Microsoft Word - 武炳义.doc
|
|
|
- 髦癸 毕
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 第 42 卷第 4 期 2018 年 7 月 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol. 42 No. 4 Jul 武炳义 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 [J]. 大气科学, 42 (4): Wu Bingyi Progresses in the impact study of Arctic sea ice loss on wintertime weather and climate variability over East Asia and key academic disputes [J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese), 42 (4): , doi: /j.issn 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 武炳义 复旦大学大气与海洋科学系 / 大气科学研究院, 上海 摘要北极历来是影响东亚冬季天气 气候的关键区域之一 北极表面增暖要比全球平均快 2~3 倍, 即所谓北极的放大效应 随着全球增暖的持续以及北极海冰的持续融化, 北极的生态环境正在发生显著的变化, 进而可能对北半球中 低纬度的天气 气候产生影响 本文概述了有关北极海冰融化影响冬季东亚天气 气候的主要研究进展, 特别是自 2000 年以来, 北极海冰异常偏少影响东亚冬季气候变率以及极端严寒事件的可能途径 存在的科学问题, 以及学术界的争论焦点 秋 冬季节是北极海冰快速形成时期, 此时北极海冰对大气环流的影响要强于大气对海冰的影响 近二十年来的研究结果表明, 北极海冰异常偏少, 不仅影响北冰洋局地的气温和降水变化, 而且通过复杂的相互作用和反馈过程, 对北半球中 低纬度的天气 气候产生影响 北极海冰通过以下两个可能机制来影响东亚冬季的天气 气候 :(1) 北极海冰的负反馈机制 ;(2) 由海冰异常偏少引起的平流层 对流层相互作用机制 秋 冬季节北极海冰持续异常偏少, 特别是, 巴伦支海 喀拉海海冰异常偏少, 既可以加强冬季西伯利亚高压 ( 东亚冬季风偏强 ), 也可以导致冬季风偏弱 导致海冰影响不确定性的部分原因是 :(1) 夏季北极大气环流状态影响北极海冰异常偏少对冬季大气环流的反馈效果 ;(2) 冬季大气环流对北极海冰异常偏少响应的位置 强度不同造成的 秋 冬季节北极海冰持续异常偏少, 在适宜的条件下 ( 例如, 前期夏季北极大气环流的热力和动力条件, 有利于加强北极海冰偏少对冬季大气的反馈作用 ), 可以激发出有利于冬季亚洲大陆极端严寒过程的大气环流异常 目前学术界争论焦点主要集中在以下两个方面 :(1) 关于北极增暖 北极海冰融化对中纬度区域影响的争论 ; (2) 关于 1980 年代后期以来, 冬季欧亚大陆表面气温呈现降温趋势的原因 目前, 有关北极海冰融化影响冬季欧亚大陆次季节变化以及极端天气 气候事件的过程和机制, 我们认知非常有限, 亟需开展深入细致的研究 关键词北极海冰极端事件西伯利亚高压东亚冬季风文章编号 (2018) 中图分类号 P466 文献标识码 A doi: /j.issn Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over East Asia and Key Academic Disputes WU Bingyi Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences/Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai Abstract The Arctic is a crucial region that influences weather and climate over East Asia during the wintertime. The 收稿日期 ; 网络预出版日期 作者简介武炳义, 男,1964 年出生, 教授, 主要从事北极海冰 气相互作用及其对东亚天气 气候变化影响的研究 bywu@fudan.edu.cn 资助项目国家自然基金项目 , 国家重点基础研究发展计划 (973) 项目 2015CB Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants , , ), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant 2015CB453200)
2 4 期 No. 4 武炳义 : 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 787 rate of Arctic surface warming is 2 3 times faster than that of the global mean, which is referred to as Arctic amplification. Accompanied by global warming and Arctic sea ice loss, the ecological environment in the Arctic has been changing rapidly. Such changes would possibly influence weather and climate in the mid- and low-latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. This paper summarizes major advances in the impact study of Arctic sea ice loss on weather and climate in the wintertime. Since 2000, special attention is paid to possible pathways, scientific problems, and key issues in the study of how Arctic sea ice loss affects the wintertime climate variability and extreme cold events. Autumn and winter are freezing seasons when the impact of Arctic sea ice on the atmosphere is stronger than the impact of atmosphere on Arctic sea ice. Over the past two decades, many studies have demonstrated that Arctic sea ice loss not only affects local air temperature and precipitation over the Arctic Ocean, but also influences weather and climate in the mid- and low-latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere due to complicated interactions and feedback processes. Arctic sea ice influences weather and climate over East Asia through two mechanisms: (1) The negative feedback process; (2) the stratosphere-troposphere interaction induced by Arctic sea ice loss. Persistent loss of Arctic sea ice from autumn to winter, particularly in the Barents-Kara Seas, can either enhance the Siberian high or weaken the East Asian winter monsoon. Uncertainties in the impact of Arctic sea ice loss on the wintertime atmosphere can be attributed to the following two reasons: (1) Arctic atmospheric circulation condition in the preceding summer influences the feedback of the persistent less sea ice on the winter atmospheric circulation variability; (2) there exist differences in both the location and strength of wintertime atmospheric response to persistent less sea ice. Under suitable conditions (for example, Arctic atmospheric circulation conditions in the preceding summer are favorable for strengthening the negative feedback of less sea ice), persistent autumn-winter loss of sea ice leads to large-scale wintertime circulation anomalies that favor the occurrence of extreme cold event over Asia. At present, the focuses of disputes in the academic community are mainly concentrated on the following two aspects: (1) The impacts of Arctic warming and Arctic sea ice loss on the mid-latitudes; (2) the reasons for the declining trend in winter surface air temperature over Eurasia since the late 1980s. Indeed, the processes and mechanisms for impacts of Arctic sea ice loss on sub-seasonal variation and extreme cold event over Eurasia still remain unclear, and these problems need to be investigated in the future. Keywords Arctic, Sea ice, Extreme event, Siberian high, East Asian winter monsoon 1 引言 北极是影响我国冬季天气 气候的关键区域之一, 这里有终年存在的大气极涡 大气遥相关型 ( 北极涛动 / 北大西洋涛动 北极偶极子异常等 ), 以及季节性和多年性北极海冰 冬季极地冷空气南下是造成欧亚大陆阶段性强降温和强降雪的主要原因之一, 由高层大气扰动和极地冷空气爆发所形成的冬季风冷涌, 甚至可以影响热带西太平洋的对流活动 近二十年来, 随着全球增暖的持续以及北极海冰的持续减少, 北极对全球增暖的放大效应越发凸显 (Screen and Simmonds, 2010), 从而加强了北极与中低纬度之间的联系, 加大了大气环流季节内和年际变率 (Wu et al.,1999;zhao et al.,2004;honda et al.,2009;liu et al.,2012;li and Wang,2012, 2013;Wu et al.,2013a,2013b,2016,2017;guo et al.,2014; Vihma, 2014; Gao et al., 2015), 从而有利于极端天气 气候 ( 甚至灾害 ) 事件的发生 (Ding et al.,2008;wang et al.,2015;wu et al.,2017) 海冰作为气候系统的重要组成部分, 其变化通 过改变反照率, 而强烈影响海洋表面对太阳辐射能量的有效吸收 海冰的存在, 阻隔或隔绝了海 气之间的热量 动量和物质交换, 同时, 由于海冰变化与海洋的淡水循环 海洋的表层浮力以及海洋的层结均有密切的关系, 进而可能影响海洋深水循环, 以及气候的长期变化趋势 因此, 北极海冰在气候系统中起冷源和稳定海洋层结的作用, 北极海冰融化意味着北极的冷源作用在削弱 这里以冬季为例, 说明不同厚度的海冰对冰 气之间热量传输的影响 在冬季, 北冰洋多年海冰 ( 厚冰 ) 的热量收支中, 失去热量最多的是辐射平衡项 强辐射冷却和海冰的隔绝作用, 使得多年海冰上表面温度低于周围大气温度 这是大气边界层稳定和感热通量向下的主要原因 冬季湍流潜热通量对于热量收支的贡献是不明显的 不同厚度海冰对海 气之间热量传输的影响研究表明, 海冰厚度在 1~100 cm 时, 感热通量和潜热通量经历了大约 2 个数量级的剧烈变化, 感热通量在海冰厚度大约 100 cm 时改变方向,20~40 cm 厚的海冰的感热通量是正的, 而且相当大 潜热通量只在海冰厚度小于 10 cm 时才比
3 788 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol. 42 较明显, 但大小不及感热通量的 10% 观测到的热通量变化最强烈的海域位于巴伦支海 喀拉海 拉普帖夫海和东西伯利亚海 (Makshtas and Andreas, 1991) 这也是冬季巴伦支海 喀拉海海冰异常偏少对欧亚大陆气候变率有重要影响, 因而受到广泛关注的重要原因 在 2006 年以前 ( 即北极大气偶极子模态被揭示出以前 ), 关于大气环流对北极海冰的强迫, 主要关注北大西洋涛动 (Wang et al., 1994; Kwok and Rothrock, 1999; Jung and Hilmer, 2001; Wu et al., 2001) 和北极涛动 (Wang and Ikeda, 2000; Vinje, 2001; Rigor et al., 2002) 的影响 海冰密集度对北大西洋涛动 ( 北极涛动 ) 的响应, 表现为在拉布拉多海以及格陵兰 巴伦支海的反向变化关系, 北冰洋海冰漂移呈现气旋或反气旋性异常 事实上, 北大西洋涛动 ( 或北极涛动 ) 对北冰洋海冰漂移以及对通过弗拉姆海峡海冰输出进入格陵兰海的影响, 明显弱于北极偶极子异常 (Wu et al., 2006, 2012; Wu and Johnson, 2007) 自 1980 年代开始, 北极海冰范围退缩 厚度变薄 (Polyakov et al.,2012; Stroeve et al., 2012) 北极大气环流的时 空变化直接影响海冰的退缩 (Wu et al., 2001; Wang et al., 2009;Overland and Wang, 2010; Wu et al.,2012), 有研究认为北极偶极子是导致夏季北极海冰融化退缩的主要原因之一 (Wang et al.,2009;overland and Wang, 2010) 而 Polyakov et al.(2012) 则强调了大气热力强迫起重要作用 此外, 来自低纬度区域向北极输送的暖湿空气平流, 以及大气长波辐射的增加均有利于海冰的退缩 (Francis and Hunter, 2007;Kapsch et al.,2013) 夏季降雪的减少也很可能对近几十年海冰的变薄有贡献 (Screen and Simmonds, 2012), 因为从降雪到降水的改变增加了裸冰的覆盖率, 从而降低了表面反照率 ( 裸冰的反照率低于有雪盖的海冰 ) 这些变化不仅有利于北冰洋对太阳辐射的吸收, 也有利于风场对海冰的压力破碎, 以及海冰和海水的动力混合, 从而进一步促进了海冰的融化和增加无冰海域的范围 ( Thorndike and Colony, 1982; Proshutinsky and Johnson,1997; Rigor et al., 2002; Serreze et al., 2007; Ogi et al., 2010; Spreen et al., 2011; Wu et al., 2012) 此时, 表面风场与海冰的耦合过程也得到加强, 风场强迫与海冰的反照率反馈, 在北极海冰快速溶化中起了关键作用 (Carmack and Melling,2011) 诸多研究探讨了导致 2007 年 9 月和 2012 年 9 月北极海冰范围出现创纪录低值的原因 在 2007 年, 导致 9 月北极海冰范围出现自有卫星观测记录以来的次低值的原因是, 大气和海洋输送大量的热量到北冰洋 (Wu et al., 2001; Shimada et al., 2006; Woodgate et al.,2010) 当北大西洋涛动处于正位相时, 不仅导致北欧和西伯利亚边缘海域气温升高, 而且加强了北大西洋暖水向巴伦支海输送, 致使巴伦支海南部海洋混合层水温升高和海冰减少 (Wu et al., 2001) 类似地, 在北太平洋一侧, 北太平洋海水经白令海峡流入到楚科奇海 波弗特海, 也有利于这些海域海冰的融化 (Shimada et al., 2006) 此外, 夏季短波辐射和春季的长波辐射也起重要作用 (Kay et al.,2008;graversen et al., 2011) 2012 年 9 月, 北极海冰范围达到自有卫星观测记录以来的最低值, 有研究认为, 发生在 2012 年 8 月的波弗特海强风暴是其产生的主要原因 (Simmonds and Rudeva, 2012) 研究还表明,9 月北极海冰范围异常偏低, 与 7~9 月北极洋表面风场变率的优势模态有密切关系, 即与北极偶极子风场模态的负位相, 以及与中心北极型风场模态的正位相有密切的联系 (Wu et al., 2012) 前者反映了一对异常高 / 低压中心分别位于北冰洋 / 巴伦支海 喀拉海 ; 后者对应异常高 / 低压中心分别位于北冰洋 / 欧亚大陆北部 风场优势模态通过其强度和出现的频次驱动 9 月北极海冰范围达到极小值, 春季 (4~ 6 月 ) 和夏季 (7~9 月 ) 中心北极型风场模态, 在 1990 年代后期出现一致性的年代际变化, 即由 1990 年代以前的气旋性表面风场异常, 转变为反气旋性风场异常, 是导致 9 月北极海冰范围在 1990 年代后期加快融化的主要动力学原因之一 除风场强迫以及反照率反馈外, 气温升高 洋流和海水温度的变化 大气辐射通量, 以及前期冬季海冰偏少也对夏季海冰融化有贡献 (Shimada et al., 2006; Polyakov et al., 2010; Lee,2014; Park et al., 2015) 北极海冰融化不仅加强了北极的放大效应 (Screen and Simmonds, 2010), 而且影响中 低纬度的天气 气候 (Alexander et al., 2004; Deser et al., 2004; Magnusdottir et al., 2004; Honda et al., 2009; Overland and Wang, 2010; Petoukhov and Semenov, 2010; Screen and Simmonds, 2010; Wu et al., 2011, 2013a, 2013b,2017; Wu, 2017; Francis and Vavrus, 2012, 2015; Liu et al., 2012; Tang et al., 2013; Cohen
4 4 期 No. 4 武炳义 : 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 789 et al., 2014; Mori et al., 2014; Vihma, 2014; Gao et al., 2015; Kug et al., 2015) 本文将概要回顾北极海冰对天气 气候影响的主要研究现状, 特别是回顾我们研究组在有关北极海冰 气相互作用及其对东亚气候变率以及极端严寒事件的最新研究进展 内容包括已经提出的影响途径和机理 存在的科学问题以及学术界的争论焦点 2 北极海冰异常偏少与东亚冬季冷暖异常 1990 年代后期以来, 北极海冰范围出现了快速融化趋势 2007 年以后,9 月北极海冰范围频繁出现创纪录新低, 而后期冬季, 东亚地区频繁经历严冬的侵袭 ( 如 2007/2008 年,2009/2010 年,2010/ 2011 年,2011/2012 年,2012/2013 年 ) 研究表明, 秋 冬季节北极海冰异常偏少, 冬季欧亚大陆容易出现冷冬 (Wu et al.,1999,2011;honda et al.,2009; Petoukhov and Semenov,2010;Wu and Zhang,2010; Inoue et al.,2012;liu et al.,2012) 冬季巴伦支海 喀拉海是影响冬季气候变化的关键海域, 该海域冬季海冰变化与 500 hpa 欧亚大陆遥相关型有密切联系, 该海域海冰异常偏多 ( 少 ), 则东亚大槽偏弱 ( 强 ), 冬季西伯利亚高压偏弱 ( 强 ), 东亚冬季风偏弱 ( 强 ), 入侵中国的冷空气偏少 ( 多 )(Wu et al.,1999) 近期的研究结果进一步证实这一结论 (Petoukhov and Semenov, 2010; Inoue et al., 2012) 数值模拟试验结果表明, 冬季巴伦支海 喀拉海海冰密集度减少, 将导致欧亚大陆出现冷冬, 并且大气环流对该海域海冰强迫的响应呈现非线性特征 (Petoukhov and Semenov,2010) 冬季巴伦支海海冰偏少, 该海域和欧亚大陆北部边缘海域反气旋活动盛行, 导致欧亚大陆北部气压升高 (Inoue et al.,2012) 事实上, 不仅是冬季北极海冰, 夏末秋初北极海冰异常偏少与后期冬季大气环流也有密切的关系 (Francis et al.,2009;honda et al.,2009;wu and Zhang, 2010) Francis et al.(2009) 指出, 这种滞后联系的主要机制是与大气行星边界层的加深有关系, 对流层低层的增暖和不稳定性加强, 增加了云量, 导致 1000~500 hpa 大气厚度经向梯度的减弱, 进而减弱了大气极夜急流 在远东地区, 初冬的显著冷异常和晚冬从欧洲至远东地区纬向分布的冷异常, 均与前期 9 月份北极海冰减少有关系, 后者能够加强西伯利亚高压 (Honda et al., 2009) 而夏 秋季节北极海冰偏少, 与后期冬季类似北极涛动负位相的大气环流异常, 有显著的统计关系 (Wu and Zhang,2010) Wu et al.(2011) 发现, 秋 冬季节北极关键海域 ( 巴伦支海 喀拉海 拉普帖夫海, 以及这些海域的北部相邻海域 ) 海冰密集度持续异常偏少, 同时, 在副北极和北大西洋海域海温异常偏高, 则后期冬季西伯利亚高压偏强, 东亚地区冬季气温偏低 Peings and Magnusdottir(2014) 利用 CAM5 大气环流模式, 模拟了冬季大气环流对 2007~2012 年观测到的北极海冰异常偏少的响应 结果表明, 冬季显著变冷只出现在亚洲大陆的中纬度地区, 而不是欧洲和北美地区 上述研究结果似乎意味着, 秋季北极海冰异常偏少是预测后期冬季东亚气温异常的潜在先兆因子 然而事情远非如此简单 诊断分析研究以及海冰强迫的数值模拟试验结果, 并非一致性地支持北极海冰异常偏少对中纬度区域可以产生显著的影响 (Screen et al.,2014;peings and Magnusdottir, 2014; Walsh, 2014) 例如,2012 年 9 月 16 日, 北极海冰范围只有 平方公里, 是 1979 年有卫星观测记录以来的最低值 但是在随后的 2012/2013 年冬季, 冬季西伯利亚高压强度接近正常 此外, 2006/2007 年冬季, 西伯利亚高压强度异常偏弱, 其前期 9 月关键海域 (76.5 ~83.5 N, 60.5 ~ E) 海冰密集度也为负异常 [ 见 Wu et al. (2011) 中的图 1 2] 除北极海冰以外, 尚有诸多其他因素影响冬季西伯利亚高压, 例如, 欧亚大陆辐射冷作用 对流层高层的大气扰动 北极涛动 ( 北大西洋涛动 ) 热带太平洋海温等 另一方面, 上述两个冬季大气环流呈现截然不同的特征 2006/2007 年冬季, 东亚大气环流异常与西伯利亚异常偏弱有密切联系, 而 2012/2013 年冬季, 东亚大气环流主要反映了亚洲 北极遥相关型的主要特征 (Wu et al.,2015) 利用北极海冰异常偏少这一单一因子, 来预测冬季截然不同的大气环流型, 很难获得理想的预测效果 事实上, 秋 冬季节北极海冰异常偏少, 既可以加强西伯利亚高压, 也可以导致类似亚洲 北极遥相关型的负位相出现, 而后者对应减弱的冬季风 (Wu et al.,2015) 这就涉及到北极海冰与中 高纬度天气 气候之间的联系, 还存在很大的不确定性 ( 包括非线性联系 )(Petoukhov and Semenov,
