174 美 國 感 染 症 醫 學 會 Methicillin 抗 藥 性 金 黃 色 葡 萄 球 菌 治 療 指 引 李 倩 瑜 1 鄭 舒 倖 2 行 政 院 衛 生 署 桃 園 醫 院 1 小 兒 科 2 感 染 科 (IDSA) 2011 methicillin (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MRSA) (practice guidelines)[1]
度 身 體 活 動 量 ; 芬 蘭 幼 兒 呈 現 中 度 身 體 活 動 量 之 比 例 高 於 臺 灣 幼 兒 (5) 幼 兒 在 投 入 度 方 面 亦 達 顯 著 差 異 (χ²=185.35, p <.001), 芬 蘭 與 臺 灣 幼 兒 多 半 表 現 出 中 度 投 入 與 高 度
 臺 灣 與 芬 蘭 幼 兒 園 室 內 自 由 遊 戲 內 涵 之 探 討 林 昭 溶 毛 萬 儀 經 國 管 理 暨 健 康 學 院 幼 兒 保 育 系 副 教 授 [email protected] 吳 敏 而 國 家 教 育 研 究 院 研 究 員 [email protected] [email protected] 摘 要 自 由 遊 戲 被 視 為 是 幼 兒 的
臺 灣 與 芬 蘭 幼 兒 園 室 內 自 由 遊 戲 內 涵 之 探 討 林 昭 溶 毛 萬 儀 經 國 管 理 暨 健 康 學 院 幼 兒 保 育 系 副 教 授 [email protected] 吳 敏 而 國 家 教 育 研 究 院 研 究 員 [email protected] [email protected] 摘 要 自 由 遊 戲 被 視 為 是 幼 兒 的
2015年4月11日雅思阅读预测机经(新东方版)
 剑 桥 雅 思 10 第 一 时 间 解 析 阅 读 部 分 1 剑 桥 雅 思 10 整 体 内 容 统 计 2 剑 桥 雅 思 10 话 题 类 型 从 以 上 统 计 可 以 看 出, 雅 思 阅 读 的 考 试 话 题 一 直 广 泛 多 样 而 题 型 则 稳 中 有 变 以 剑 桥 10 的 test 4 为 例 出 现 的 三 篇 文 章 分 别 是 自 然 类, 心 理 研 究 类,
剑 桥 雅 思 10 第 一 时 间 解 析 阅 读 部 分 1 剑 桥 雅 思 10 整 体 内 容 统 计 2 剑 桥 雅 思 10 话 题 类 型 从 以 上 统 计 可 以 看 出, 雅 思 阅 读 的 考 试 话 题 一 直 广 泛 多 样 而 题 型 则 稳 中 有 变 以 剑 桥 10 的 test 4 为 例 出 现 的 三 篇 文 章 分 别 是 自 然 类, 心 理 研 究 类,
中 文 摘 要 芦 荟 和 金 银 花 抗 菌 成 分 提 取 及 其 对 棉 织 物 的 整 理 中 文 摘 要 随 着 生 活 水 平 的 提 高 和 健 康 环 保 意 识 的 增 强, 人 们 对 棉 织 物 卫 生 保 健 功 能 的 要 求 越 来 越 高, 故 对 棉 织 物 进 行
 高 等 学 校 教 师 硕 士 学 位 论 文 (2008 届 ) 芦 荟 和 金 银 花 抗 菌 成 分 提 取 及 其 对 棉 织 物 的 整 理 Extraction of Aloe and Honey Suckle Antibacterial Ingredients and Application to Antibiotic Finishing of Cotton 研 究 生 姓 名 指 导
高 等 学 校 教 师 硕 士 学 位 论 文 (2008 届 ) 芦 荟 和 金 银 花 抗 菌 成 分 提 取 及 其 对 棉 织 物 的 整 理 Extraction of Aloe and Honey Suckle Antibacterial Ingredients and Application to Antibiotic Finishing of Cotton 研 究 生 姓 名 指 导
Microsoft Word - 20101483毕业论文+-+副本
 密 级 : 公 开 学 号 :20101483 硕 士 学 位 论 文 祛 斑 玉 容 方 对 色 素 沉 着 小 鼠 血 酪 氨 酸 酶 及 皮 肤 形 态 的 影 响 研 究 生 王 茜 指 导 教 师 学 科 专 业 所 在 学 院 毕 业 时 间 孙 亦 农 中 医 康 复 学 第 二 临 床 医 学 院 2013 年 6 月 Freckle of Yurong side of pigmentation
密 级 : 公 开 学 号 :20101483 硕 士 学 位 论 文 祛 斑 玉 容 方 对 色 素 沉 着 小 鼠 血 酪 氨 酸 酶 及 皮 肤 形 态 的 影 响 研 究 生 王 茜 指 导 教 师 学 科 专 业 所 在 学 院 毕 业 时 间 孙 亦 农 中 医 康 复 学 第 二 临 床 医 学 院 2013 年 6 月 Freckle of Yurong side of pigmentation
2012 10 32 10 765 2006 61. 3% GH nmol /L ng /ml 1 ng = 0. 047 nmol /L 1 40 ~ prolactin 125 /100 3 ~ 4 /100 PRL GH 13 /10 IGF-1 1034 /100 2 40 4% ~ 14%
 764 2011 1005-2194 2012 10-0764 - 11 R584 A Interpretation of medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly - 2011 update. TIAN Dan CEN Jing GU Feng. Key Laboratory
764 2011 1005-2194 2012 10-0764 - 11 R584 A Interpretation of medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly - 2011 update. TIAN Dan CEN Jing GU Feng. Key Laboratory
9-1396-2015-0883.doc
 1396 药 学 学 报 Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 2015, 50 (11): 1396 1401 MedDRA 及 其 在 不 良 事 件 分 析 中 的 应 用 * 陆 梦 洁, 刘 玉 秀 ( 南 京 军 区 南 京 总 医 院 医 务 部, 江 苏 南 京 210002) 摘 要 : 临 床 试 验 的 安 全 性 评 价 很 大 程 度 上 依 赖 于 对 不
1396 药 学 学 报 Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 2015, 50 (11): 1396 1401 MedDRA 及 其 在 不 良 事 件 分 析 中 的 应 用 * 陆 梦 洁, 刘 玉 秀 ( 南 京 军 区 南 京 总 医 院 医 务 部, 江 苏 南 京 210002) 摘 要 : 临 床 试 验 的 安 全 性 评 价 很 大 程 度 上 依 赖 于 对 不
 Master CAM Abstract With the great progress on the transition of mankind's living type attitude and medical science, mankind's present average life span is all in the extension year by year, increasing
Master CAM Abstract With the great progress on the transition of mankind's living type attitude and medical science, mankind's present average life span is all in the extension year by year, increasing
<46495420446F63756D656E7428442D2D796E2DD6D0D2BDD2A92DB5DA3132C6DA2DB7E2C3E6CDC6BDE9A3A8323031342D3132A3A9CCE6BBBB2E6D6469>
 2014 第十六卷 第十二期 绎Vol.16 No.12 清热利湿化瘀汤联合针灸治疗慢性盆腔炎 湿热瘀结证临床研究 周 萍 1 曾志华 1元元 向阳红 2 1. 重庆医科大学中医药学院 摘 重庆 401331 2. 重庆市中医研究院 重庆 400020 要 目的 观察清热利湿化瘀汤联合针灸治疗慢性盆腔炎湿热瘀结证的临床疗效 方法 将 120 例病例随机分为 每组各 40 例 给予口服清热利湿化瘀汤
2014 第十六卷 第十二期 绎Vol.16 No.12 清热利湿化瘀汤联合针灸治疗慢性盆腔炎 湿热瘀结证临床研究 周 萍 1 曾志华 1元元 向阳红 2 1. 重庆医科大学中医药学院 摘 重庆 401331 2. 重庆市中医研究院 重庆 400020 要 目的 观察清热利湿化瘀汤联合针灸治疗慢性盆腔炎湿热瘀结证的临床疗效 方法 将 120 例病例随机分为 每组各 40 例 给予口服清热利湿化瘀汤
<46495420446F63756D656E7428452D2D796E2D31C6DABFAF2D31D6D0D2BDD2A9CFD6B4FABBAF2D32303134C4EA2DB5DA34C6DA2DC4BFC2BC2D34C6DA2E6D6469>