5 790 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol. 42 图 1 北极海冰强迫模拟试验中,(a) 前期秋季和 (b) 冬季北极海冰密集度之差 ( 冬季西伯利亚高压型的正位相的合成平均减去负位相的合成平均, 合成个例同图 2) (c) 和 (d) 分别与 (a) 和 (b) 类似, 但由冬季亚洲 北极遥相关型的负位相合成平均减去正位相的合成平均计算得到, 合成个例同图 3(Wu et al., 2015) Fig. 1 Differences in mean SIC (sea ice concentrations) in the forced model simulations between the composites of positive and negative phases of the Siberian High (SH) pattern in (a) the previous autumn (SON) and (b) winter (DJF). (c, d) As in Figs. a, b, respectively, but for differences between the composites of negative and positive phases of the Asia Arctic (AA) pattern. The composite cases for the SH and AA patterns are the same as those in Figs. 2 and 3, respectively (Wu et al., 2015) 2010;Rinke et al.,2013;screen et al.,2014;overland et al.,2015,2016;perlwitz et al.,2015;semenov and Latif,2015;Wu et al.,2015) 关于亚洲冬季气候变率的西伯利亚高压型以及亚洲 北极型的详细内容, 请参见具体的文献, 这里不再赘述 Rinke et al.(2013) 利用区域耦合气候模式, 研究了冬季大气环流对晚夏北极海冰偏少的响应 结果表明, 模拟的冬季大气环流响应对区域海冰异常的位置 强度, 以及分析的时段非常敏感 北极海冰强迫的数值模拟试验也支持这一结论, 如图 1 至图 3 所示 图中显示, 同样是秋 冬季节 北极海冰异常偏少, 对东亚冬季的影响效果迥异, 秋季北极海冰越是偏少, 越有利于冬季风的加强 因此, 北极海冰异常偏少, 而东亚冬季风偏弱 气温正常偏高, 并非意味着海冰强迫不起作用, 而是受多种因素的影响, 大气响应的强度和位置不同造成的 ( 这里没有考虑海冰影响的非线性 ) 对某一特定区域, 大气环流异常空间位置小的差异, 其影响效果迥异 此外, 北极海冰的背景条件 夏季北极大气环流的热力和动力状态, 可以影响北极海冰偏少对后期大气环流的影响效果 (Semenov and Latif,2015;Wu et al.,2016), 进
6 武炳义 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 4期 No. 4 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 791 图 2 a 模式模拟的冬季平均海平面气压 SLP 之差 单位 hpa 由冬季西伯利亚高压型的正位相合成平均减去负位相合成平均计算得到 标 准化的冬季西伯利亚高压型强度指数 /1981 年 1985/1986 年 2005/2006 年 标准化的冬季西伯利亚高压型强度指数 /1989 年 1991/1992 年 1992/1993 年 1996/1997 年 1997/1998 年 2003/2004 年 2006/2007 年 共计进行了 40 个不同初值的强迫模拟试验 正 负 位相分别包含 120 个和 280 个冬季个例 紫色的细实 虚 线和粗实 虚 线分别表示正 负 的 SLP 异常在 0.05 和 0.01 显著性水平 b c 同 a 但分别为冬季 500 hpa 高度和表面气温之差 Wu et al., 2015 Fig. 2 (a) Simulated differences mean SLP (in the wintertime) between the composites of positive and negative phases of the SH pattern (the normalized winter Siberian high intensity index 0.8: 1980/1981, 1985/1986, 2005/2006; the normalized winter Siberian high intensity index 0.8: 1988/1989, 1991/1992, 1992/1993, 1996/1997, 1997/1998, 2003/2004, 2006/2007) derived from 40 experiments. The positive and negative phases contain 120 and 280 winters, respectively; thin solid (dashed) and thick solid (dashed) purple contours denote positive (negative) SLP anomalies at 0.05 and 0.01 significance levels, respectively. Figs. b, c as in Fig. a, but for differences in wintertime 500 hpa height and SAT (Surface Atmosphere Temperature), respectively (Wu et al., 2015) 一步加大了海冰影响的不确定性 3 北极海冰异常偏少影响天气和气 候的两种可能机制 诸多研究揭示了在北大西洋和北冰洋区域 海 冰异常对大气环流的负反馈机制 Newson 1973 Royer et al Murray and Simmonds 1995 Parkinson et al Alexander et al Deser et al Magnusdottir et al 通过数值 试验 Newson 1973 指出 在没有北极海冰的情 况下 中 高纬度温度梯度减弱有利于行星波的放 大 从而有利于阻塞环流的形成 北极海冰偏少 将导致中纬度地区西风风速的减弱和风暴活动的 加强 以及副热带西风的加强 北极海冰偏多则影 响相反 Royer et al Murray and Simmonds 1995 Wu et al Francis and Vavrus 2012
7 792 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol ) Alexander et al.(2004) 对比了模拟的大气环流对北极海冰异常的响应和观测的大气环流异常 对比后发现, 观测到的异常几乎与模拟的大气环流异常相反 这表明, 在北大西洋区域, 北极海冰与大气环流的相互作用是减弱原本的大气环流异常,Magnusdottir et al.(2004) 和 Deser et al.(2004) 的模拟研究也支持这一结论, 这就是北极海冰影响北大西洋区域大气环流的负反馈机制 但是, 在北太平洋一侧, 海冰异常对大气环流的影响表现为正反馈 (Alexander et al., 2004) 平流层和对流层相互作用, 也是北极海冰异常偏少影响大气环流的可能途径之一 当初冬巴伦支海 喀拉海海冰偏少时, 可以激发出大气行星波从对流层向平流层传播 当波传播到平流层时, 发生波破碎, 进而影响平流层极涡强度, 导致平流层极涡减弱 在冬季的中 后期, 减弱的平流层极涡下传到对流层, 引起对流层大气环流出现类似北极涛动负位相的异常, 进而影响中纬度天气 气候 (Jaiser et al., 2013; Cohen et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2014; Nakamura et al., 2015) 4 北极海冰异常偏少与冬季极端事件 自 1980 年代后期以来, 欧亚大陆北部冬季表面气温呈现降温趋势 这显然与全球变暖趋势不一致 (Wu et al., 2011; Cohen et al.,2012), 但与冬季西伯利亚高压的加强 ( 或恢复 ) 趋势是吻合的 近期的研究结果表明, 秋季北极海冰减少, 以及北冰洋和北大西洋海温升高, 可能是造成欧亚大陆北部冬季气温呈现下降趋势的主要原因 (Wu et al., 2011,2013a; Cohen et al.,2012; Cohen, 2016) 在这一气候背景下, 秋 冬季节北极海冰的异常偏少, 不仅导致近年来欧亚大陆冷冬频繁出现, 而且可能加剧极端天气 气候灾害的发生 如 年 9 月北极海冰范围 ( 北极海冰范围数据取自美国雪冰中心 ) 异常偏低 ( 自 1978 年以来,9 月海冰范围最低值从小到大顺序是 : 和 2005 年 ), 后期 2005 年 12 月, 日本发生了极端降雪事件 ;2008 年初, 我国南方出现了历史上罕见的雨雪冰冻灾害 ;2008 年 12 月至 2009 年初, 我国经历了严重的旱灾 ;2010 年秋 冬季节, 我国华北大部 黄淮及江淮北部降水量普遍较常年同期异常偏少, 冬小麦受旱面积超过 1 亿亩, 导致几十 万人畜饮水困难 导致极端干旱的直接原因是西伯利亚高压异常偏强,2010 年 12 月至 2011 年 1 月, 西伯利亚高压平均强度接近 1034 hpa, 是过去 30 年以来的第二高值 秋 冬季节北大西洋海温持续偏高, 以及北极海冰持续偏少 (2011 年 1 月, 北极海冰范围是自 1979 年有卫星观测记录以来最小的一年 ) 可能是导致冬季西伯利亚高压异常偏强的主要原因 (Wu et al.,1999,2011) 2012 年 1 月 17 日至 2 月 1 日, 亚洲大陆经历了罕见的严寒过程, 此后, 冷空气向西席卷欧亚大陆 据媒体报道, 这次严寒过程导致欧亚大陆超过 700 人被冻死 2012 年 12 月中下旬, 俄罗斯遭遇自 1938 年以来最强的寒流, 西伯利亚地区气温降到 50 C,12 月 24 日莫斯科气温低至 25 C, 俄罗斯至少有 88 人被冻死 1200 多人被冻伤 我国东北 华北平均气温为过去 27 年同期的最低值 尽管 2013/ /2015 连续两个冬季我国平均气温明显偏高, 尤其是我国北方地区, 气温偏高尤为突出, 但是, 这两个冬季北美地区却经历了罕见的强降雪和严寒天气过程 特别是 2013/2014 冬季, 北美多地气温降至 35 C, 位于美国与加拿大边境的五大湖几乎完全被冻住, 这是过去 35 年以来首次出现这种现象 (Van Oldenborgh et al.,2015) 2016 年 1 月 20 日至 25 日, 受北极大气环流变化的影响, 我国自北向南陆续出现大风降温天气 22 日至 25 日, 全国出现了一次大范围的寒潮过程 据国家气候中心数据显示,1 月 20 日至 25 日, 全国共 529 个气象站过程降温超过 12 C,49 个气象站发生极端日降温事件, 8 个气象站日降温幅度突破历史极值 ; 有 690 个气象站发生极端低温事件, 其中,67 个县 ( 市 ) 日最低气温突破历史极值 这次强寒潮过程还对日本西部地区造成影响, 导致冲绳出现了有观测记录以来的首次降雪 尽管这些极端事件均发生在北极海冰异常偏少的后期秋 冬季节, 但是还不能把海冰异常偏少与极端事件的个例直接联系起来 通过回归分析,Tang et al.(2013) 把冬季极端冷事件的发生频次与北极海冰融化联系起来, 认为与北极海冰融化有联系的冬季大气环流异常, 有利于北半球大陆中纬度地区出现极端严寒事件 他们还认为, 与夏季北极海冰偏少相比, 极端冷事件与冬季北极海冰偏少的关系更为密切 从动力学角度出发,Wu et al. (2013a) 揭示了欧亚大陆中 高纬度 (40 ~70 N)
8 4 期 No. 4 武炳义 : 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 793 图 3 (a) 模式模拟的冬季平均 SLP 之差, 由冬季亚洲 北极型负位相的合成平均减去正位相的合成平均计算得到 ( 标准化的冬季亚洲 北极型强度指数 < 0.8: 1989/1990 年 2000/2001 年 2008/2009 年 2009/2010 年 ; 标准化的冬季亚洲 北极型强度指数 >0.8:1982/1983 年 1994/1995 年 1995/1996 年 1999/2000 年 2001/2002 年 2007/2008 年 ), 共计进行了 40 个不同初值的强迫模拟试验, 负 正位相分别包含 160 个和 240 个冬季个例 紫色的细实 ( 虚 ) 线和粗实 ( 虚 ) 线分别表示正 ( 负 ) 的 SLP 异常在 0.05 和 0.01 显著性水平 (b) 和 (c) 同 (a), 但分别为冬季 500 hpa 高度和表面气温之差 (Wu et al., 2015) Fig. 3 (a) Simulated differences mean SLP (in the wintertime) between the composites of negative and positive phases of the Asia-Arctic (AA) pattern (the normalized AA pattern intensity index< 0.8: 1989/1990, 2000/2001, 2008/2009, 2009/2010; the normalized AA pattern intensity index>0.8: 1982/1983, 1994/1995, 1995/1996, 1999/2000, 2001/2002, 2007/2008) derived from 40 experiments. The negative and positive phases contain 160 and 240 winters, respectively; thin solid (dashed) and thick solid (dashed) purple contours denote positive (negative) SLP anomalies at 0.05 and 0.01 significance levels, respectively. Figs. b, c as in Fig. a, but for differences in wintertime 500 hpa height and SAT, respectively (Wu et al., 2015) 地区冬季逐日风场变率的最优天气型, 该天气型包含两个不同子型 ( 偶极子型和三极子型 ) 研究发现, 只有三极子型的年际变化 ( 包括强度和极端负位相的发生频次 ) 与前期秋季北极海冰变化有密切关系, 北极海冰减少的数值模拟试验也支持这一结论 [ 图 4, 引自 Wu et al.(2013a)] 在该研究中, 极端负位相的定义为标准化的三极型强度小于 1.28, 对应其发生概率小于 10%( 属于极端天气事 件 ) 从这一点看, 北极海冰融化与冬季欧亚大陆盛行天气型的极端事件有联系 就极端严寒事件的个例而言, 发生在 2012 年 1 月中 下旬的亚洲大陆极端严寒过程, 很可能是北极海冰异常偏少与前期夏季北极大气环流共同作用的结果 (Wu et al., 2017) 亚洲大陆的这次极端严寒事件持续长达 16 d[2012 年 1 月 17 日至 2 月 1 日 ; 图 5a, 图 5 至图 10 引自 Wu et al.(2017)],
9 794 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol. 42 图 4 北极海冰异常偏少如何影响冬季欧亚大陆对流层低层盛行天气型以及表面气温和降水趋势的示意图, 其中, 弯曲的箭头表示与冬季欧亚大陆三极子型的负位相所对应的异常气旋和反气旋的空间分布, 褐色线表示 500 hpa 等高线, 黄色和绿色区域分别表示冬季降水偏少和偏多区域, 红色和紫色区域分别表示正 负表面气温异常 Fig. 4 Schematic diagram how reduced Arctic sea ice affects wintertime SAT and precipitation tendencies across Eurasia in the lower troposphere. Arrows denote the spatial distribution of the anomalous anticyclone and cyclone associated with the negative phase of the tripole wind pattern. The brown line represents the 500-hPa height isoline. Yellow and green areas indicate abnormally low and high precipitation, respectively. Red and purple areas depict positive and negative SAT anomalies, respectively 图 5 (a)2011 年 12 月 1 日至 2012 年 2 月 28 日区域 (40 ~60 N,80 ~120 E) 平均表面气温的逐日演变曲线 ( 蓝色 ), 绿色曲线为该区域 1979~ 2012 年冬季 (12 月 1 日至次年 2 月 28 日 ) 逐日表面气温平均值的演变曲线, 红色虚线为该区域冬季逐日表面气温平均值 ± 标准偏差 (b)2011 年 12 月 1 日至 2012 年 2 月 28 日区域 (40 ~60 N,80 ~120 E) 平均 SLP( 即西伯利亚高压强度指数 ) 的逐日演变曲线 ( 蓝色 ) 和区域 (50 ~70 N, 150 ~180 W) 平均 SLP( 即阿留申低压强度指数 ) 的逐日演变曲线 ( 红色 ) Fig. 5 (a) Wintertime (1 December to 28 February) daily SAT (blue line) averaged over the region (40 60 N, E) in The green line is the same as the blue one but for the daily climatological mean over 33 winters from 1979 to 2012, and the two dashed red lines represent daily climatological mean ± σ (daily standard deviation). (b) Wintertime (1 December 2011 to 28 February 2012) daily Siberian High index (SHI) (blue line), which is defined as the regionally averaged SLP over the region (40 60 N, E). The red line represents daily Aleutian Low index (ALI) in winter of , which is defined as the regionally averaged SLP over the region (50 70 N, W)
10 武炳义 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 4期 No. 4 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 已经不是天气尺度事件 而是一次短期极端气候事 件 这次极端严寒事件的突出特征是 在冷空气爆 发前阿留申低压经历了一次极端减弱的过程 并于 1 月 16 日达到最弱 1040 hpa 当其气压开始回 落时 冷空气爆发 并且阿留申低压最弱超前西伯 利亚高压最强 4 d 图 5b SLP 异常演变清楚地表 795 明 图 6 在 1 月初 5 7 日 在东北太平洋出 现正的 SLP 异常中心 随着时间的推移 该正异常 中心逐渐移向阿留申区域 并且异常振幅在逐渐增 大 并于 日正异常达到最大值 此后 SLP 正异常开始减弱 冷空气在亚洲大陆爆发 图中显 示 SLP 正异常主要是从北太平洋向西传播 即大 图 年 1 月 SLP 异常 相对于 1979 至 2012 年冬季逐日平均值 的演变特征 a 1 月 5 7 日 SLP 异常的平均值 b i 同 a 但为 以及 日异常的平均值 Fig. 6 Evolution of SLP anomaly (relative to the daily means averaged over ) during January 2012: (a) SLP anomaly averaged over 5 to 7 January; (b i) as in Fig. a, but for 8 10, 11 13, 14 16, 17 19, 20 22, 23 25, 26 28, and January
11 796 大 气 科 学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 气环流的 下游效应 在本次极端严寒事件中起重 要作用 为了更好地理解导致这次极端严寒事件的可 能原因 非常有必要分析 2011/2012 年冬季平均以 及该冬季逐月大气环流异常的主要特征 它可以作 为评价海冰强迫模拟试验 能否有再现观测到的冬 季大气环流异常的能力 2011/2012 年冬季 SLP 异常的主要特征是 加强的西伯利亚高压与正位相 的北极涛动并存 并且 有三个独立 SLP 正异常中 心 分别位于乌拉尔山 北大西洋东北部 以及北 太平洋东北部 图 7 一个相似的 SLP 异常的空 间分布型也出现在 2011 年 12 月 但是 位于乌拉 42 卷 Vol. 42 尔山的正异常与冬季平均相比明显减弱 而另外两 个 SLP 正异常中心明显加强 2012 年 1 月 SLP 异常在欧亚大陆北部以及阿留申区域呈现哑铃型 分布 与极端严寒持续期间 2012 年 1 月 17 日至 2 月 1 日 的 SLP 异常相似 图略 2012 年 2 月 正的 SLP 异常主要出现在乌拉尔山和北大西洋东 北部 而此时的阿留申低涡明显偏强 在欧亚大陆 以及北太平洋的中 高纬度区域 冬季和 2012 年 1 月平均 SLP 异常的空间分布呈现相似特征 部分原 因是受到持续的极端严寒事件的影响 大气环流模式 ECHAM5 Roeckner et al., 2003 是否可以再现 2011/2012 年冬季大气环流异 图 7 a 2011/2012 年观测的冬季 SLP 异常 相对于 1979 至 2012 年冬季平均值 的空间分布 b 同 a 但为 2011 年 12 月 相对于 1979 至 2011 年 12 月平均值 c 同 a 但为 2012 年 1 月 相对于 1980 至 2012 年 1 月平均值 d 同 c 但为 2012 年 2 月 相对于 1980 至 2012 年 2 月平均值 Fig. 7 (a) Observed SLP anomaly in the winter of 2011/2012 relative to the mean value of (b) As in Fig. a, but for December 2011 relative to the mean value of (c) As in Fig. a, but for January 2012 relative to the mean value of (d) As in Fig. c, but for February 2012 relative to the mean value of
12 武炳义 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 4期 No. 4 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 常的主要特征 包括季节和月的平均异常 这个问 题对于确定北极海冰异常偏少是否对该极端严寒 事件有贡献至关重要 然而 数值模拟试验清楚地 表明 仅凭北极海冰强迫 以 2011 年 8 月至 2012 年 2 月观测的北极海冰为强迫 模式大气的初值由 控制试验提供 该组试验简称为海冰强迫试验 模式模拟的冬季大气环流响应 尚不能再现观测到 的冬季环流的主要特征 图略 因此 除了模式 自身的性能外 模式中大气初值也是影响模拟结果 的因素之一 当同时考虑观测到的北极海冰强迫以 及 2011 年夏季大气初值条件 6 月 1 日至 8 月 31 日 92 个不同模式大气初值由 NCEP/NCAR 逐日再 分析资料经空间插值计算得到 时 该组试验简称 797 不同初值的海冰强迫试验 模拟的冬季大气响应 再现了观测到的 SLP 异常的主要特征 图 8 模 拟的冬季 SLP 正异常呈现带状结构 从北美东海岸 向东跨越北大西洋 欧亚大陆到北太平洋 最大正 异常中心出现在阿留申区域 大于 4 hpa 次大值 中心位于里海北部的欧亚大陆中部 大于 1 hpa 而负异常主要出现在北极 北美以及正异常的南部 区域 SLP 异常的空间分布 某种程度上令人回想 起北极涛动 AO 与观测的 SLP 异常大致是一致 的 在欧亚大陆中部以及北大西洋北部 模拟的 SLP 正异常明显偏弱 而在北太平洋 模拟的 SLP 正异 常明显偏强 模拟的 2011 年 12 月的 SLP 异常与观 测结果很相似 模拟的 2012 年 1 月 SLP 异常与冬 图 8 a 模式模拟的冬季 SLP 异常 由模拟的 92 个冬季的集成平均减去控制试验 紫色细线和粗线 虚线和实线 分别表示 SLP 异常达到 0.05 和 0.01 显著性水平 b d 同 a 但为 2011 年 12 月 2012 年 1 月以及 2012 年 2 月 Fig. 8 (a) Simulated wintertime mean SLP difference between the ensemble mean of 92 winters and the control run (the ensemble mean minus the control run simulation). Thin and thick purple lines denote SLP differences at the 0.05 and 0.01 significance levels, respectively. (b) (d) As in Fig. a, but for December 2011, January 2012, and February 2012, respectively