 绎 1 援 401331 2. 400030 3. 400020 4. 400080 5. 400012 88 44 44 猿 孕 约 0.05 ESR 悦 CRP RF 孕 约 0.05 doi: 10.11842/wst.2014.04.018 R593.22 A Rheumatoid Arthritis RA 44 19 25 32 耀 75 47.71 依 8.53 5 耀 28 4.39
绎 1 援 401331 2. 400030 3. 400020 4. 400080 5. 400012 88 44 44 猿 孕 约 0.05 ESR 悦 CRP RF 孕 约 0.05 doi: 10.11842/wst.2014.04.018 R593.22 A Rheumatoid Arthritis RA 44 19 25 32 耀 75 47.71 依 8.53 5 耀 28 4.39
84 針 藥 併 施 治 療 偏 頭 痛 次 發 作 症 狀 為 左 顳 側 頭 脹 痛, 多 為 夜 間 發 作 影 響 睡 眠 或 工 作, 頻 率 為 一 天 發 作 一 次, 持 續 一 至 二 小 時, 疼 痛 指 數 7 分 (0 分 為 不 痛, 最 痛 為 滿 分 10 分 ), 需
 J Chin Med 26(1): 83-91, 2015 DOI: 10.3966/101764462015062601008 83 針 藥 併 施 治 療 偏 頭 痛 經 驗 - 病 例 報 告 1, 眞 # 1, #, * 1, 2 1, 2 1 高 雄 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 中 醫 科 系, 高 雄, 台 灣 2 長 庚 大 學 中 醫 系, 桃 園, 台 灣 103 12 26 104
J Chin Med 26(1): 83-91, 2015 DOI: 10.3966/101764462015062601008 83 針 藥 併 施 治 療 偏 頭 痛 經 驗 - 病 例 報 告 1, 眞 # 1, #, * 1, 2 1, 2 1 高 雄 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 中 醫 科 系, 高 雄, 台 灣 2 長 庚 大 學 中 醫 系, 桃 園, 台 灣 103 12 26 104
The Clinical and Experimental Study on the Relationship Between Fibrinogen and Development of Coronary Artery Disease 2
 2004 5 10 The Clinical and Experimental Study on the Relationship Between Fibrinogen and Development of Coronary Artery Disease 2 3...4...6...9... 9......13... 15 LDL/HDL......17....20.....25....29......33......38......39......44......44......57.....65......66
2004 5 10 The Clinical and Experimental Study on the Relationship Between Fibrinogen and Development of Coronary Artery Disease 2 3...4...6...9... 9......13... 15 LDL/HDL......17....20.....25....29......33......38......39......44......44......57.....65......66
壹、前言
 DOH93-DC-1116 93 3 1 93 12 31 ... 1... 4... 6... 7... 8... 9... 13... 13 ()... 13 ()... 14 ()... 14... 16... 16... 16... 17... 18 1 ... 19... 24... 27... 29... 31... 31... 33... 34... 35... 36... 36 ()...
DOH93-DC-1116 93 3 1 93 12 31 ... 1... 4... 6... 7... 8... 9... 13... 13 ()... 13 ()... 14 ()... 14... 16... 16... 16... 17... 18 1 ... 19... 24... 27... 29... 31... 31... 33... 34... 35... 36... 36 ()...