13 798 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol. 42 季异常在空间结构上相似, 但异常振幅加大, 整体上与观测结果是一致的 因此, 模拟试验结果意味着,2011 年 8 月至 2012 年 2 月北极海冰密集度异常, 以及 2011 年夏季北极大气环流初值条件的共同影响, 对 2011/2012 年冬季观测到的 SLP 异常有贡献 特别是, 持续减弱的阿留申低压是大气对北极海冰异常偏少响应的优势特征, 这可能是由于单独天气系统的累积影响所致 基于不同初值海冰强迫试验的输出结果, 计算了 92 个冬季逐日阿留申低压强度指数, 当该指数大于等于 hpa 时, 对应一个小概率事件, 即极端偏弱的阿留申低压发生概率小于 10% 对于海冰强迫试验, 当阿留申低压指数大于或等于 hpa 时, 其发生概率小于 10% 2011 年夏季北极大气初值条件, 明显影响冬季阿留申低压对北极海冰异常偏少的响应, 导致发生的概率分布系统地移向阿留申低压偏弱一侧 ( 图 9a) 阿留申低压指数处于 1033 至 1043 hpa 时, 其发生概率比海冰强迫试 验明显偏大, 在北极海冰异常偏少时期 (2007~ 2012 年 ) 尤为突出 ( 图 9b) 进一步分析发现, 当阿留申低压指数大于或等于 hpa 时, 不同初值的海冰强迫试验和海冰强迫试验的发生概率分别为 10.0% 和 7.8%, 这意味着前者更容易出现小概率极端事件 因此,2011 年夏季大气初值不仅加强了北极海冰偏少对冬季欧亚大陆和北美气候变率的影响, 而且也加强了对冬季阿留申低压的影响 为选出不同初值的海冰强迫试验中的极端严寒事件, 人为地设定以下三个标准 :(1) 冬季逐日表面气温在西伯利亚高压区域 (40 ~60 N, 80 ~ 120 E) 的平均值小于或等于 21.2 度 ( 发生概率小于 10%), 同时, 阿留申低压指数大于或等于 hpa;(2) 满足 (1) 中条件的极端事件至少持续 3 d; (3) 连续两次极端事件的间隔超过 15 d 共计检测出 10 次满足上述标准的极端严寒事件, 其中,9 次发生在 1 月,1 次发生在 2 月 图 10 显示了海平面气压异常的合成分析结果 在极端严寒事件爆发 图 9 (a) 模拟的冬季逐日阿留申低压指数的概率分布曲线, 红色 ( 蓝色 ) 曲线表示不同大气初值的北极海冰强迫 ( 海冰强迫 ) 模拟试验, 绿色曲线表示海冰强迫模拟试验在 6 个冬季 (2007/2008~2012/2013) 的概率分布 (b) 模拟的冬季逐日阿留申低压指数的概率分布之差, 由不同大气初值的北极海冰强迫模拟试验的概率分布减去海冰强迫试验中 6 个冬季 (2007/2008~2012/2013) 的概率分布得到 Fig. 9 (a) Probability distribution curves of simulated wintertime daily Aleutian low index (ALI) in the sea ice-forced experiments with different initial atmospheric conditions (red), sea ice-forced experiments (blue), and sea ice-forced experiments in six winters (2007/ /2013) (green). (b) Differences in the probability distribution of simulated wintertime daily ALI between the sea ice-forced experiments with different initial atmospheric conditions (red curve in Fig. a) and the sea ice-forced experiments in six winters (2007/ /2013) (green curve in Fig. a)
14 武炳义 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 4期 No. 4 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 前的 d 海平面气压异常的正中心出现在北 美大陆 随后该正异常中心逐渐西移 在事件爆发 前的 3 1 d 到达阿留申区域 在演变过程中 其强 度逐渐加强 并在 0 2 d 达到峰值 在此过程中 799 位于欧亚大陆的海平面气压正异常向东移向日本 在东移过程中强度加强 控制范围增大 自极端严 寒事件爆发后的 3 5 d 开始 已经减弱并向西南扩 展的海平面气压出现在阿留申和西北太平洋区域 图 10 模拟的 10 个极端严寒事件的 SLP 异常合成结果 由不同大气初值的北极海冰强迫模拟试验减去控制试验得到 的演变 a 极端严寒事件 爆发前 d 的 SLP 异常的平均值空间分布 b d 同 a 但分别为 9 7 d 6 4 d 3 1 d 的 SLP 异常的平均值空间分布 e i 同 a 但为极端严寒事件爆发以后 0 2 d 3 5 d 6 8 d 9 11 d 以及 d 的 SLP 异常的平均值空间分布 Fig. 10 Evolution of composites of simulated wintertime daily SLP anomalies for the 10 selected extreme cold events derived from results of the sea ice-forced experiments with different initial atmospheric conditions minus results of the control run: (a) SLP anomalies averaged from 12 to 10 days prior to the extreme cold events; (b) (d) As in Fig. a, but for 9 7, 6 4, and 3 1 days prior to the extreme cold events; (e) (i) As in Fig. a, but for 0 2, 3 5, 6 8, 9 11, and days after the peak of the extreme cold events
15 800 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol. 42 至此, 我们看到, 北极海冰 气相互作用可以影响冬季的大气环流, 而后者又提供了有利于极端严寒事件出现的背景条件 2011 年夏季北极大气环流呈现如下主要特征 :(1) 对流层中 低层异常偏暖 ; (2) 北冰洋表面风场呈现反气旋性异常, 对应夏季海平面气压为正异常 [Wu et al.(2017) 的图 7] 这种大气环流的热力和动力特征, 不仅对夏 秋季节北极海冰异常偏少有重要贡献, 而且可以加强北极海冰异常偏少对冬季大气环流的负反馈, 从而进一步加强了冬季西伯利亚高压的强度 因此, 夏季北极大气环流的热力和动力状态是预测冬季西伯利亚高压强度以及东亚气温的重要前兆信号 (Wu et al.,2016) 历史上, 以及 2016 年夏季, 北极对流层中 低层异常偏冷, 同时, 夏季北冰洋表面风场呈现气旋性异常, 后期冬季西伯利亚高压异常偏弱 ( 冬季风偏弱 ), 我国大部分区域气温偏高 不可否认, 有关北极海冰 气相互作用导致这次极端严寒的具体过程依然不清楚, 特别是, 伴随着冷空气的爆发, 在太平洋一侧出现极地阻塞高压, 其对冷空气在东亚区域的维持起重要作用 [Wu et al.(2017) 的图 4] 尽管北极海冰异常偏少以及北极增暖有利于极地阻塞高压的出现, 但是它们之间的可能联系过程并不清楚 北极海冰融化如何影响冬季中纬度地区的天气过程 ( 特别是季节内变化过程 ), 包括极端天气事件, 是学术界关注的焦点问题之一, 更是当前国际研究的热点和前沿问题 目前, 这方面研究工作还非常有限, 因此, 亟需开展深入细致的研究 5 学术争论以及需要澄清的模糊问题 关于北极增暖 北极海冰融化对中纬度区域的影响, 学术界还存在争论 Francis and Vavrus(2012) 指出, 北极增暖将有利于大气波动传播速度变慢, 环流的径向性加大, 使得北半球某些区域容易出现阻塞型环流异常, 因而, 有利于极端天气事件的发生 按照这一观点, 北半球的阻塞型环流异常在某些区域应该有明显增加趋势, 但是,Barnes(2013) 的分析结果表明, 阻塞型环流并无显著的上升趋势 这一结果导致北极增暖可以影响中纬度急流, 进而影响中纬度地区的极端天气事件备受质疑 与这两个研究不同的是,Luo et al.(2016a, 2016b) 近期研究指出, 北极海冰融化 ( 即北极增暖 ) 主要是 导致高纬度阻塞频率增加且持续时间变长, 而中纬度阻塞频率减少且持续时间变短 Francis and Vavrus(2012) 和 Barnes(2013) 分别代表了截然不同两种观点, 他们的争论已经不仅仅局限于对中纬度急流和极端天气的影响, 已延伸到是北极增暖 ( 或北极海冰减少 ) 的影响重要, 还是中 低纬度对北极的影响重要 Barnes and Screen(2015) 认为, 北极增暖是否对中 低纬度天气有影响, 尚无定论 他们认为, 尽管数值模拟试验结果支持北极增暖可以显著地影响中纬度大气环流, 但是, 这并非意味着北极增暖已经影响了, 或将要影响中纬度大气环流 持这种观点的主要依据是, 中 高纬度区域大气内部变率远大于北极增暖的影响, 并且, 多数模拟试验结果显示, 模式大气对北极海冰融化的响应振幅明显偏小 此外, 目前可用的观测记录太少, 尚不足以研究北极增暖的确切影响, 他们 (Barnes and Screen, 2015) 更倾向于中 低纬度大气环流影响了北极增暖 目前, 还有一些学者认为, 评估近期北极变化对现在和未来天气 气候影响的可能性将是困难的, 甚至是颇具争议的话题 (Jung et al.,2015) 在问题的描述 研究方法, 以及影响机制方面, 学术界还少有一致性, 更有甚者, 利用相同的资料, 却得出不同的结论 以下简单概述目前存在的不同观点 : (1) 热带海温强迫对北极海冰强迫中 高纬度增暖和变化主要受热带海温影响 (Ding et al.,2014),ding et al.(2014) 指出, 自 1979 年以来, 北极地区最显著的年平均表面和对流层增暖, 出现在加拿大东北部和格陵兰 该区域温度的年际变率与 NAO 有关系, 即该区域增暖与 NAO 负的趋势有密切关系, 是对热带海温强迫的响应 因此, 他们的结论是该区域增暖是自然变率所致 然而,Cohen(2016) 指出, 在北极增暖期间, 观测到的大气环流趋势更像与北极下垫面强迫有关的变率, 而非热带强迫 尽管 2015/2016 年冬季发生了强厄尔尼诺事件, 但它并不能掩盖北极海冰融化对冬季西伯利亚高压的影响 ( 武炳义和杨琨, 2016) (2) 北极海冰融化与冬季欧亚大陆的降温趋势一些研究认为, 北极海冰融化 ( 包括海温升高 ) 是导致冬季欧亚大陆出现降温趋势的主要原因之一 (Wu et al.,2011,2013a; Cohen et al.,2012; Cohen, 2016), 而这一点是温室气体排放和热带海温强迫
16 4 期 No. 4 武炳义 : 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 801 所无法解释的 Cohen et al.(2012) 认为, 欧亚大陆变冷趋势是全球增暖趋缓的原因之一 而另外一些研究则认为, 欧亚大陆的降温趋势与北极海冰融化没有关系, 是大气内部变率所产生的异常环流决定的 (McCusker et al.,2016;sun et al.,2016) 北极海冰融化对高纬度大陆的影响是减少逐日温度变率和极端冷事件 (Sun et al.,2016) 事实上, 这里有几个问题需要明确 其一, 北极增暖是北极气候长期变化趋势, 而非逐年变率 因此, 北极增暖的影响是指增暖趋势的影响, 与特定年份北极海冰异常对北半球中纬度地区的影响是截然不同的 尽管北极增暖与北极海冰融化有密切关系, 但是, 北极增暖并非始终随海冰减少而持续加强 (Yim et al.,2016) 对于特定的冬季 ( 如 2015/2016 冬季 ), 北极表面气温的正异常与北极海冰异常减少并不存在对应关系 ( 武炳义和杨琨,2016) 其二, 对于北极海冰融化模拟试验, 模拟的集成平均大气环流响应振幅明显偏小问题 ( 与观测相比 ) 主要原因很可能与大气环流模式中海冰的处理方式有关系, 一般大气环流模式均指定海冰厚度 ( 例如, 指定北半球海冰厚度为 2 m, 而南半球海冰厚度为 1 m) 因此, 这种处理不能正确反映北冰洋边缘海域薄海冰的影响 此外, 很可能与指定的月的北极海冰密集度作为外强迫有关, 如果用观测的逐日海冰密集度将加大响应振幅 同时, 与模式大气内部变率有关, 为增加强迫试验结果的稳定性和可信性, 必须增加海冰强迫试验的次数, 但不可否认, 模式的集成平均样本数也影响大气的响应振幅 大气环流异常是多种因素共同作用的结果, 北极和次北极海表温度与北极海冰密集度是协同变化的, 在模式中同时考虑海冰和海表温度的影响, 可能将大幅度地提高模式大气的响应振幅 其三, 北极海冰融化影响的不确定问题 由于大气环流内部的复杂性及其与不同下垫面的相互作用, 就决定了亚洲大气环流异常与特定下垫面异常之间不存在一一对应关系 但是, 这并不意味着北极海冰偏少影响大气环流的机制发生了改变, 也不意味着北极海冰强迫变得不重要 北极海冰的影响效果不仅取决于海冰密集度异常的空间分布以及异常振幅的大小, 还与大气环流自身的动力和热力状态有密切的关系 (Wu et al.,2016) 这些因素决定了大气环流响应的位置和振幅强弱 6 结论和讨论 本文概要分析总结了针对以下问题的代表性研究进展 :(1) 北极大气表面风场变率的优势模态, 及其对 9 月北极海冰范围极小值以及海冰融化趋势的影响 ;(2) 北极海冰异常偏少与东亚冬季冷暖异常的联系 ;(3) 北极海冰异常偏少影响天气 气候的两种可能机制 ;(4) 北极海冰异常偏少与冬季极端事件的可能联系 ;(5) 目前的学术争论以及需要澄清的模糊问题 北极海冰通过以下两个可能机制来影响东亚冬季的天气 气候 :(1) 北极海冰的负反馈机制,(2) 由海冰异常偏少引起的平流层 对流层相互作用机制 秋 冬季节北极海冰异常偏少, 特别是, 巴伦支海 喀拉海海冰异常偏少, 既可以加强冬季西伯利亚高压 ( 东亚冬季风偏强 ), 也可以导致冬季风偏弱 导致海冰影响不确定性的部分原因是 :(1) 夏季北极大气环流状态影响北极海冰异常偏少对冬季大气环流的反馈效果,(2) 冬季大气环流对北极海冰异常偏少响应的位置 强度不同造成的 秋 冬季节北极海冰持续异常偏少, 在适宜的条件下 ( 例如, 前期夏季北极大气环流的热力和动力条件, 有利于加强北极海冰偏少对冬季大气的反馈作用 ), 可以激发出有利于冬季亚洲大陆极端严寒过程的大气环流异常 ( 例如, 发生在 2012 年 1 月中 下旬的极端严寒过程 ) 当然, 有关秋 冬季节北极海冰持续异常偏少影响冬季欧亚大陆季节内变化以及极端天气 气候事件的过程和机制, 依然尚不清楚 尽管北极海冰异常偏少对北极暖异常有贡献, 但是它们之间的联系并不简单 海冰异常直接影响局地的表面气温, 但表面气温异常不一定反应北极对流层中 低层的气温异常 利用冬季北极表面气温来反应中 高纬度的热力梯度, 将人为地夸大了北极的影响 近期研究表明, 冬季北极对流层中 低层平均气温在 2004 年冬季以后, 进入异常偏暖阶段 (Wu,2017) 对应冬季北极异常偏暖, 北太平洋 北部非洲 以及亚洲和北美洲的低纬度区域均异常偏暖, 同时, 在欧亚大陆和北美大陆的中纬度地区异常偏冷 研究表明, 以前少有关注的一个冬季大气环流异常与北极对流层中 低层异常偏暖有密切关系 该大气环流异常不同于北极偶极子异常 ( 以往研究认为, 北极偶极子异常对北极暖异常有贡献 ), 与北极相比, 它与中 低纬度大气环流
17 802 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol. 42 异常关系更为密切 该大气环流异常与冬季欧亚大陆 EU 遥相关型以及太平洋 北美 (PNA) 型均有显著的相关关系 秋季北极海冰异常偏少以及热带太平洋海温异常偏低, 特别是 La Niña 状态下的海温异常, 对冬季北极对流层中 低层暖异常有贡献 冬季北极暖异常主要是中 高纬度区域大气环流向北极输送暖平流造成的 (Feng and Wu, 2015; Wu et al., 2017; Wu, 2017) 主要有两个区域, 其一是格陵兰以东至乌拉尔山以西区域, 另外一个区域是东北太平洋至北美西部 一方面, 在这两个区域大气环流向北极输送暖湿气流, 同时, 在其下游把高纬度区域的冷空气释放到中 高纬度地区 秋 冬季节北极海冰异常偏少, 通过影响冬季中 高纬度大气环流, 进而间接地影响冬季北极对流层中 低层气温异常 如上文所述, 有大量研究工作均涉及到北极海冰融化的影响, 一些研究工作甚至可以追溯到 1970 年代 本文只是选择性地分析总结了一些有代表性的研究成果, 不可避免地遗漏了一些重要工作 同时, 由于个人的学术积累和认知有限, 对于问题的理解会有偏颇 针对上述问题, 敬请阅读者谅解, 更欢迎指正 参考文献 (References) Alexander M A, Bhatt U S, Walsh J E, et al The atmospheric response to realistic arctic sea ice anomalies in an AGCM during winter [J]. J. Climate, 17 (5): , doi: / (2004)017<0890: TARTRA>2.0.CO;2. Barnes E A Revisiting the evidence linking Arctic amplification to extreme weather in midlatitudes [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40 (17): , doi: /grl Barnes E A, Screen J A The impact of Arctic warming on the midlatitude jet-stream: Can it? has it? will it? [J]. WIREs Climate Change, 6 (3): , doi: /wcc.337. Carmack E, Melling H Cryosphere: Warmth from the deep [J]. Nat. Geosci., 4 (1): 7 8, doi: /ngeo1044. Cohen J An observational analysis: Tropical relative to Arctic influence on midlatitude weather in the era of Arctic amplification [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 43 (10): , doi: /2016gl Cohen J, Screen J A, Furtado J C, et al Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather [J]. Nat. Geosci., 7 (9): , doi: /ngeo2234. Cohen J L, Furtado J C, Barlow M A, et al Arctic warming, increasing snow cover and widespread boreal winter cooling [J]. Environ. Res. Lett., 7 (1): , doi: / /7/1/ Deser C, Magnusdottir G, Saravanan R, et al The effects of North Atlantic SST and sea ice anomalies on the winter circulation in CCM3. Part II: Direct and indirect components of the response [J]. J. Climate, 17 (5): , doi: / (2004)017<0877:teonas>2.0.co; 2. Ding Q H, Wallance J M, Battisiti D S, et al Tropical forcing of the recent rapid Arctic warming in northeastern Canada and Greenland [J]. Nature, 509 (7499): , doi: /nature Ding Y H, Wang Z Y, Song Y F, et al Causes of the unprecedented freezing disaster in January 2008 and its possible association with the global warming [J]. Acta Meteor. Sinica (in Chinese), 66 (5): , doi: /qxxb Feng C, Wu B Y Enhancement of winter arctic warming by the Siberian high over the past decade [J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 8 (5): , doi: /aosl Francis J A, Hunter E Changes in the fabric of the Arctic s greenhouse blanket [J]. Environ. Res. Lett., 4 (4): , doi: / /2/4/ Francis J A, Vavrus S J Evidence linking Arctic amplification to extreme weather in mid-latitudes [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 39 (6): L06801, doi: /2012gl Francis J A, Chan W H, Leathers D J, et al Winter Northern Hemisphere weather patterns remember summer Arctic sea-ice extent [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36 (7): L07503, doi: /2009gl Francis J A, Vavrus S J Evidence for a wavier jet stream in response to rapid Arctic warming [J]. Environ. Res. Lett., 10 (1): , doi: / /10/1/ Gao Y Q, Sun J Q, Li F, et al Arctic sea ice and Eurasian climate: A review [J]. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 32 (1): , doi: /s Graversen R G, Mauritsen T, Drijfhout S, et al Warm winds from the Pacific caused extensive Arctic sea-ice melt in summer 2007 [J]. Climate Dyn., 36 (11 12): , doi: /s z. Guo D, Gao Y Q, Bethke I, et al Mechanism on how the spring Arctic sea ice impacts the East Asian summer monsoon [J]. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 115 (1 2): , doi: /s Honda M, Inoue J, Yamane S Influence of low Arctic sea-ice minima on anomalously cold Eurasian winters [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36 (8): L08707, doi: /2008gl Inoue J, Hori M, Takaya K The role of Barents Sea ice in the wintertime cyclone track and emergence of a warm-arctic cold-siberian anomaly [J]. J. Climate, 25 (7): , doi: /jcli-d Jaiser R, Dethloff D, Handorf D Stratospheric response to Arctic sea ice retreat and associated planetary wave propagation changes [J]. Tellus A, 65 (1): 19375, doi: /tellusa.v65i Jung T, Hilmer M The link between the North Atlantic oscillation and Arctic sea ice export through Fram Strait [J]. J. Climate, 14 (19): , doi: / (2001)014<3932:tlbtna>2.0.co;2. Jung T, Doblas-Reyes F, Goessling H, et al Polar lower-latitude linkages and their role in weather and climate prediction [J]. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 96 (11): ES197 ES200, doi: /bams-d Kapsch M L, Graversen R G, Tjernström M Springtime atmospheric energy transport and the control of Arctic summer sea-ice extent [J]. Nature Climate Change, 3 (8): , doi: /nclimate1884.
18 4 期 No. 4 武炳义 : 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over 803 Kay J E, L Ecuyer T, Gettelman A, et al The contribution of cloud and radiation anomalies to the 2007 Arctic sea ice extent minimum [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35 (8): L08503, doi: /2008gl Kim B M, Son S W, Son S K, et al Weakening of the stratospheric polar vortex by Arctic sea-ice loss [J]. Nature Communications, 5: 4646, doi: /ncomms5646. Kug J S, Jeong J H, Jang Y S, et al Two distinct influences of Arctic warming on cold winters over North America and East Asia [J]. Nat. Geosci., 8 (10): , doi: /ngeo2517. Kwok R, Rothrock D A Variability of Fram Strait ice flux and North Atlantic oscillation [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 104 (C3): , doi: /1998jc Lee S A theory for polar amplification from a general circulation perspective [J]. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci., 50 (1): 31 43, doi: / s Li F, Wang H J Autumn sea ice cover, winter Northern Hemisphere annular mode, and winter precipitation in Eurasia [J]. J. Climate, 26 (11): , doi: /jcli-d Li F, Wang H J Relationship between Bering Sea ice cover and East Asian winter monsoon year-to-year variations [J]. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30 (1): 48 56, doi: /s Liu J P, Curry J A, Wang H J, et al Impact of declining Arctic sea ice on winter snowfall [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 109 (11): , doi: /pnas Luo D H, Xiao Y Q, Yao Y, et al. 2016a. Impact of Ural blocking on winter warm Arctic-cold Eurasian anomalies. Part I: Blocking-induced amplification [J]. J. Climate, 29 (11): , doi: /jcli-d Luo D H, Xiao Y Q, Diao Y N, et al. 2016b. Impact of Ural blocking on winter warm Arctic cold Eurasian anomalies. Part II: The link to the North Atlantic oscillation [J]. J. Climate, 29 (11): , doi: /JCLI-D Magnusdottir G, Deser C, Saravanan R The effects of North Atlantic SST and sea ice anomalies on the winter circulation in CCM3. Part I: Main features and storm track characteristics of the response [J]. J. Climate, 17 (5): , doi: / (2004)017<0857: TEONAS>2.0.CO;2. Makshtas A P, Andreas E L The heat budget of Arctic ice in the winter [M]. Cambridge: International Glaciological Society, 77pp. McCusker K E, Fyfe J C, Sigmond M Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss [J]. Nat. Geosci., 9 (11): , doi: /ngeo2820. Mori M, Watanabe M, Shiogama H, et al Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades [J]. Nat. Geosci., 7 (12): , doi: /ngeo2277. Murray R J, Simmonds I Responses of climate and cyclones to reductions in Arctic winter sea ice [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 100 (C3): , doi: /94jc Nakamura T, Yamazaki K, Iwamoto K, et al A negative phase shift of the winter AO/NAO due to the recent Arctic sea-ice reduction in late autumn [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 120 (8): , doi: / 2014JD Newson R L Response of a general circulation model of the atmosphere to removal of the Arctic ice-cap [J]. Nature, 241 (5384): 39 40, doi: /241039b0. Ogi M, Yamazaki K, Wallace J M Influence of winter and summer surface wind anomalies on summer Arctic sea ice extent [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37 (7): L07701, doi: /2009gl Overland J, Francis J A, Hall R, et al The melting Arctic and midlatitude weather patterns: Are they connected? [J] J. Climate, 28 (20): , doi: /jcli-d Overland J E, Wang M Y Large-scale atmospheric circulation changes are associated with the recent loss of Arctic sea ice [J]. Tellus A, 62 (1): 1 9, doi: /j x. Overland J E, Dethloff K, Francis J A, et al Nonlinear response of mid-latitude weather to the changing Arctic [J]. Nature Climate Change, 6 (11): , doi: /nclimate3121. Park D S R, Lee S, Feldstein S B Attribution of the recent winter sea ice decline over the Atlantic sector of the Arctic Ocean [J]. J. Climate, 28 (10): , doi: /jcli-d Parkinson C L, Rind D, Healy R J, et al The impact of sea ice concentration accuracies on climate model simulations with the GISS GCM [J]. J. Climate, 14 (12): , doi: / (2001) 014<2606:TIOSIC>2.0.CO;2. Peings Y, Magnusdottir G Response of the wintertime Northern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline: A numerical study with CAM5 [J]. J. Climate, 27 (1): , doi: /jcli-d Perlwitz J, Hoerling M, Dole R Arctic tropospheric warming: Causes and linkages to lower latitudes [J]. J. Climate, 28 (6): , doi: /jcli-d Petoukhov V, Semenov V A A link between reduced Barents-Kara sea ice and cold winter extremes over northern continents [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 115 (D21): D21111, doi: /2009jd Polyakov I V, Walsh J E, Kwok R Recent changes of Arctic multiyear sea ice coverage and the likely causes [J]. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 93 (2): , doi: /bams-d Polyakov I V, Timokhov L A, Alexeev V A, et al Arctic Ocean warming contributes to reduced polar ice cap [J]. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 40 (12): , doi: /2010jpo Proshutinsky A Y, Johnson M A Two circulation regimes of the winddriven Arctic Ocean [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 102 (C6): , doi: /97jc Rigor I G, Wallace J M, Colony R I Response of sea ice to the Arctic Oscillation [J]. J. Climate, 15 (18): , doi: / (2002)015<2648:rositt>2.0.co;2. Rinke A, Dethloff K, Dorn W, et al Simulated Arctic atmospheric feedbacks associated with late summer sea ice anomalies [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 118 (14): , doi: /jgrd Roeckner E, Bäuml G, Bonaventura L, et al The atmospheric general circulation model ECHAM5. Part I: Model description [R]. Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Report No. 349, 127 pp. Royer J F, Planton S, Déqué M A sensitivity experiment for the removal of Arctic sea ice with the French spectral general circulation
19 804 大气科学 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42 卷 Vol. 42 model [J]. Climate Dyn., 5 (1): 1 17, doi: /bf Screen J A, Simmonds I The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification [J]. Nature, 464 (7293): , doi: /nature Screen J A, Simmonds I Declining summer snowfall in the Arctic: Causes, impacts and feedbacks [J]. Climate Dyn., 38 (11 12): , doi: /s Screen J A, Deser C, Simmonds I, et al Atmospheric impacts of Arctic sea-ice loss, : Separating forced change from atmospheric internal variability [J]. Climate Dyn., 43 (1 2): , doi: /s Semenov V A, Latif M Nonlinear winter atmospheric circulation response to Arctic sea ice concentration anomalies for different periods during [J]. Environ. Res. Lett., 10 (5): , doi: / /10/5/ Serreze M C, Holland M M, Stroeve J Perspectives on the Arctic s shrinking sea-ice cover [J]. Science, 315 (5818): , doi: / science Shimada K, Kamoshida T, Itoh M, et al Pacific Ocean inflow: Influence on catastrophic reduction of sea ice cover in the Arctic Ocean [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33 (8): L08605, doi: /2005gl Simmonds I, Rudeva I The great Arctic cyclone of August 2012 [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 39 (23): L23709, doi:1029/2012gl Spreen G, Kwok G, Menemenlis D Trends in Arctic sea ice drift and role of wind forcing: [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38 (19): L19501, doi: /2011gl Stroeve J C, Serreze M C, Holland M M, et al The Arctic s rapidly shrinking sea ice cover: A research synthesis [J]. Climatic Change, 110 (3 4): , doi: /s Sun L T, Perlwitz J, Hoerling M What caused the recent Warm Arctic, Cold Continents trend pattern in winter temperatures? [J] Geophys. Res. Lett., 43 (10): , doi: /2016gl Tang Q H, Zhang X D, Yang X H, et al Cold winter extremes in northern continents linked to Arctic sea ice loss [J]. Environ. Res. Lett., 8 (1): , doi: / /8/1/ Thorndike A S, Colony R Sea ice motion in response to geostrophic winds [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 87 (C8): , doi: / JC087iC08p Van Oldenborgh G J, Haarsma R, De Vries H, et al Cold extremes in North America vs. mild weather in Europe: The winter of in the context of a warming world [J]. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 96 (5): , doi: /bams-d Vihma T Effects of Arctic sea ice decline on weather and climate: A review [J]. Surv. Geophys., 35 (5): , doi: /s Vinje T Fram Strait ice fluxes and atmospheric circulation: [J]. J. Climate, 14 (16): , doi: / (2001)014<3508:FSIFAA>2.0.CO;2. Walsh J E Intensified warming of the Arctic: Causes and impacts on middle latitudes [J]. Global Planet. Change, 117: 52 63, doi: /j. gloplacha Wang H J, Chen H P, Liu J P Arctic Sea ice decline intensified haze pollution in eastern China [J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 8 (1): 1 9, doi: /aosl Wang J, Ikeda M Arctic oscillation and arctic sea-ice oscillation [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 27 (9): , doi: /1999gl Wang J, Mysak L A, Ingram R G Interannual variability of sea-ice cover in Hudson Bay, Baffin Bay and the Labrador Sea [J]. Atmos. Ocean, 32 (2): , doi: / Wang J, Zhang J L, Watanabe E, et al Is the dipole anomaly a major driver to record lows in Arctic summer sea ice extent? [J] Geophys. Res. Lett., 36 (5): L05706, doi: /2008gl Woodgate R A, Weingartner T, Lindsay R The 2007 Bering Strait oceanic heat flux and anomalous Arctic sea-ice retreat [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37 (1): L01602, doi: /2009gl Wu B Y Winter atmospheric circulation anomaly associated with recent Arctic winter warm anomalies [J]. J. Climate, 30 (21): , doi: /jcli-d Wu B Y, Johnson M A seesaw structure in SLP anomalies between the Beaufort Sea and the Barents Sea [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34 (5): L05811, doi: /2006gl Wu B Y, Huang R H, Gao D Y Effects of variation of winter sea-ice area in Kara and Barents seas on East Asia winter monsoon [J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 13 (2): Wu B Y, Wang J, Walsh J E Dipole anomaly in the winter Arctic atmosphere and its association with sea ice motion [J]. J. Climate, 19 (2): , doi: /jcli Wu B Y, Huang R H, Gao D Y Arctic sea ice bordering on the North Atlantic and interannual climate variations [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 46 (2): , doi: /bf Wu B Y, Su J Z, Zhang R H Effects of autumn-winter arctic sea ice on winter Siberian high [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56 (30): , doi: /s Wu B Y, Overland J E, D Arrigo R Anomalous Arctic surface wind patterns and their impacts on September sea ice minima and trend [J]. Tellus A, 64 (1): 18590, doi: /tellusa.v64i Wu B Y, Su J Z, D Arrigo R Patterns of Asian winter climate variability and links to Arctic sea ice [J]. J. Climate, 28 (17): , doi: /jcli-d Wu B Y, Yang K, Francis J A Summer Arctic dipole wind pattern affects the winter Siberian high [J]. Int. J. Climatol., 36 (13): , doi: /joc Wu B Y, Handorf D, Dethloff K, et al. 2013a. Winter weather patterns over northern Eurasia and Arctic sea ice loss [J]. Mon. Wea. Rev., 141 (11): , doi: /mwr-d Wu B Y, Zhang R H, D Arrigo R, et al. 2013b. On the relationship between winter sea ice and summer atmospheric circulation over Eurasia [J]. J. Climate, 26 (15): , doi: /jcli-d 武炳义, 杨琨 从 2011/2012 和 2015/2016 年冬季大气环流异常看北极海冰以及前期夏季北极大气环流异常的作用 [J]. 气象学报, 74 (5): Wu B Y, Yang K Roles of Arctic sea ice and the preceding summer Arctic atmospheric circulation anomalies in the atmospheric circulations anomalies of 2011/2012 and 2015/2016 winters [J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica (in Chinese), 74 (5): , doi:10.