中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 46 卷 第 9 期 2015 年 5 月 1339 非 酒 精 性 脂 肪 性 肝 病 (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,nafld) 是 一 种 与 胰 岛 素 抵 抗 遗
 1338 中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 46 卷 第 9 期 2015 年 5 月 九 味 肝 泰 胶 囊 对 高 脂 饮 食 诱 导 大 鼠 非 酒 精 性 脂 肪 肝 的 治 疗 作 用 陈 菲 1 2,, 艾 国 3, 盛 柳 青 1, 麻 佳 蕾 1, 黄 正 明 1. 金 华 职 业 技 术 学 院 医 学 院, 浙 江 金 华
1338 中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 46 卷 第 9 期 2015 年 5 月 九 味 肝 泰 胶 囊 对 高 脂 饮 食 诱 导 大 鼠 非 酒 精 性 脂 肪 肝 的 治 疗 作 用 陈 菲 1 2,, 艾 国 3, 盛 柳 青 1, 麻 佳 蕾 1, 黄 正 明 1. 金 华 职 业 技 术 学 院 医 学 院, 浙 江 金 华
入學考試網上報名指南
 入 學 考 試 網 上 報 名 指 南 On-line Application Guide for Admission Examination 16/01/2015 University of Macau Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 A. 新 申 請 網 上 登 記 帳 戶 /Register for New Account... 2 B. 填
入 學 考 試 網 上 報 名 指 南 On-line Application Guide for Admission Examination 16/01/2015 University of Macau Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 A. 新 申 請 網 上 登 記 帳 戶 /Register for New Account... 2 B. 填
Chinese oil import policies and reforms 随 着 经 济 的 发 展, 目 前 中 国 石 油 消 费 总 量 已 经 跃 居 世 界 第 二 作 为 一 个 负 责 任 的 大 国, 中 国 正 在 积 极 推 进 能 源 进 口 多 元 化, 鼓 励 替 代
 Chinese oil import policies and reforms SINOPEC EDRI 2014.8 Chinese oil import policies and reforms 随 着 经 济 的 发 展, 目 前 中 国 石 油 消 费 总 量 已 经 跃 居 世 界 第 二 作 为 一 个 负 责 任 的 大 国, 中 国 正 在 积 极 推 进 能 源 进 口 多 元 化,
Chinese oil import policies and reforms SINOPEC EDRI 2014.8 Chinese oil import policies and reforms 随 着 经 济 的 发 展, 目 前 中 国 石 油 消 费 总 量 已 经 跃 居 世 界 第 二 作 为 一 个 负 责 任 的 大 国, 中 国 正 在 积 极 推 进 能 源 进 口 多 元 化,
Microsoft PowerPoint - IAS 21 - IFRS宣導會.pptx
 IAS 21 Nov 19, 2010 Agenda Page 1 1 2 4 3 11 4 17 5 IFRS 23 Section 1 Section 1 WHY IAS 21? IAS 21 2 Section 1 Determination Functional Currency Presentation Currency First Time Adoption IFRS IAS 21 2
IAS 21 Nov 19, 2010 Agenda Page 1 1 2 4 3 11 4 17 5 IFRS 23 Section 1 Section 1 WHY IAS 21? IAS 21 2 Section 1 Determination Functional Currency Presentation Currency First Time Adoption IFRS IAS 21 2
2
 專題報導 台灣石化業的美麗與哀愁 從石化業的健康經驗談起 國家衛生研究院溫啟邦教授 3 101 9 5 一 前言 1 2 ( ) 1875 700 120 3 二 研究方法的文獻 in vitro ( ) 4 三 石化業員工健康經驗的文獻 (cohort) SMR(Standardized Mortality Ratio) SMR PMR (Proportionate Mortality Ratio)
專題報導 台灣石化業的美麗與哀愁 從石化業的健康經驗談起 國家衛生研究院溫啟邦教授 3 101 9 5 一 前言 1 2 ( ) 1875 700 120 3 二 研究方法的文獻 in vitro ( ) 4 三 石化業員工健康經驗的文獻 (cohort) SMR(Standardized Mortality Ratio) SMR PMR (Proportionate Mortality Ratio)