20 4 期 No. 4 武炳义 : 北极海冰融化影响东亚冬季天气和气候的研究进展以及学术争论焦点问题 WU Bingyi. Progresses in the Impact Study of Arctic Sea Ice Loss on Wintertime Weather and Climate Variability over /qxxb Wu B Y, Yang K, Francis J A A cold event in Asia during January February 2012 and its possible association with Arctic sea ice loss [J]. J. Climate, 30 (19): , doi: /jcli-d Wu Q G, Zhang X D Observed forcing-feedback processes between Northern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation and Arctic sea ice coverage [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 115 (D14): D14119, doi: /2009jd Yim B Y, Min H S, Kim B M, et al Sensitivity of Arctic warming to sea ice concentration [J]. J. Geophys. Res., 121 (12): , doi: /2015jd Zhao P, Zhang X D, Zhou X J, et al The sea ice extent anomaly in the North Pacific and its impact on the East Asian summer monsoon rainfall [J]. J. Climate, 17 (17): , doi: / (2004)017< 3434:TSIEAI>2.0.CO;2.
Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol. 42 No. 4 Jul [J]., 42 (4): Wu Bingyi Progresses in the impact st
![Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol. 42 No. 4 Jul [J]., 42 (4): Wu Bingyi Progresses in the impact st Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol. 42 No. 4 Jul [J]., 42 (4): Wu Bingyi Progresses in the impact st](/thumbs/100/144518094.jpg) 42 4 2018 7 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol. 42 No. 4 Jul. 2018. 2018. [J]., 42 (4): 786 805. Wu Bingyi. 2018. Progresses in the impact study of Arctic sea ice loss on wintertime weather and
42 4 2018 7 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol. 42 No. 4 Jul. 2018. 2018. [J]., 42 (4): 786 805. Wu Bingyi. 2018. Progresses in the impact study of Arctic sea ice loss on wintertime weather and
Microsoft Word - 1--齐继峰_new_.doc
 45 6 Vol.45, No.6 2014 11 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Nov., 2014 * 1, 2, 3 1, 2 1, 2 1, 2 (1. 266071; 2. 266071; 3. 100049) 1956 2005 PN, NCEP,, (PDO),, 19 33Sv, 24.30Sv(1Sv=10 6 m 3 /s);, 1956 2005
45 6 Vol.45, No.6 2014 11 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Nov., 2014 * 1, 2, 3 1, 2 1, 2 1, 2 (1. 266071; 2. 266071; 3. 100049) 1956 2005 PN, NCEP,, (PDO),, 19 33Sv, 24.30Sv(1Sv=10 6 m 3 /s);, 1956 2005
~ a 3 h NCEP ~ 24 3 ~ ~ 8 9 ~ km m ~ 500 m 500 ~ 800 m 800 ~ m a 200
 31 1 2013 3 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 31 No. 1 March 2013. J. 2013 31 1 62-69. doi 10. 11755 /j. issn. 1006-7639 2013-01 - 0062 211101 2000 ~ 2010 3 h 2. 5 2. 5 NCEP 2 5 ~ 7 02 11 05 ~ 08 2 ~ 8
31 1 2013 3 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 31 No. 1 March 2013. J. 2013 31 1 62-69. doi 10. 11755 /j. issn. 1006-7639 2013-01 - 0062 211101 2000 ~ 2010 3 h 2. 5 2. 5 NCEP 2 5 ~ 7 02 11 05 ~ 08 2 ~ 8
decades and get distant from each other in other decades which is observed in the last three decades. Key words East China precipitation extrem
 35 5 Vol. 35 No. 5 2012 10 Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences Oct. 2012. 2012. 50 a J. 35 5 591-602. Li Ming-gang Guan Zhao-yong Han Jie et al. 2012. Interdecadal changes of summertime precipitation
35 5 Vol. 35 No. 5 2012 10 Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences Oct. 2012. 2012. 50 a J. 35 5 591-602. Li Ming-gang Guan Zhao-yong Han Jie et al. 2012. Interdecadal changes of summertime precipitation
南京气象学院学报第 卷
 Ò Ò 潘敖大 孙照渤 在对长江中下游夏季降水进行分型的基础上 分析了长江流域南北两支雨带与春季太平洋海温的相关关系 并采用 大气环流模式对前期海温进行了敏感性试验 结果表明 赤道东太平洋区域 的海温异常对两支雨带夏季降水有重要影响 海温正异常时南支雨带旱 北支雨带不明显 海温负异常时南支雨带涝 北支雨带旱 前期赤道东太平洋海温强迫可以在北半球对流层激发出遥相关波列 并影响长江流域南北两支雨带的旱涝分布
Ò Ò 潘敖大 孙照渤 在对长江中下游夏季降水进行分型的基础上 分析了长江流域南北两支雨带与春季太平洋海温的相关关系 并采用 大气环流模式对前期海温进行了敏感性试验 结果表明 赤道东太平洋区域 的海温异常对两支雨带夏季降水有重要影响 海温正异常时南支雨带旱 北支雨带不明显 海温负异常时南支雨带涝 北支雨带旱 前期赤道东太平洋海温强迫可以在北半球对流层激发出遥相关波列 并影响长江流域南北两支雨带的旱涝分布
cm hpa hpa 2 45 N hpa ~ 12 Fig. 1 The observed rainfall distribution of Shanxi
 28 3 2010 9 1006-7639 2010-03 - 0332-06 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 28 No. 3 Sept 2010 1 1 2 1 3 1. 046000 2. 030404 3. 034000 2009 11 10 ~ 12 1 10 11 2300 hpa 3500 hpa 41 500 m 2 850 hpa 5FY - 2C
28 3 2010 9 1006-7639 2010-03 - 0332-06 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 28 No. 3 Sept 2010 1 1 2 1 3 1. 046000 2. 030404 3. 034000 2009 11 10 ~ 12 1 10 11 2300 hpa 3500 hpa 41 500 m 2 850 hpa 5FY - 2C
mm 400 mm 15 mm EOF mm/10a Fig. 1 Distributions
 7 2 2011 3 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol. 7 No. 2 March 2011 1673-1719 (2011) 02-0097-07 1961 2007 77 5 5 6 2 3 8 11 1980 1980 1990 2015 8 11 P426.6 A 7.86% 4 50 0.35 5 6 19 7 8 9 1 1906 2005
7 2 2011 3 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol. 7 No. 2 March 2011 1673-1719 (2011) 02-0097-07 1961 2007 77 5 5 6 2 3 8 11 1980 1980 1990 2015 8 11 P426.6 A 7.86% 4 50 0.35 5 6 19 7 8 9 1 1906 2005
IPCC CO (IPCC2006) 1 : = ( 1) 1 (kj/kg) (kgc/gj) (tc/t)
 2011 5 5 (278 ) China Industrial Economics May 2011 No.5 1 12 (1. 100005; 2. 066004) [ ] : ; ; : ; ; [ ] ; ; ; [ ]F290 [ ]A [ ]1006-480X(2011)05-0047-11 2008 CO 2 ( ) (2009) (GDP) (Binhocker et al. 2008)
2011 5 5 (278 ) China Industrial Economics May 2011 No.5 1 12 (1. 100005; 2. 066004) [ ] : ; ; : ; ; [ ] ; ; ; [ ]F290 [ ]A [ ]1006-480X(2011)05-0047-11 2008 CO 2 ( ) (2009) (GDP) (Binhocker et al. 2008)
Microsoft Word - 赖芬芬284-校对
 28 5 Vol.28 No.5 2012 10 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Oct. 2012. [J]. 2012 28(5): 609-620. :1004-4965(2012)05-0609-12 ( 210093) 1949 2007 CMA-STI 1949 1975 1976 1987 1988 2007 7 10 ( TC) TC TC ( ) TC
28 5 Vol.28 No.5 2012 10 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Oct. 2012. [J]. 2012 28(5): 609-620. :1004-4965(2012)05-0609-12 ( 210093) 1949 2007 CMA-STI 1949 1975 1976 1987 1988 2007 7 10 ( TC) TC TC ( ) TC
Microsoft Word - N072015-00201-160006-已统稿(0321)
 中 国 科 学 : 地 球 科 学 2016 年 第 46 卷 第 4 期 : 555 ~ 562 SCIENTIA SINICA Terrae earth.scichina.com 中 国 科 学 杂 志 社 SCIENCE CHINA PRESS 论 文 北 冰 洋 中 心 区 夏 季 大 气 边 界 层 结 构 特 征 及 其 与 海 冰 范 围 变 化 的 关 系 卞 林 根 12*, 丁
中 国 科 学 : 地 球 科 学 2016 年 第 46 卷 第 4 期 : 555 ~ 562 SCIENTIA SINICA Terrae earth.scichina.com 中 国 科 学 杂 志 社 SCIENCE CHINA PRESS 论 文 北 冰 洋 中 心 区 夏 季 大 气 边 界 层 结 构 特 征 及 其 与 海 冰 范 围 变 化 的 关 系 卞 林 根 12*, 丁
Climatic and Environmental Research Vol. 22, No. 4 Jul. 2017, [J]. 22 (4): Zhang Dongling, Lu Xu Analysis of abnorm
![Climatic and Environmental Research Vol. 22, No. 4 Jul. 2017, [J]. 22 (4): Zhang Dongling, Lu Xu Analysis of abnorm Climatic and Environmental Research Vol. 22, No. 4 Jul. 2017, [J]. 22 (4): Zhang Dongling, Lu Xu Analysis of abnorm](/thumbs/98/137100100.jpg) 22 4 2017 7 Vol. 22, No. 4 Jul. 2017,. 2017. [J]. 22 (4): 463 472. Zhang Dongling, Lu Xu. 2017. Analysis of abnormal upper circulation over the tropical Indian Ocean in winter [J]. (in Chinese), 22 (4):
22 4 2017 7 Vol. 22, No. 4 Jul. 2017,. 2017. [J]. 22 (4): 463 472. Zhang Dongling, Lu Xu. 2017. Analysis of abnormal upper circulation over the tropical Indian Ocean in winter [J]. (in Chinese), 22 (4):
, 2 : ; 4 8, mm, mm, 43. 3% ; 350 mm, 70% , 32 d, d mm, 45. 1% mm, mm, 850 hpa (
 26 1 2008 3 : 1006-7639 (2008) - 01-0001 - 07 AR ID METEOROLOGY Vol. 26 No. 1 March, 2008 2006, (, 211101) : NCEP OLR SST 2006, :, : ; ; ; ; : P458. 1 + 1 : A,,, [ 1 ] [ 2-5 ],, ( 400 m ),,, [ 6 ], 2006,
26 1 2008 3 : 1006-7639 (2008) - 01-0001 - 07 AR ID METEOROLOGY Vol. 26 No. 1 March, 2008 2006, (, 211101) : NCEP OLR SST 2006, :, : ; ; ; ; : P458. 1 + 1 : A,,, [ 1 ] [ 2-5 ],, ( 400 m ),,, [ 6 ], 2006,
254 22 [11] Bennetts (1988) [12] and Locatelli (1994) [13] e 1999 6 23 08 24 08 2 1 1 23 12 3033 N 900 hpa 23 14 950 hpa23 16 23 18 23 20 23 22 3033 N
![254 22 [11] Bennetts (1988) [12] and Locatelli (1994) [13] e 1999 6 23 08 24 08 2 1 1 23 12 3033 N 900 hpa 23 14 950 hpa23 16 23 18 23 20 23 22 3033 N 254 22 [11] Bennetts (1988) [12] and Locatelli (1994) [13] e 1999 6 23 08 24 08 2 1 1 23 12 3033 N 900 hpa 23 14 950 hpa23 16 23 18 23 20 23 22 3033 N](/thumbs/40/20608965.jpg) 22 3 Vol.22, No.3 2006 06 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Jun., 2006 1004-4965200603-0253-06 ( 211101) 1999 6 P433 A 1 [13] Xu [4] [5] Emanuel [6] Jascourt [7] Xu [8] upscale development Xu downscale development
22 3 Vol.22, No.3 2006 06 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Jun., 2006 1004-4965200603-0253-06 ( 211101) 1999 6 P433 A 1 [13] Xu [4] [5] Emanuel [6] Jascourt [7] Xu [8] upscale development Xu downscale development
km km mm km m /s hpa 500 hpa E N 41 N 37 N 121
 32 2 2014 4 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 32 No. 2 Apr 2014. 08. 03 J. 2014 32 2256-262 LU Guirong WANG Wen YU Huaizhenget al. The Influence of Damrey Typhoon on 08. 03 Rainstorm Process in Rizhao of
32 2 2014 4 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 32 No. 2 Apr 2014. 08. 03 J. 2014 32 2256-262 LU Guirong WANG Wen YU Huaizhenget al. The Influence of Damrey Typhoon on 08. 03 Rainstorm Process in Rizhao of
一次辽宁暴雨过程的诊断及风场反演分析
 Climate Change Research Letters 气 候 变 化 研 究 快 报, 2013, 2, 139-146 http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/ccrl.2013.24024 Published Online October 2013 (http://www.hanspub.org/journal/ccrl.html) Analysis of the Diagnosis
Climate Change Research Letters 气 候 变 化 研 究 快 报, 2013, 2, 139-146 http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/ccrl.2013.24024 Published Online October 2013 (http://www.hanspub.org/journal/ccrl.html) Analysis of the Diagnosis
720 () 2009,,, , ( ) (6 8 ), ( 5) ( 6).,,119 E, 150 km., 25. 5, 25,., 5b. 3 ROMS 3. 1 ROMS, S,.,,,, [ 9 ]. 1/ 32 ( ),25, 18 s, 180 s
![720 () 2009,,, , ( ) (6 8 ), ( 5) ( 6).,,119 E, 150 km., 25. 5, 25,., 5b. 3 ROMS 3. 1 ROMS, S,.,,,, [ 9 ]. 1/ 32 ( ),25, 18 s, 180 s 720 () 2009,,, , ( ) (6 8 ), ( 5) ( 6).,,119 E, 150 km., 25. 5, 25,., 5b. 3 ROMS 3. 1 ROMS, S,.,,,, [ 9 ]. 1/ 32 ( ),25, 18 s, 180 s](/thumbs/91/107334961.jpg) 48 5 2009 9 () Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) Vol. 48 No. 5 Sep. 2009 Argos 1, 1, 1 3, 1, 2 (1.,, 361005 ; 2., 361005) :,Argos,( ROMS), 120. 75 E,.,,,,,. :120. 75 E,,( ),,,, 1. 305 10 7
48 5 2009 9 () Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) Vol. 48 No. 5 Sep. 2009 Argos 1, 1, 1 3, 1, 2 (1.,, 361005 ; 2., 361005) :,Argos,( ROMS), 120. 75 E,.,,,,,. :120. 75 E,,( ),,,, 1. 305 10 7
5期xin
 中 国 农 学 通 报 2014,30(5):276-283 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 基 于 综 合 模 糊 评 价 方 法 的 西 安 旅 游 气 候 舒 适 度 分 析 卢 珊 1, 王 百 朋 2, 贺 皓 1, 李 建 科 1 1, 高 红 燕 ( 1 陕 西 省 气 象 服 务 中 心, 西 安 710014; 2 陕 西 省 防 雷 中
中 国 农 学 通 报 2014,30(5):276-283 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 基 于 综 合 模 糊 评 价 方 法 的 西 安 旅 游 气 候 舒 适 度 分 析 卢 珊 1, 王 百 朋 2, 贺 皓 1, 李 建 科 1 1, 高 红 燕 ( 1 陕 西 省 气 象 服 务 中 心, 西 安 710014; 2 陕 西 省 防 雷 中
30 26, ;,,,, ;, 500 hpa, [ 8 ], 0. 01, > 0. 5,, ( 1) 1,,, [ 9 ] 31 ( 2a), II 2 ( b c) 1 ( 1963, 1968, 1971, 1974, 1976, 1985) ( 1973, 1983, 1988, 1993
![30 26, ;,,,, ;, 500 hpa, [ 8 ], 0. 01, > 0. 5,, ( 1) 1,,, [ 9 ] 31 ( 2a), II 2 ( b c) 1 ( 1963, 1968, 1971, 1974, 1976, 1985) ( 1973, 1983, 1988, 1993 30 26, ;,,,, ;, 500 hpa, [ 8 ], 0. 01, > 0. 5,, ( 1) 1,,, [ 9 ] 31 ( 2a), II 2 ( b c) 1 ( 1963, 1968, 1971, 1974, 1976, 1985) ( 1973, 1983, 1988, 1993](/thumbs/93/111724282.jpg) 26 3 2008 9 : 1006-7639 (2008) - 03-0029 - 05 AR ID METEOROLOGY Vol. 26 No. 3 Sep t, 2008,,,, (, 810001) :, 3 3, ( ) II ( ) ; ( ) II III ( ) 2 500 hpa, : ( ), ( ) ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ) ; ( ), 500 hpa
26 3 2008 9 : 1006-7639 (2008) - 03-0029 - 05 AR ID METEOROLOGY Vol. 26 No. 3 Sep t, 2008,,,, (, 810001) :, 3 3, ( ) II ( ) ; ( ) II III ( ) 2 500 hpa, : ( ), ( ) ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ) ; ( ), 500 hpa
~4 197~ [8] [11].5.5 A grid V grid A r ϕ ϕ λ r ϕ 2 2 grid = cos = (π /36) cos V grid = A grid P grid 1 6 r ϕ A grid km 2
![~4 197~ [8] [11].5.5 A grid V grid A r ϕ ϕ λ r ϕ 2 2 grid = cos = (π /36) cos V grid = A grid P grid 1 6 r ϕ A grid km 2 ~4 197~ [8] [11].5.5 A grid V grid A r ϕ ϕ λ r ϕ 2 2 grid = cos = (π /36) cos V grid = A grid P grid 1 6 r ϕ A grid km 2](/thumbs/52/29507912.jpg) 24 3 Vol.24, No.3 8 6 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Jun., 8 :14-4965(8)3-233-6 1 2 2 2 1. 442. 181 7 mm 1 mm 4~12 8 1957~4 : :P444 :A 1 [1] 4 5 6 199 [23] [4] 198~199 [5] [6] Rodgers [7] 444 km [8] [91]
24 3 Vol.24, No.3 8 6 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Jun., 8 :14-4965(8)3-233-6 1 2 2 2 1. 442. 181 7 mm 1 mm 4~12 8 1957~4 : :P444 :A 1 [1] 4 5 6 199 [23] [4] 198~199 [5] [6] Rodgers [7] 444 km [8] [91]
2016,36(4) 961~969 China Environmental Science 1960~ , 2, 3, 1 (1.,,,,, , , ) 1960~2012,. :,,., 20 80, ;,.,,,, ,
 16,36(4) 961~969 China Environmental Science 19~12 1 1, 2, 3, 1 (1.,,,,, 244 2., 28 3., 81) 19~12,.:,,.,, ;,.,,,,. 9.,,,,. X513 A 6923(16)4 961 9 Spatial and temporal distribution characteristic of fog
16,36(4) 961~969 China Environmental Science 19~12 1 1, 2, 3, 1 (1.,,,,, 244 2., 28 3., 81) 19~12,.:,,.,, ;,.,,,,. 9.,,,,. X513 A 6923(16)4 961 9 Spatial and temporal distribution characteristic of fog
1 : 97,,, ; , , ; :, h 15. 2, h ,, 1,, 3, : 1 1 d, 2 2 d;, , , 0812
 28 1 2010 3 : 1006-7639 (2010) - 01-0096 - 06 Journal of A rid M eteorology Vol. 28 No. 1 March, 2010,,,, (, 050081) : 2008, 3, 10 a 2008 12 3 5 3 T213 ( EC),, : T213 EC, T213, : ; ; : P458. 1 + 22 : A,,,
28 1 2010 3 : 1006-7639 (2010) - 01-0096 - 06 Journal of A rid M eteorology Vol. 28 No. 1 March, 2010,,,, (, 050081) : 2008, 3, 10 a 2008 12 3 5 3 T213 ( EC),, : T213 EC, T213, : ; ; : P458. 1 + 22 : A,,,
48 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 29 Vol hpa, Flohn [2 ] 7 8 d W = F + (thermal anticyclonic cell), d a Q, (1) t ( ), F, Q, a,, W = P
![48 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 29 Vol hpa, Flohn [2 ] 7 8 d W = F + (thermal anticyclonic cell), d a Q, (1) t ( ), F, Q, a,, W = P 48 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 29 Vol hpa, Flohn [2 ] 7 8 d W = F + (thermal anticyclonic cell), d a Q, (1) t ( ), F, Q, a,, W = P](/thumbs/93/111300563.jpg) 29 1 2005 1 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol1 29, No1 1 Jan1 2005 1 1 2 1 1 1, 100029 2, 100085, 100629895 (2005) 0120047210 P641 A How the Heating over the Tibetan Plateau Affects the Asian
29 1 2005 1 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol1 29, No1 1 Jan1 2005 1 1 2 1 1 1, 100029 2, 100085, 100629895 (2005) 0120047210 P641 A How the Heating over the Tibetan Plateau Affects the Asian
142 () Fig. 2 Tracks of typhoon 35 m/ s.,. NASA QuikSCA T L3 (10 m ),, km, 25 km,20, 2 m/ s (320 m/ s) 10 %(2030 m/ s)., ()
 46 1 () Vol. 46 No. 1 2007 1 Journal of Xiamen University (Nat ural Science) Jan. 2007 1,2, 1,2 3, 2, 2 (1.,2. ( ), 361005) : 19992005 QuikSCA T,.,,,. ( > 10 m/ s) ()..,. : ; ;; ;QuikSCA T : P 444 :A :043820479
46 1 () Vol. 46 No. 1 2007 1 Journal of Xiamen University (Nat ural Science) Jan. 2007 1,2, 1,2 3, 2, 2 (1.,2. ( ), 361005) : 19992005 QuikSCA T,.,,,. ( > 10 m/ s) ()..,. : ; ;; ;QuikSCA T : P 444 :A :043820479
 T42 300 100 Wilson and Mitchell 1987 Diskinson et al 1989 Giorgi 1990 IPCC Houghton et al.2001 2~4-40~80 2 50 Purdue Regional Model, PRM PRM PRM 1990~2000 15 1 PRM (Sun and Hsu 1988Sun and Chern 1993)
T42 300 100 Wilson and Mitchell 1987 Diskinson et al 1989 Giorgi 1990 IPCC Houghton et al.2001 2~4-40~80 2 50 Purdue Regional Model, PRM PRM PRM 1990~2000 15 1 PRM (Sun and Hsu 1988Sun and Chern 1993)
408 30,, [ 225 ],,,,, [ 629 ],, , 2008,,,,, mm, mm, 3115 mm /h, (34193 N, E), mm, 8511 mm /h,, :,, (5 1
![408 30,, [ 225 ],,,,, [ 629 ],, , 2008,,,,, mm, mm, 3115 mm /h, (34193 N, E), mm, 8511 mm /h,, :,, (5 1 408 30,, [ 225 ],,,,, [ 629 ],, , 2008,,,,, mm, mm, 3115 mm /h, (34193 N, E), mm, 8511 mm /h,, :,, (5 1](/thumbs/93/113902845.jpg) 30 3 Vol. 30, No. 3 2010 6 SC IENTIA METEOROLOGICA SIN ICA Jun., 2010,,,.., 2010, 30 ( 3) : 4072413. Zhang J ingying, Chen J inm in, L iu Yingjie, et al. Analysis of mechanism s of short2time rainfall
30 3 Vol. 30, No. 3 2010 6 SC IENTIA METEOROLOGICA SIN ICA Jun., 2010,,,.., 2010, 30 ( 3) : 4072413. Zhang J ingying, Chen J inm in, L iu Yingjie, et al. Analysis of mechanism s of short2time rainfall
17 4 Vol. 17, No CHIN ESE JOU RNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH December , 2 ( 1, ; 2,, ) NCEP , 30,,,, 28/ 10a,, - 3.
 17 4 Vol. 17, No. 4 2005 12 CHIN ESE JOU RNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH December 2005 30 1, 2 ( 1, 100081 ; 2,, 100081) NCEP 1973 2002, 30,,,, 28/ 10a,, - 3. 5/ 10a 1/ 3,, 10 3 5 2 1 (Budd, 1975 ; Chiul, 1985
17 4 Vol. 17, No. 4 2005 12 CHIN ESE JOU RNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH December 2005 30 1, 2 ( 1, 100081 ; 2,, 100081) NCEP 1973 2002, 30,,,, 28/ 10a,, - 3. 5/ 10a 1/ 3,, 10 3 5 2 1 (Budd, 1975 ; Chiul, 1985
~ 10 2 P Y i t = my i t W Y i t 1000 PY i t Y t i W Y i t t i m Y i t t i 15 ~ 49 1 Y Y Y 15 ~ j j t j t = j P i t i = 15 P n i t n Y
 * 35 4 2011 7 Vol. 35 No. 4 July 2011 3 Population Research 1950 ~ 1981 The Estimation Method and Its Application of Cohort Age - specific Fertility Rates Wang Gongzhou Hu Yaoling Abstract Based on the
* 35 4 2011 7 Vol. 35 No. 4 July 2011 3 Population Research 1950 ~ 1981 The Estimation Method and Its Application of Cohort Age - specific Fertility Rates Wang Gongzhou Hu Yaoling Abstract Based on the
4 : 255 [ 2, 4 7 ] [ 8 11 ],,,, [ 12 ] Koldewey , [ 13 ],,, NCEP Koldewey, NCEP 2,, 1231km, 107km Koldewey ( N, E, 11m) A lfre
![4 : 255 [ 2, 4 7 ] [ 8 11 ],,,, [ 12 ] Koldewey , [ 13 ],,, NCEP Koldewey, NCEP 2,, 1231km, 107km Koldewey ( N, E, 11m) A lfre 4 : 255 [ 2, 4 7 ] [ 8 11 ],,,, [ 12 ] Koldewey , [ 13 ],,, NCEP Koldewey, NCEP 2,, 1231km, 107km Koldewey ( N, E, 11m) A lfre](/thumbs/51/28695540.jpg) 18 4 Vol. 18, No. 4 2006 12 CH INESE JOURNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH December 2006 (, 100081), Koldewey 1993 2003,,, 32. 2%,, ;, 10, NCEP /NCAR, NCEP Koldewey NCEP /NCAR 1,, [ 1 ],,, 90 1991,, [ 2 ] ; 1999 2003,
18 4 Vol. 18, No. 4 2006 12 CH INESE JOURNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH December 2006 (, 100081), Koldewey 1993 2003,,, 32. 2%,, ;, 10, NCEP /NCAR, NCEP Koldewey NCEP /NCAR 1,, [ 1 ],,, 90 1991,, [ 2 ] ; 1999 2003,
000封面.doc
 (91 5 ) 2001 GIMEX Green Island Mesoscale Experiment GIMEX 2001 5 24 250 500 1000 600 8 8 500 750 10 5 250 1000 7 10 i ii iii i iii iv v.. 1 1.1. 1 1.2. 2 1.3. 6.. 7 2.1. 7 2.2. 8 2.3 12. 13 3.1.. 13 3.2..
(91 5 ) 2001 GIMEX Green Island Mesoscale Experiment GIMEX 2001 5 24 250 500 1000 600 8 8 500 750 10 5 250 1000 7 10 i ii iii i iii iv v.. 1 1.1. 1 1.2. 2 1.3. 6.. 7 2.1. 7 2.2. 8 2.3 12. 13 3.1.. 13 3.2..
谢今范
 第 34 卷 第 期 2 年 1 月 PLATEAU METEOROLOGY Vol. 34 No. October,2 谢 今 范, 刘 玉 英, 李 宇 凡. 吉 林 地 面 和 高 空 风 速 变 化 特 征 及 成 因 分 析 [J].,2,34():1424-1434,1. 722/ j. issn. 1-34. 2. 47. 吉 林 地 面 和 高 空 风 速 变 化 特 征 及 成 因
第 34 卷 第 期 2 年 1 月 PLATEAU METEOROLOGY Vol. 34 No. October,2 谢 今 范, 刘 玉 英, 李 宇 凡. 吉 林 地 面 和 高 空 风 速 变 化 特 征 及 成 因 分 析 [J].,2,34():1424-1434,1. 722/ j. issn. 1-34. 2. 47. 吉 林 地 面 和 高 空 风 速 变 化 特 征 及 成 因
16 29 km ,, t, 1.56 t 71.2%, ( 1) 4511km , 144 /km %,, t [16],, t,, t, 9.2 km 2
![16 29 km ,, t, 1.56 t 71.2%, ( 1) 4511km , 144 /km %,, t [16],, t,, t, 9.2 km 2 16 29 km ,, t, 1.56 t 71.2%, ( 1) 4511km , 144 /km %,, t [16],, t,, t, 9.2 km 2](/thumbs/92/108816918.jpg) 29 1 2010 01 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.29, No.1 Jan., 2010 1,2 1 1,2 1,2 (1. 100101; 2. 100049) : 1956-2007, :1 1994-2002 1.43 t/a 91.2% ;2003-2007 4.50 t/a 14.1%, 39.8% 46.2% 2 1983-2000 0.48 t/a 74.7%
29 1 2010 01 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.29, No.1 Jan., 2010 1,2 1 1,2 1,2 (1. 100101; 2. 100049) : 1956-2007, :1 1994-2002 1.43 t/a 91.2% ;2003-2007 4.50 t/a 14.1%, 39.8% 46.2% 2 1983-2000 0.48 t/a 74.7%
9-2 西南日本における短期的スロースリップイベント(2008年11月~2009年4月)
 (2008 11 2009 4 ) Short-term slow slip event with non-volcanic tremors in southwest Japan (November, 2008 April, 2009) National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (SSE) 1, 2)
(2008 11 2009 4 ) Short-term slow slip event with non-volcanic tremors in southwest Japan (November, 2008 April, 2009) National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (SSE) 1, 2)
Z-I A b Z-I A b Z Z-I A A b Z-I Miller [5] Z i I i Z-I [6] Z-I Z-I Z-I Z-I Z I Wilson [7] 1970 [8] [9] 20.32% Sasaki [10] Nino- miya [11] [12]
![Z-I A b Z-I A b Z Z-I A A b Z-I Miller [5] Z i I i Z-I [6] Z-I Z-I Z-I Z-I Z I Wilson [7] 1970 [8] [9] 20.32% Sasaki [10] Nino- miya [11] [12] Z-I A b Z-I A b Z Z-I A A b Z-I Miller [5] Z i I i Z-I [6] Z-I Z-I Z-I Z-I Z I Wilson [7] 1970 [8] [9] 20.32% Sasaki [10] Nino- miya [11] [12]](/thumbs/50/26692510.jpg) 24 2 Vol.24, No.2 2008 04 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Apr., 2008 1004-4965(2008)02-0147-09 1 2 2 3 3 (1. 310017 2. 100081 3. 325001) Z-I A b Z I (Haitang) (Matsa) Z-I Z-I P458.1.24 A 1 [1] [2] [3]
24 2 Vol.24, No.2 2008 04 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Apr., 2008 1004-4965(2008)02-0147-09 1 2 2 3 3 (1. 310017 2. 100081 3. 325001) Z-I A b Z I (Haitang) (Matsa) Z-I Z-I P458.1.24 A 1 [1] [2] [3]
the wave train is out-of-phase and extends in a more southern path 2 in the higher level atmosphere during phase 3 a significant positive anoma
 34 3 Vol. 34 No. 3 2011 6 Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences Jun. 2011. 2011. J. 34 3 297-304. Yin Zhi-cong Wang Ya-fei Yuan Dong-min. 2011. Analysis of the interannual variability of the Meiyu quasi-biweekly
34 3 Vol. 34 No. 3 2011 6 Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences Jun. 2011. 2011. J. 34 3 297-304. Yin Zhi-cong Wang Ya-fei Yuan Dong-min. 2011. Analysis of the interannual variability of the Meiyu quasi-biweekly
2015-6
 第 32 卷 第 6 期 205 年 2 月 海 洋 预 报 MARINE FORECASTS Vol.32,No.6 Dec.205 DOI:0.737/j.issn.003-0239.205.06.02 天 津 近 海 可 能 最 大 风 暴 潮 模 拟 研 究 武 双 全, 崔 晓 健, 高 志 刚, 潘 嵩, 陈 琛 2, 张 建 立, 耿 姗 姗, 李 响 (. 国 家 海 洋 信 息 中
第 32 卷 第 6 期 205 年 2 月 海 洋 预 报 MARINE FORECASTS Vol.32,No.6 Dec.205 DOI:0.737/j.issn.003-0239.205.06.02 天 津 近 海 可 能 最 大 风 暴 潮 模 拟 研 究 武 双 全, 崔 晓 健, 高 志 刚, 潘 嵩, 陈 琛 2, 张 建 立, 耿 姗 姗, 李 响 (. 国 家 海 洋 信 息 中
Microsoft Word 叶然_new_.doc
 46 2 Vol.46, No.2 2015 3 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Mar., 2015 * 1 ( 315012) 2013 (120 128 E 25 33 N) 4, : (1) DIN( )P( ) Si( )DIN SiP, DINP,, SiDIN SiP, (2) N P, 126 E P, 126 E N ; (3) 2001 2010,
46 2 Vol.46, No.2 2015 3 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Mar., 2015 * 1 ( 315012) 2013 (120 128 E 25 33 N) 4, : (1) DIN( )P( ) Si( )DIN SiP, DINP,, SiDIN SiP, (2) N P, 126 E P, 126 E N ; (3) 2001 2010,
(ICL),, 5 ( ), 40,, , [2,15-19], 3, (THI) (WCI) ( 1) 1 Tab.1 THI WCI and ICL grade standard,, ( ); 3, ;, 1 1, Fig.1 Structur
![(ICL),, 5 ( ), 40,, , [2,15-19], 3, (THI) (WCI) ( 1) 1 Tab.1 THI WCI and ICL grade standard,, ( ); 3, ;, 1 1, Fig.1 Structur (ICL),, 5 ( ), 40,, , [2,15-19], 3, (THI) (WCI) ( 1) 1 Tab.1 THI WCI and ICL grade standard,, ( ); 3, ;, 1 1, Fig.1 Structur](/thumbs/91/107412131.jpg) 28 5 2009 09 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.28, No.5 Sept., 2009, (, 710062 ) :,, 26,, 3 :,, ;, 4, W, M,, : ; ; ; ; 1,2006 ( )14, 4943, 259.5,, 80.5% 85.8%,, 28,,,,,,, 14 26 40,, 30, 1966 (W H Terjung), [1]
28 5 2009 09 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.28, No.5 Sept., 2009, (, 710062 ) :,, 26,, 3 :,, ;, 4, W, M,, : ; ; ; ; 1,2006 ( )14, 4943, 259.5,, 80.5% 85.8%,, 28,,,,,,, 14 26 40,, 30, 1966 (W H Terjung), [1]
168 健 等 木醋对几种小浆果扦插繁殖的影响 第1期 the view of the comprehensive rooting quality, spraying wood vinegar can change rooting situation, and the optimal concent
 第 31 卷 第 1 期 2013 年 3 月 经 济 林 研 究 Nonwood Forest Research Vol. 31 No.1 Mar. 2013 木醋对几种小浆果扦插繁殖的影响 健 1,2 杨国亭 1 刘德江 2 (1. 东北林业大学 生态研究中心 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040 2. 佳木斯大学 生命科学学院 黑龙江 佳木斯 154007) 摘 要 为了解决小浆果扦插繁殖中生根率及成活率低等问题
第 31 卷 第 1 期 2013 年 3 月 经 济 林 研 究 Nonwood Forest Research Vol. 31 No.1 Mar. 2013 木醋对几种小浆果扦插繁殖的影响 健 1,2 杨国亭 1 刘德江 2 (1. 东北林业大学 生态研究中心 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040 2. 佳木斯大学 生命科学学院 黑龙江 佳木斯 154007) 摘 要 为了解决小浆果扦插繁殖中生根率及成活率低等问题
United Nations ~ ~ % 2010
 42 3 2018 5 Vol. 42 No. 3 May 2018 38 Population Research 2014 60 3% ~ 4% 10% 60 +
42 3 2018 5 Vol. 42 No. 3 May 2018 38 Population Research 2014 60 3% ~ 4% 10% 60 +
: ;,, 0 0, 60, 0 80,, 76 78, (Deregulation),,,, (Open Sky), (ACI),006.%.8%,.7% 008,, 000, ( ), ( )0, / 6, ; 8, ;, ; 7, ; 06, 6, 006 0, ( ) 0,.%; 0 60,
 7 0 0 8 WORLD REGIONAL STUDIES Vol. 7, No. Jun., 0 0 8 : 007(008)000088,,, (., 000;., 000) :,,, :,,, ( ) :,,,, : F6 : A,, ( ),, GDP (00 ), 000, 000 ~006.%, GDP.6%, ( ), [8] [] [0, ] [] [67] [8], [] [],,
7 0 0 8 WORLD REGIONAL STUDIES Vol. 7, No. Jun., 0 0 8 : 007(008)000088,,, (., 000;., 000) :,,, :,,, ( ) :,,,, : F6 : A,, ( ),, GDP (00 ), 000, 000 ~006.%, GDP.6%, ( ), [8] [] [0, ] [] [67] [8], [] [],,
May Arab World Studies No
 2014 5 May. 2014 3 Arab World Studies No.3. 2004 50 2010 5 32 1955 2004 1 2004 7 2014 1 2010 5 13 14 Gaafar K.Ahmed, Sino- Arab Relations, Ph.D. Dissertation, Nanjing University, June 1996. Gaafar K.Ahmed,
2014 5 May. 2014 3 Arab World Studies No.3. 2004 50 2010 5 32 1955 2004 1 2004 7 2014 1 2010 5 13 14 Gaafar K.Ahmed, Sino- Arab Relations, Ph.D. Dissertation, Nanjing University, June 1996. Gaafar K.Ahmed,
72 (2001) group waves. Key words: Correlation coefficient for consecutive wave heights, mean run length (1993) (1996) (1998) (1999) (1993) (
 (2001) 1 1 71-82 71 1 2 3 1. chtsai@mail.ntou.edu.tw 2. 3. hsiang@mail.ihmt.gov.tw 1998 9 500 (mean run length) Group waves and dangerous waves at the coast Tsai Cheng-Han Lin Yin-Chern Tseng Hsiang-Mao