東吳大學
 律 律 論 論 療 行 The Study on Medical Practice and Coercion 林 年 律 律 論 論 療 行 The Study on Medical Practice and Coercion 林 年 i 讀 臨 療 留 館 讀 臨 律 六 礪 讀 不 冷 療 臨 年 裡 歷 練 禮 更 老 林 了 更 臨 不 吝 麗 老 劉 老 論 諸 見 了 年 金 歷 了 年
律 律 論 論 療 行 The Study on Medical Practice and Coercion 林 年 律 律 論 論 療 行 The Study on Medical Practice and Coercion 林 年 i 讀 臨 療 留 館 讀 臨 律 六 礪 讀 不 冷 療 臨 年 裡 歷 練 禮 更 老 林 了 更 臨 不 吝 麗 老 劉 老 論 諸 見 了 年 金 歷 了 年
Microsoft Word - 第四組心得.doc
 徐 婉 真 這 四 天 的 綠 島 人 權 體 驗 營 令 我 印 象 深 刻, 尤 其 第 三 天 晚 上 吳 豪 人 教 授 的 那 堂 課, 他 讓 我 聽 到 不 同 於 以 往 的 正 義 之 聲 轉 型 正 義, 透 過 他 幽 默 熱 情 的 語 調 激 起 了 我 對 政 治 的 興 趣, 願 意 在 未 來 多 關 心 社 會 多 了 解 政 治 第 一 天 抵 達 綠 島 不 久,
徐 婉 真 這 四 天 的 綠 島 人 權 體 驗 營 令 我 印 象 深 刻, 尤 其 第 三 天 晚 上 吳 豪 人 教 授 的 那 堂 課, 他 讓 我 聽 到 不 同 於 以 往 的 正 義 之 聲 轉 型 正 義, 透 過 他 幽 默 熱 情 的 語 調 激 起 了 我 對 政 治 的 興 趣, 願 意 在 未 來 多 關 心 社 會 多 了 解 政 治 第 一 天 抵 達 綠 島 不 久,
2015 Chinese FL Written examination
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2015 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER CHINESE FIRST LANGUAGE Written examination Monday 16 November 2015 Reading time: 11.45 am to 12.00
Victorian Certificate of Education 2015 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER CHINESE FIRST LANGUAGE Written examination Monday 16 November 2015 Reading time: 11.45 am to 12.00
124 第十三期 Conflicts in the Takeover of the Land in Taiwan after the Sino-Japanese War A Case in the Change of the Japanese Names of the Taiwanese Peopl
 123 戰後初期臺灣土地接收的糾紛 以更改日式姓名的臺人遭遇為例 124 第十三期 Conflicts in the Takeover of the Land in Taiwan after the Sino-Japanese War A Case in the Change of the Japanese Names of the Taiwanese People Abstract By Ho Fung-jiao
123 戰後初期臺灣土地接收的糾紛 以更改日式姓名的臺人遭遇為例 124 第十三期 Conflicts in the Takeover of the Land in Taiwan after the Sino-Japanese War A Case in the Change of the Japanese Names of the Taiwanese People Abstract By Ho Fung-jiao
居家式保母之嬰幼兒健康照護知能研究
 國 立 臺 北 護 理 健 康 大 學 嬰 幼 兒 保 育 系 碩 士 論 文 GRADUATE PROGRAM OF INFANT AND CHILD CARE DEPARTMENT NATIONAL TAIPEI UNIVERSITY OF NURSING AND HEALTH SCIENCES 指 導 教 授 段 慧 瑩 博 士 Advisor: Dr. Duan, Hui-Ying 居 家
國 立 臺 北 護 理 健 康 大 學 嬰 幼 兒 保 育 系 碩 士 論 文 GRADUATE PROGRAM OF INFANT AND CHILD CARE DEPARTMENT NATIONAL TAIPEI UNIVERSITY OF NURSING AND HEALTH SCIENCES 指 導 教 授 段 慧 瑩 博 士 Advisor: Dr. Duan, Hui-Ying 居 家