(2001) 1 1 71-82 71 1 2 3 1. chtsai@mail.ntou.edu.tw 2. 3. hsiang@mail.ihmt.gov.tw 1998 9 500 (mean run length) Group waves and dangerous waves at the coast Tsai Cheng-Han Lin Yin-Chern Tseng Hsiang-Mao
4期
 中 国 农 学 通 报 05,3(4):58-63 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 近 50 年 青 海 海 南 地 区 灾 害 性 天 气 事 件 变 化 特 征 李 金 红, 丁 生 祥, 郭 连 云 ( 青 海 省 海 南 州 气 象 局, 青 海 共 和 83099; 青 海 省 同 德 县 气 象 局, 青 海 同 德 830) 摘 要 : 为
中 国 农 学 通 报 05,3(4):58-63 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 近 50 年 青 海 海 南 地 区 灾 害 性 天 气 事 件 变 化 特 征 李 金 红, 丁 生 祥, 郭 连 云 ( 青 海 省 海 南 州 气 象 局, 青 海 共 和 83099; 青 海 省 同 德 县 气 象 局, 青 海 同 德 830) 摘 要 : 为
untitled
 20 1 2010 10 Vol.20 Special 1 The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals Oct. 2010 1004-0609(2010)S1-s0127-05 Ti-6Al-4V 1 2 2 (1. 710016 2., 710049) 500~1 000 20 Ti-6Al-4V(TC4) TC4 800 TC4 800 TC4 TC4 800
20 1 2010 10 Vol.20 Special 1 The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals Oct. 2010 1004-0609(2010)S1-s0127-05 Ti-6Al-4V 1 2 2 (1. 710016 2., 710049) 500~1 000 20 Ti-6Al-4V(TC4) TC4 800 TC4 800 TC4 TC4 800
 35 2 2011 3 Vol. 35 No. 2 March 2011 83 Population Research * 2 100872 Birth Interval between First and Second Child and Its Policy Implications Liu Shuang Zou Mingru Abstract Using data of international
35 2 2011 3 Vol. 35 No. 2 March 2011 83 Population Research * 2 100872 Birth Interval between First and Second Child and Its Policy Implications Liu Shuang Zou Mingru Abstract Using data of international
by industrial structure evolution from 1952 to 2007 and its influence effect was first acceleration and then deceleration second the effects of indust
 2011 2 1 1 2 3 4 1. 100101 2. 100124 3. 100039 4. 650092 - - - 3 GDP U 20-30 60% 10% TK01 A 1002-9753 2011 02-0042 - 10 Analysis on Character and Potential of Energy Saving and Carbon Reducing by Structure
2011 2 1 1 2 3 4 1. 100101 2. 100124 3. 100039 4. 650092 - - - 3 GDP U 20-30 60% 10% TK01 A 1002-9753 2011 02-0042 - 10 Analysis on Character and Potential of Energy Saving and Carbon Reducing by Structure
1678 (Chinese J Geophys ) m 2 s - 1, FGCM20 2, 211, NCAR ( Community Atmosphere Model, CAM2), CAM2 NCAR CCM3 [15 ], CCM3,CAM2,,
![1678 (Chinese J Geophys ) m 2 s - 1, FGCM20 2, 211, NCAR ( Community Atmosphere Model, CAM2), CAM2 NCAR CCM3 [15 ], CCM3,CAM2,, 1678 (Chinese J Geophys ) m 2 s - 1, FGCM20 2, 211, NCAR ( Community Atmosphere Model, CAM2), CAM2 NCAR CCM3 [15 ], CCM3,CAM2,,](/thumbs/93/113593988.jpg) 50 6 2007 11 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol 50, No 6 Nov, 2007,, LASG 1,2007,50 (6) :1677 1687 Yu Y Q, Zheng W P, Zhang X H, et al LASG coupled climate system model FGCM21 0 Chinese J Geophys (in Chinese),
50 6 2007 11 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol 50, No 6 Nov, 2007,, LASG 1,2007,50 (6) :1677 1687 Yu Y Q, Zheng W P, Zhang X H, et al LASG coupled climate system model FGCM21 0 Chinese J Geophys (in Chinese),
Microsoft Word - 正文.doc
 中 国 农 业 气 象 (Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology) 2015 年 doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.04.007 刘 逵, 杨 靖 新, 杨 旺, 等. 低 纬 高 原 冬 季 与 春 季 降 水 特 征 及 其 环 流 背 景 差 异 分 析 [J]. 中 国 农 业 气 象,2015,36(4):437-445 7
中 国 农 业 气 象 (Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology) 2015 年 doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.04.007 刘 逵, 杨 靖 新, 杨 旺, 等. 低 纬 高 原 冬 季 与 春 季 降 水 特 征 及 其 环 流 背 景 差 异 分 析 [J]. 中 国 农 业 气 象,2015,36(4):437-445 7
LaDefense Arch Petronas Towers 2009 CCTV MOMA Newmark Hahn Liu 8 Heredia - Zavoni Barranco 9 Heredia - Zavoni Leyva
 39 6 2011 12 Journal of Fuzhou University Natural Science Edition Vol 39 No 6 Dec 2011 DOI CNKI 35-1117 /N 20111220 0901 002 1000-2243 2011 06-0923 - 07 350108 105 m 14 69% TU311 3 A Seismic analysis of
39 6 2011 12 Journal of Fuzhou University Natural Science Edition Vol 39 No 6 Dec 2011 DOI CNKI 35-1117 /N 20111220 0901 002 1000-2243 2011 06-0923 - 07 350108 105 m 14 69% TU311 3 A Seismic analysis of
E T 0 = γ 0 = 1 + R γ = nσ n nσ n ΔT 2 i - Σ n ΔT i T Pi - Σ n Σ n
 27 2 147 ~ 154 2011 6 EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH IN CHINA Vol. 27 No. 2 Jun. 2011 2011 5. 6 27 2 147 ~ 154 5. 6 42 830011 2008 8 30 5. 6 1 5. 6 70km 65km NE 5. 6 2 5. 6 10 - - 0. 05 99. 0% 5. 6 1001-4683 2011
27 2 147 ~ 154 2011 6 EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH IN CHINA Vol. 27 No. 2 Jun. 2011 2011 5. 6 27 2 147 ~ 154 5. 6 42 830011 2008 8 30 5. 6 1 5. 6 70km 65km NE 5. 6 2 5. 6 10 - - 0. 05 99. 0% 5. 6 1001-4683 2011
Microsoft Word - 呂芳川
 呂 芳 川 教 授 職 稱 : 教 授 兼 所 長 最 高 學 歷 : 中 央 大 學 大 氣 物 理 博 士 電 話 :06-6523111#2101 email:fclu@mail.njtc.edu.tw 專 長 : 數 值 模 擬 資 訊 平 台 整 合 應 用 GIS 應 用 經 歷 : 南 榮 技 術 學 院 主 任 秘 書 南 榮 技 術 學 院 工 程 科 技 學 群 學 群 長 南
呂 芳 川 教 授 職 稱 : 教 授 兼 所 長 最 高 學 歷 : 中 央 大 學 大 氣 物 理 博 士 電 話 :06-6523111#2101 email:fclu@mail.njtc.edu.tw 專 長 : 數 值 模 擬 資 訊 平 台 整 合 應 用 GIS 應 用 經 歷 : 南 榮 技 術 學 院 主 任 秘 書 南 榮 技 術 學 院 工 程 科 技 學 群 學 群 長 南
%
 38 1 2014 1 Vol. 38No. 1 January 2014 51 Population Research 2010 2010 2010 65 100028 Changing Lineal Families with Three Generations An Analysis of the 2010 Census Data Wang Yuesheng Abstract In contemporary
38 1 2014 1 Vol. 38No. 1 January 2014 51 Population Research 2010 2010 2010 65 100028 Changing Lineal Families with Three Generations An Analysis of the 2010 Census Data Wang Yuesheng Abstract In contemporary
Microsoft Word - 072010-736-120048.doc
 中 国 科 学 : 地 球 科 学 2012 年 第 42 卷 第 4 期 : 520 ~ 525 www.scichina.com earth.scichina.com SCIENCE CHINA PRESS 论 文 地 球 磁 层 - 电 离 层 系 统 对 超 强 太 阳 风 暴 响 应 的 数 值 模 拟 研 究 王 赤 1* 12 1 12 1, 李 晖, 郭 孝 城, 丁 凯, 黄 朝
中 国 科 学 : 地 球 科 学 2012 年 第 42 卷 第 4 期 : 520 ~ 525 www.scichina.com earth.scichina.com SCIENCE CHINA PRESS 论 文 地 球 磁 层 - 电 离 层 系 统 对 超 强 太 阳 风 暴 响 应 的 数 值 模 拟 研 究 王 赤 1* 12 1 12 1, 李 晖, 郭 孝 城, 丁 凯, 黄 朝
Microsoft Word 張嘉玲-_76-83_
 64 4 Journal of Taiwan Agricultural Engineering 107 12 Vol. 64, No. 4, December 2018 DOI: 10.29974/JTAE.201812_64(4).0005 WASP - Applying the WASP Model to Evaluate the Effect of Wastewater Sewer Takeover
64 4 Journal of Taiwan Agricultural Engineering 107 12 Vol. 64, No. 4, December 2018 DOI: 10.29974/JTAE.201812_64(4).0005 WASP - Applying the WASP Model to Evaluate the Effect of Wastewater Sewer Takeover
216 40 卷 Vol. 40 predictors of Niño3 index and AEAT Index (AEATI). Rather than fixed models for every year, indices are classified into several types
 第 40 卷 第 1 期 2016 年 1 月 Vol. 40 No. 1 Jan. 2016 阮 成 卿, 李 建 平. 2016. 华 北 汛 期 降 水 分 离 时 间 尺 度 降 尺 度 预 测 模 型 的 改 进 [J]., 40 (1): 215 226. Ruan Chengqing, Li Jianping. 2016. An improvement in a time-scale
第 40 卷 第 1 期 2016 年 1 月 Vol. 40 No. 1 Jan. 2016 阮 成 卿, 李 建 平. 2016. 华 北 汛 期 降 水 分 离 时 间 尺 度 降 尺 度 预 测 模 型 的 改 进 [J]., 40 (1): 215 226. Ruan Chengqing, Li Jianping. 2016. An improvement in a time-scale
Corpus Word Parser 183
 95 182 2010 1946 5 15 1948 6 15 1949 3 15 8 1 2011 2012 11 8 2015 12 31 Corpus Word Parser 183 2017. 1 ROST Content Mining 2003 20 60 2003 184 2003 20 60 1999 2009 2003 Discourse Analysis 1952 Language
95 182 2010 1946 5 15 1948 6 15 1949 3 15 8 1 2011 2012 11 8 2015 12 31 Corpus Word Parser 183 2017. 1 ROST Content Mining 2003 20 60 2003 184 2003 20 60 1999 2009 2003 Discourse Analysis 1952 Language
Microsoft Word 聂雪梅.doc
 4 4 Vol. 4 No. 4 2013 8 Journal of Food Safety and Quality Aug., 2013 聂雪梅 *, 李立, 孙利, 高飞 (, 100123) 摘要 : 2011 12,, 2007~2011,,,, 关键词 : ; ; ; ; Trade and notification situation on food import and export
4 4 Vol. 4 No. 4 2013 8 Journal of Food Safety and Quality Aug., 2013 聂雪梅 *, 李立, 孙利, 高飞 (, 100123) 摘要 : 2011 12,, 2007~2011,,,, 关键词 : ; ; ; ; Trade and notification situation on food import and export
Microsoft Word - review-v3.doc
 1 1 Ø. 2 3 . 4 5 http://www.wmo.int/thorpex 6 NCEP operational S1 scores at 36 and 72 hr over North America (500 hpa) 75 e r o c s 1 S 65 55 45 36 hr forecast "useless forecast" 72 hr forecast 35 10-20
1 1 Ø. 2 3 . 4 5 http://www.wmo.int/thorpex 6 NCEP operational S1 scores at 36 and 72 hr over North America (500 hpa) 75 e r o c s 1 S 65 55 45 36 hr forecast "useless forecast" 72 hr forecast 35 10-20
km <.5 km.5 < 1. km 4 1 km ~ % 23.3 % 23.3 % 36.5 %.5 km 64.5 % 7 % /%
 17 2 218 6 JOURAL OF ATOG VOCATIOAL & TCHICAL HIPPIG COLLG Vol.17 o.2 Jun. 218 218 doi: 1.3969/j.issn.1671-9891.218.2.7 (, 2261) :, 1981 21, :, 16 17, (.5 km) 6 % ;, ;, : 9 %, ---, 4 m/s, 1 1.5~1 3. kpa,
17 2 218 6 JOURAL OF ATOG VOCATIOAL & TCHICAL HIPPIG COLLG Vol.17 o.2 Jun. 218 218 doi: 1.3969/j.issn.1671-9891.218.2.7 (, 2261) :, 1981 21, :, 16 17, (.5 km) 6 % ;, ;, : 9 %, ---, 4 m/s, 1 1.5~1 3. kpa,
气象 第 卷 第 期 对流不稳定度
 张芳华 张 涛 周庆亮 杨克明 国家气象中心 北京 中国气象科学研究院灾害天气重点实验室 利用上海自动观测站资料 的逐 小时分析资料 水汽云图和 多普勒雷达探测等资料 对 年 月 日上海飑线天气过程进行天气 动力学诊断分析 结果表明 上海处在上干冷 下暖湿的不稳定大气层结中 对流层上层干冷空气的侵入和边界层暖湿气流强烈辐合是飑线天气的触发机制 飑线以断 续线型与后续线型相结合的型式形成 在对流单体的右侧不断新生单体
张芳华 张 涛 周庆亮 杨克明 国家气象中心 北京 中国气象科学研究院灾害天气重点实验室 利用上海自动观测站资料 的逐 小时分析资料 水汽云图和 多普勒雷达探测等资料 对 年 月 日上海飑线天气过程进行天气 动力学诊断分析 结果表明 上海处在上干冷 下暖湿的不稳定大气层结中 对流层上层干冷空气的侵入和边界层暖湿气流强烈辐合是飑线天气的触发机制 飑线以断 续线型与后续线型相结合的型式形成 在对流单体的右侧不断新生单体
Microsoft Word - 赵巧莲.doc
 第 18 卷 第 2 期 2013 年 3 月 气 候 与 环 境 研 究 Climatic and Environmental Research Vol. 18, No. 2 Mar. 2013 赵 巧 莲, 李 崇 银, 李 琳. 2013. 东 亚 经 向 型 气 压 异 常 偶 极 模 与 冬 季 北 太 平 洋 关 键 区 域 海 温 的 关 系 及 其 数 值 模 拟 试 验 [J].
第 18 卷 第 2 期 2013 年 3 月 气 候 与 环 境 研 究 Climatic and Environmental Research Vol. 18, No. 2 Mar. 2013 赵 巧 莲, 李 崇 银, 李 琳. 2013. 东 亚 经 向 型 气 压 异 常 偶 极 模 与 冬 季 北 太 平 洋 关 键 区 域 海 温 的 关 系 及 其 数 值 模 拟 试 验 [J].