211 better than those in the control group, with significant difference between two groups (P < 0.05). The ocular hypertension of patients in the cont
 210 毛 果 芸 香 碱 联 合 拉 坦 前 列 素 治 疗 原 发 性 急 性 闭 角 型 青 光 眼 的 疗 效 观 察 符 元 党 1, 郑 振 优 2, 林 再 雄 2, 周 吉 良 1. 昌 江 黎 族 自 治 县 中 西 医 结 合 医 院, 海 南 昌 江 572700 2. 海 南 医 学 院 附 属 医 院 眼 科, 海 南 海 口 570100 1 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨
210 毛 果 芸 香 碱 联 合 拉 坦 前 列 素 治 疗 原 发 性 急 性 闭 角 型 青 光 眼 的 疗 效 观 察 符 元 党 1, 郑 振 优 2, 林 再 雄 2, 周 吉 良 1. 昌 江 黎 族 自 治 县 中 西 医 结 合 医 院, 海 南 昌 江 572700 2. 海 南 医 学 院 附 属 医 院 眼 科, 海 南 海 口 570100 1 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨
2014年1月A 1期 排版.FIT)
 第 26 卷 第 15 期 中 国 现 代 医 学 杂 志 Vol. 26 No.15 2016 年 8 月 China Journal of Modern Medicine Aug. 2016 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2016.15.022 文 章 编 号 : 1005-8982(2016)15-0114-05 声 检 查 对 产 前 出 血 病 因 诊 断 的
第 26 卷 第 15 期 中 国 现 代 医 学 杂 志 Vol. 26 No.15 2016 年 8 月 China Journal of Modern Medicine Aug. 2016 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2016.15.022 文 章 编 号 : 1005-8982(2016)15-0114-05 声 检 查 对 产 前 出 血 病 因 诊 断 的
國家圖書館典藏電子全文
 A Study on the Job Stress and the Ways of Coping for the Director of Elementary School in the Middle Area of Taiwan Abstract This study aims at probing the subject current status as related to stress and
A Study on the Job Stress and the Ways of Coping for the Director of Elementary School in the Middle Area of Taiwan Abstract This study aims at probing the subject current status as related to stress and
Pharmaceutical Sciences -Its Potential as a Career
 药 物. 生 命. 社 会 程 能 能 [email protected] 药 学 的 任 务 及 分 科 研 制 新 药 : 高 效 低 毒 药 ; 针 对 新 发 疾 病 的 药 ; 药 物 化 学 生 药 学 微 生 物 和 生 化 制 药 学 药 物 分 析 学 克 服 耐 药 病 原 微 生 物 的 药 ; 阐 明 药 物 作 用 及 机 理 : 药 理 学 研 制 新 制 剂 :
药 物. 生 命. 社 会 程 能 能 [email protected] 药 学 的 任 务 及 分 科 研 制 新 药 : 高 效 低 毒 药 ; 针 对 新 发 疾 病 的 药 ; 药 物 化 学 生 药 学 微 生 物 和 生 化 制 药 学 药 物 分 析 学 克 服 耐 药 病 原 微 生 物 的 药 ; 阐 明 药 物 作 用 及 机 理 : 药 理 学 研 制 新 制 剂 :
東方設計學院文化創意設計研究所
 東 方 設 計 學 院 文 化 創 意 設 計 研 究 所 碩 士 學 位 論 文 應 用 德 爾 菲 法 建 立 社 區 業 餘 油 畫 課 程 之 探 討 - 以 高 雄 市 湖 內 區 為 例 指 導 教 授 : 薛 淞 林 教 授 研 究 生 : 賴 秀 紅 中 華 民 國 一 o 四 年 一 月 東 方 設 計 學 院 文 化 創 意 設 計 研 究 所 碩 士 學 位 論 文 Graduate
東 方 設 計 學 院 文 化 創 意 設 計 研 究 所 碩 士 學 位 論 文 應 用 德 爾 菲 法 建 立 社 區 業 餘 油 畫 課 程 之 探 討 - 以 高 雄 市 湖 內 區 為 例 指 導 教 授 : 薛 淞 林 教 授 研 究 生 : 賴 秀 紅 中 華 民 國 一 o 四 年 一 月 東 方 設 計 學 院 文 化 創 意 設 計 研 究 所 碩 士 學 位 論 文 Graduate
GCT presentation 16.12.98
 老 年 人 便 秘 之 面 面 觀 臺 中 榮 民 總 醫 院 胃 腸 肝 膽 科 張 繼 森 醫 師 胃 腸 症 狀 之 三 個 月 盛 行 率 症 狀 描 述 陽 性 人 數 三 個 月 盛 行 率 (%) 1. 吃 完 飯 後 有 好 幾 小 時 覺 得 腹 脹, 或 是 覺 得 食 物 在 胃 中 停 留 過 久 133 13.0 2. 感 覺 吃 一 點 就 飽, 或 無 法 吃 完 正
老 年 人 便 秘 之 面 面 觀 臺 中 榮 民 總 醫 院 胃 腸 肝 膽 科 張 繼 森 醫 師 胃 腸 症 狀 之 三 個 月 盛 行 率 症 狀 描 述 陽 性 人 數 三 個 月 盛 行 率 (%) 1. 吃 完 飯 後 有 好 幾 小 時 覺 得 腹 脹, 或 是 覺 得 食 物 在 胃 中 停 留 過 久 133 13.0 2. 感 覺 吃 一 點 就 飽, 或 無 法 吃 完 正
(As 4 S 4 ) APL 10 80% P NP (HGAAS) APL APL µg/L µg/L µg/L µg/L µg/L
 1 ABSTRACT 3 6 7 1 8 2 10 3 19 4 22 23 1 24 2 26 3 31 4 34 35 48 58 60 61 (As 4 S 4 ) APL 10 80% P NP (HGAAS) APL APL 7-9 10-12 13-15 51.7 18.7µg/L 61.7 22.7µg/L 62.8 29.1µg/L 2359.1 1910.6µg/L 2834.0
1 ABSTRACT 3 6 7 1 8 2 10 3 19 4 22 23 1 24 2 26 3 31 4 34 35 48 58 60 61 (As 4 S 4 ) APL 10 80% P NP (HGAAS) APL APL 7-9 10-12 13-15 51.7 18.7µg/L 61.7 22.7µg/L 62.8 29.1µg/L 2359.1 1910.6µg/L 2834.0
國立中山大學學位論文典藏.PDF
 I II III The Study of Factors to the Failure or Success of Applying to Holding International Sport Games Abstract For years, holding international sport games has been Taiwan s goal and we are on the way
I II III The Study of Factors to the Failure or Success of Applying to Holding International Sport Games Abstract For years, holding international sport games has been Taiwan s goal and we are on the way
Microsoft Word - 8QH _修复的_
 CJCM 中 医 临 床 研 究 2010 年 VOL.(2) NO.8-1- 治 未 病 在 早 期 乙 肝 肝 硬 化 防 治 中 的 应 用 Application of treating diseases in the future in preventing liver cirrhosis at the early stage 刘 战 河 吴 玉 叶 刘 艳 霞 杜 小 清 ( 济 源 市
CJCM 中 医 临 床 研 究 2010 年 VOL.(2) NO.8-1- 治 未 病 在 早 期 乙 肝 肝 硬 化 防 治 中 的 应 用 Application of treating diseases in the future in preventing liver cirrhosis at the early stage 刘 战 河 吴 玉 叶 刘 艳 霞 杜 小 清 ( 济 源 市
厦 门 大 学 学 位 论 文 原 创 性 声 明 本 人 呈 交 的 学 位 论 文 是 本 人 在 导 师 指 导 下, 独 立 完 成 的 研 究 成 果 本 人 在 论 文 写 作 中 参 考 其 他 个 人 或 集 体 已 经 发 表 的 研 究 成 果, 均 在 文 中 以 适 当 方
 学 校 编 码 :10384 分 类 号 密 级 学 号 : UDC 硕 士 学 位 论 文 浙 江 省 人 事 考 试 突 发 事 件 应 对 策 略 探 析 An Exploration of Zhejiang Province Personnel Examination Emergency Strategy 姜 海 峰 指 导 教 师 姓 名 : 王 玉 琼 教 授 专 业 名 称 : 公 共
学 校 编 码 :10384 分 类 号 密 级 学 号 : UDC 硕 士 学 位 论 文 浙 江 省 人 事 考 试 突 发 事 件 应 对 策 略 探 析 An Exploration of Zhejiang Province Personnel Examination Emergency Strategy 姜 海 峰 指 导 教 师 姓 名 : 王 玉 琼 教 授 专 业 名 称 : 公 共