% GIS / / Fig. 1 Characteristics of flood disaster variation in suburbs of Shang
 20 6 2011 12 JOURNAL OF NATURAL DISASTERS Vol. 20 No. 6 Dec. 2011 1004-4574 2011 06-0094 - 05 200062 1949-1990 1949 1977 0. 8 0. 03345 0. 01243 30 100 P426. 616 A Risk analysis of flood disaster in Shanghai
20 6 2011 12 JOURNAL OF NATURAL DISASTERS Vol. 20 No. 6 Dec. 2011 1004-4574 2011 06-0094 - 05 200062 1949-1990 1949 1977 0. 8 0. 03345 0. 01243 30 100 P426. 616 A Risk analysis of flood disaster in Shanghai
CMIP5 MIROC RCP m RCP 0.2m RCP km
 1 1 2 1 1 980-8579 6-6 2 980-8579 6-6 E-mail: udo@irides.tohoku.ac.jp CMIP5MIROC520312050 2081210020 RCP8.50.3mRCP 0.2mRCP8.580180km 2 60130km 2 RCP Key Words : MIROC5, Bruun rule, beach erosion, sea level
1 1 2 1 1 980-8579 6-6 2 980-8579 6-6 E-mail: udo@irides.tohoku.ac.jp CMIP5MIROC520312050 2081210020 RCP8.50.3mRCP 0.2mRCP8.580180km 2 60130km 2 RCP Key Words : MIROC5, Bruun rule, beach erosion, sea level
1.0 % 0.25 % 85μm % U416 Sulfate expansion deformation law and mechanism of cement stabilized macadam base of saline areas in Xinjiang Song
 1.0 % 0.25 % 85μm 0.97 0.136 % U416 Sulfate expansion deformation law and mechanism of cement stabilized macadam base of saline areas in Xinjiang Song Liang 1,2 Wang Xuan-cang 1 1 School of Highway, Chang
1.0 % 0.25 % 85μm 0.97 0.136 % U416 Sulfate expansion deformation law and mechanism of cement stabilized macadam base of saline areas in Xinjiang Song Liang 1,2 Wang Xuan-cang 1 1 School of Highway, Chang
[6 ] (20 35 N, E, ( N, E, (25 35 N, [7 ], E 60 %,, : ;,,,, 3, ISCCP W/ m 2 [8 ] Bergman [9 ], 5 15 W/ m 2, 1 5 W/
![[6 ] (20 35 N, E, ( N, E, (25 35 N, [7 ], E 60 %,, : ;,,,, 3, ISCCP W/ m 2 [8 ] Bergman [9 ], 5 15 W/ m 2, 1 5 W/ [6 ] (20 35 N, E, ( N, E, (25 35 N, [7 ], E 60 %,, : ;,,,, 3, ISCCP W/ m 2 [8 ] Bergman [9 ], 5 15 W/ m 2, 1 5 W/](/thumbs/91/104866920.jpg) 61 6 2003 12 ACTA METEOROLO GICA SIN ICA Vol. 61,No. 6 December 2003 Ξ (,LASG,100029 ;,211101 (,LASG,100029 ;,430074 (,LASG,100029 (20 35 N,103 120 E : 1 ISCCP ( International Satellite Cloud Climatology
61 6 2003 12 ACTA METEOROLO GICA SIN ICA Vol. 61,No. 6 December 2003 Ξ (,LASG,100029 ;,211101 (,LASG,100029 ;,430074 (,LASG,100029 (20 35 N,103 120 E : 1 ISCCP ( International Satellite Cloud Climatology
 0 6 Jun. 0 China's Borderland History and Geography Studies Vol. No. * 方铁黄禾雨 99 985 65009 ** 0 &ZD5 00 00 006 00 00 0 9 0 0 009 9 9 80 0 69 5 6 7 8 5 6 8 86 58 86 8 008 9 7 9 5 07 50 5 6769 00 60 5 7 96
0 6 Jun. 0 China's Borderland History and Geography Studies Vol. No. * 方铁黄禾雨 99 985 65009 ** 0 &ZD5 00 00 006 00 00 0 9 0 0 009 9 9 80 0 69 5 6 7 8 5 6 8 86 58 86 8 008 9 7 9 5 07 50 5 6769 00 60 5 7 96
标题
 2016 年 第 3 期 ( 总 第 216 期 ) 人 口 与 经 济 POPULATION & ECONOMICS No. 3, 2016 ( Tot. No. 216) 同 胞 数 量 与 教 育 获 得 的 性 别 差 异 黎 煦, 刘 华 ( 首 都 经 济 贸 易 大 学 劳 动 经 济 学 院, 北 京 100070) 摘 要 : 同 胞 数 量 对 教 育 获 得 的 影 响 存 在
2016 年 第 3 期 ( 总 第 216 期 ) 人 口 与 经 济 POPULATION & ECONOMICS No. 3, 2016 ( Tot. No. 216) 同 胞 数 量 与 教 育 获 得 的 性 别 差 异 黎 煦, 刘 华 ( 首 都 经 济 贸 易 大 学 劳 动 经 济 学 院, 北 京 100070) 摘 要 : 同 胞 数 量 对 教 育 获 得 的 影 响 存 在
untitled
 19932005 1 1993-2005 The Urban Residential Housing System in Shanghai 1993-2005: the Marketization Process and Housing Affordability Jie Chen, Assistant Professor, Management School of Fudan University,
19932005 1 1993-2005 The Urban Residential Housing System in Shanghai 1993-2005: the Marketization Process and Housing Affordability Jie Chen, Assistant Professor, Management School of Fudan University,
Microsoft Word - 34 罗晓凡.doc
 43 3 Vol.43, No.3 2012 5 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA May, 2012 * ( 300457) 6, 3 4 5 1 9 30 : (1), POM ; (2) POM,,, / ; /,, ; (3) 9,,, /,,, P731,, (, 2000),, (, 1989;, 2004;, 2006) ( 筰, 1992) (2001),,
43 3 Vol.43, No.3 2012 5 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA May, 2012 * ( 300457) 6, 3 4 5 1 9 30 : (1), POM ; (2) POM,,, / ; /,, ; (3) 9,,, /,,, P731,, (, 2000),, (, 1989;, 2004;, 2006) ( 筰, 1992) (2001),,
06王胜
 第 31 卷 第 1 期 2012 年 01 月 地 理 科 学 进 展 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.31, No.1 Jan., 2012 近 50 年 安 徽 省 气 候 舒 适 度 变 化 特 征 及 区 划 研 究 王 胜, 田 红, 谢 五 三, 唐 为 安, 丁 霞 ( 安 徽 省 气 候 中 心, 合 肥 230031) 1 引 言 摘 要 : 利 用 安 徽
第 31 卷 第 1 期 2012 年 01 月 地 理 科 学 进 展 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.31, No.1 Jan., 2012 近 50 年 安 徽 省 气 候 舒 适 度 变 化 特 征 及 区 划 研 究 王 胜, 田 红, 谢 五 三, 唐 为 安, 丁 霞 ( 安 徽 省 气 候 中 心, 合 肥 230031) 1 引 言 摘 要 : 利 用 安 徽
2 ( 自 然 科 学 版 ) 第 20 卷 波 ). 这 种 压 缩 波 空 气 必 然 有 一 部 分 要 绕 流 到 车 身 两 端 的 环 状 空 间 中, 形 成 与 列 车 运 行 方 向 相 反 的 空 气 流 动. 在 列 车 尾 部, 会 产 生 低 于 大 气 压 的 空 气 流
 第 20 卷 第 3 期 2014 年 6 月 ( 自 然 科 学 版 ) JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY (NATURAL SCIENCE) Vol. 20 No. 3 June 2014 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2861.2013.07.031 基 于 FLUENT 测 轨 道 交 通 隧 道 中 电 波 折 射 率 结 构 常 数 张 永
第 20 卷 第 3 期 2014 年 6 月 ( 自 然 科 学 版 ) JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY (NATURAL SCIENCE) Vol. 20 No. 3 June 2014 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2861.2013.07.031 基 于 FLUENT 测 轨 道 交 通 隧 道 中 电 波 折 射 率 结 构 常 数 张 永
國立高雄大學○○○○○○學系(研究所)(標楷體18號字
 國 立 高 雄 大 學 都 市 發 展 與 建 築 研 究 所 碩 士 論 文 高 雄 後 勁 地 區 傳 統 民 居 特 徵 之 研 究 The Study of The Characteristic of Traditional Residential Buildings of Houjing District in Kaohsiung 研 究 生 : 許 輝 隆 撰 指 導 教 授 : 陳 啟
國 立 高 雄 大 學 都 市 發 展 與 建 築 研 究 所 碩 士 論 文 高 雄 後 勁 地 區 傳 統 民 居 特 徵 之 研 究 The Study of The Characteristic of Traditional Residential Buildings of Houjing District in Kaohsiung 研 究 生 : 許 輝 隆 撰 指 導 教 授 : 陳 啟
[12 ( ), ],, [13 ] [14, ], ;,, 1 6 [15 ], ( ) [1618 ], Blackmon [16,19 ],,, [20, ],, ;,,, ( ), [8,9 ], Mak [21 ] [22,23 ],? ( )?, Orlanski [24
![[12 ( ), ],, [13 ] [14, ], ;,, 1 6 [15 ], ( ) [1618 ], Blackmon [16,19 ],,, [20, ],, ;,,, ( ), [8,9 ], Mak [21 ] [22,23 ],? ( )?, Orlanski [24 [12 ( ), ],, [13 ] [14, ], ;,, 1 6 [15 ], ( ) [1618 ], Blackmon [16,19 ],,, [20, ],, ;,,, ( ), [8,9 ], Mak [21 ] [22,23 ],? ( )?, Orlanski [24](/thumbs/92/109994115.jpg) 28 6 2004 11 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol128 No16 Nov1 2004 3 1) 2) 1) 1) (, 266003) 2) (, 100029),,,,,,, :,, :, ;,, : ; ; ; ; 100629895 (2004) 0620901224 P433 A 1 :, [1,, ], [26 ] [7,8,?
28 6 2004 11 Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Vol128 No16 Nov1 2004 3 1) 2) 1) 1) (, 266003) 2) (, 100029),,,,,,, :,, :, ;,, : ; ; ; ; 100629895 (2004) 0620901224 P433 A 1 :, [1,, ], [26 ] [7,8,?
http / /yxxy. cbpt. cnki. net / % % %
 2017 3 Mar. 2017 5 2 Chongqing Higher Education Research Vol. 5 No. 2 DOI 10. 15998 /j. cnki. issn1673-8012. 2017. 02. 006 230039 2011 2015 2016 G649. 21 A 1673-8012 2017 02-0037-11 2017-01-03 2015zdjy024
2017 3 Mar. 2017 5 2 Chongqing Higher Education Research Vol. 5 No. 2 DOI 10. 15998 /j. cnki. issn1673-8012. 2017. 02. 006 230039 2011 2015 2016 G649. 21 A 1673-8012 2017 02-0037-11 2017-01-03 2015zdjy024
Microsoft Word - 廖镜彪284—new
 28 4 Vol.28 No.4 2012 8 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Aug. 2012. WRF [J]. 2012 28(4): 461-470. :1004-4965(2012)04-0461-10 1, 2 1 1 2 1 (1. 510275 2. 210093) ( ) WRF 3 km WSM6 KF BMJ GD G3 2010 5 14 KF
28 4 Vol.28 No.4 2012 8 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY Aug. 2012. WRF [J]. 2012 28(4): 461-470. :1004-4965(2012)04-0461-10 1, 2 1 1 2 1 (1. 510275 2. 210093) ( ) WRF 3 km WSM6 KF BMJ GD G3 2010 5 14 KF
畜牧 动物医学 蚕 蜂
 中国农学通报 2015,31(20):181-185 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 老河口市砂梨花期的物候特点分析 邓 环 1 马德栗 1 徐洪海 2 洪国平 1 2 武汉区域气候中心 武汉 430074 老河口气象局 湖北老河口 441800 1 摘 要 为掌握湖北省老河口市砂梨花期的物候规律 利用老河口市 20 年的砂梨裂蕾期 初花期 和盛花期 4
中国农学通报 2015,31(20):181-185 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 老河口市砂梨花期的物候特点分析 邓 环 1 马德栗 1 徐洪海 2 洪国平 1 2 武汉区域气候中心 武汉 430074 老河口气象局 湖北老河口 441800 1 摘 要 为掌握湖北省老河口市砂梨花期的物候规律 利用老河口市 20 年的砂梨裂蕾期 初花期 和盛花期 4
~ 05 55% / 4 04 IMF Regional Economic Outlook: Middle East and Central Asia January 05 p.. BP
 05 Nov. 05 6 Arab World Studies No. 6 04 04 0 05 05 ~ 06 00007 67-56 05 06-0045 - D85 A 04 05 05 7 http / /forex. hexun. com / 05-0 - 7 /744678. html 45 05 6 04 0 04 0 04 6 04 9 ~ 05 55% 04 05 0 04 60
05 Nov. 05 6 Arab World Studies No. 6 04 04 0 05 05 ~ 06 00007 67-56 05 06-0045 - D85 A 04 05 05 7 http / /forex. hexun. com / 05-0 - 7 /744678. html 45 05 6 04 0 04 0 04 6 04 9 ~ 05 55% 04 05 0 04 60
z
 * 光 与 电 子 的 电 磁 感 应 相 互 作 用 张 涛 http://www.paper.edu.cn 北 京 师 范 大 学 核 科 学 与 技 术 学 院 ( 低 能 核 物 理 研 究 所 ) 北 京 市 辐 射 中 心, 北 京,(100875) taozhang@bnu.edu.cn 摘 要 本 文 论 述 了 光 与 电 子 的 电 磁 感 应 相 互 作 用 和 电 子 云 导
* 光 与 电 子 的 电 磁 感 应 相 互 作 用 张 涛 http://www.paper.edu.cn 北 京 师 范 大 学 核 科 学 与 技 术 学 院 ( 低 能 核 物 理 研 究 所 ) 北 京 市 辐 射 中 心, 北 京,(100875) taozhang@bnu.edu.cn 摘 要 本 文 论 述 了 光 与 电 子 的 电 磁 感 应 相 互 作 用 和 电 子 云 导
Dan Buettner / /
 39 1 2015 1 Vol. 39 No. 1 January 2015 74 Population Research 80 + /60 + 90 + 90 + 0 80 100028 Measuring and Comparing Population Longevity Level across the Regions of the World Lin Bao Abstract Appropriate
39 1 2015 1 Vol. 39 No. 1 January 2015 74 Population Research 80 + /60 + 90 + 90 + 0 80 100028 Measuring and Comparing Population Longevity Level across the Regions of the World Lin Bao Abstract Appropriate
: 307, [], [2],,,, [3] (Response Surface Methodology, RSA),,, [4,5] Design-Expert 6.0,,,, [6] VPJ33 ph 3,, ph, OD, Design-Expert 6.0 Box-Behnken, VPJ3
![: 307, [], [2],,,, [3] (Response Surface Methodology, RSA),,, [4,5] Design-Expert 6.0,,,, [6] VPJ33 ph 3,, ph, OD, Design-Expert 6.0 Box-Behnken, VPJ3 : 307, [], [2],,,, [3] (Response Surface Methodology, RSA),,, [4,5] Design-Expert 6.0,,,, [6] VPJ33 ph 3,, ph, OD, Design-Expert 6.0 Box-Behnken, VPJ3](/thumbs/42/23094730.jpg) 微 生 物 学 通 报 FEB 20, 2008, 35(2) 306~30 Microbiology 2008 by Institute of Microbiology, CAS tongbao@im.ac.cn 生 物 实 验 室 响 应 面 分 析 法 优 化 副 溶 血 性 弧 菌 生 长 条 件 刘 代 新 宁 喜 斌 * 张 继 伦 2 (. 200090) (2. 20202) 摘 要
微 生 物 学 通 报 FEB 20, 2008, 35(2) 306~30 Microbiology 2008 by Institute of Microbiology, CAS tongbao@im.ac.cn 生 物 实 验 室 响 应 面 分 析 法 优 化 副 溶 血 性 弧 菌 生 长 条 件 刘 代 新 宁 喜 斌 * 张 继 伦 2 (. 200090) (2. 20202) 摘 要
地質調査研究報告/Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Japan
 Shigeru Suto, Takayuki Inomata, Hisashi Sasaki and Sakae Mukoyama (2007) Data base of the volcanic ash fall distribution map of Japan. Bull. Geol. Surv. Japan, vol. 58(9/10), p.261-321, 8 figs, 2 tables,
Shigeru Suto, Takayuki Inomata, Hisashi Sasaki and Sakae Mukoyama (2007) Data base of the volcanic ash fall distribution map of Japan. Bull. Geol. Surv. Japan, vol. 58(9/10), p.261-321, 8 figs, 2 tables,
PowerPoint Presentation
 北极海冰快速减少 对北半球冬季气候的影响 黄建斌 jbh@tsinghua.edu.cn 地球系统科学研究中心 / 全球变化研究院 2013 年 4 月 29 日 CONTENTS 北极海冰 研究北极海冰的重要性 北极放大效应 北极海冰快速减少对气候的影响 未来北极海冰的变化 小结 一 北极海冰 与南极海冰不同, 北极海冰四周由陆地环绕, 与北大西洋和北太平洋相连 ; 北极海冰占海洋面积的 1.7-3.9%;
北极海冰快速减少 对北半球冬季气候的影响 黄建斌 jbh@tsinghua.edu.cn 地球系统科学研究中心 / 全球变化研究院 2013 年 4 月 29 日 CONTENTS 北极海冰 研究北极海冰的重要性 北极放大效应 北极海冰快速减少对气候的影响 未来北极海冰的变化 小结 一 北极海冰 与南极海冰不同, 北极海冰四周由陆地环绕, 与北大西洋和北太平洋相连 ; 北极海冰占海洋面积的 1.7-3.9%;
CONTENTS 目 录 大 事 要 闻 2 两 学 一 做 5 科 研 动 态 8 交 流 合 作 14 队 伍 建 设 17 人 才 培 养 19 运 行 管 理 21
 2016 ISSUE 01 1-5 月 SKLEC BULLETIN 河 口 海 岸 学 国 家 重 点 实 验 室 ( 华 东 师 范 大 学 ) State Key Laboratory of Estuarine and Coastal Research (East China Normal University) CONTENTS 目 录 大 事 要 闻 2 两 学 一 做 5 科 研 动 态
2016 ISSUE 01 1-5 月 SKLEC BULLETIN 河 口 海 岸 学 国 家 重 点 实 验 室 ( 华 东 师 范 大 学 ) State Key Laboratory of Estuarine and Coastal Research (East China Normal University) CONTENTS 目 录 大 事 要 闻 2 两 学 一 做 5 科 研 动 态
Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 28 No. 4 Dec a
 28 4 2010 12 1006-7639 2010-04 - 0411-07 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 28 No. 4 Dec 2010 50 a 1 2 3 4 1 1. 737200 2. 733300 3. 737100 4. 733000 1959 ~ 2009 Mann - Kendall T - Yamamoto 1990 1996 50 a
28 4 2010 12 1006-7639 2010-04 - 0411-07 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 28 No. 4 Dec 2010 50 a 1 2 3 4 1 1. 737200 2. 733300 3. 737100 4. 733000 1959 ~ 2009 Mann - Kendall T - Yamamoto 1990 1996 50 a
度 ) 圖 1 是 康 芮 颱 風 路 徑 圖, 警 報 資 料 發 布 詳 見 表 1 康 芮 颱 風 形 成 後, 沿 著 副 熱 帶 高 壓 的 南 緣 往 北 北 西 方 向 移 動, 強 度 始 終 維 持 在 颱 風, 暴 風 半 徑 有 120 公 里, 朝 著 臺 灣 東 部 面 靠
 民 國 102 年 颱 風 調 查 報 告 - 第 15 號 康 芮 (Kong-Rey) 颱 風 (1315) 林 秉 煜 中 央 氣 象 局 氣 象 預 報 中 心 摘 要 康 芮 (Kong-Rey) 颱 風 是 民 國 102 年 在 西 北 太 平 洋 域 發 生 的 第 15 颱 風, 也 是 該 年 中 央 氣 象 局 發 布 警 報 的 第 4 個 颱 風 8 月 26 日 在 菲
民 國 102 年 颱 風 調 查 報 告 - 第 15 號 康 芮 (Kong-Rey) 颱 風 (1315) 林 秉 煜 中 央 氣 象 局 氣 象 預 報 中 心 摘 要 康 芮 (Kong-Rey) 颱 風 是 民 國 102 年 在 西 北 太 平 洋 域 發 生 的 第 15 颱 風, 也 是 該 年 中 央 氣 象 局 發 布 警 報 的 第 4 個 颱 風 8 月 26 日 在 菲
 苏 洁 吴辉碇 刘钦政 张蕴斐 白 珊 在国内外冰 海洋耦合模式研究基础上 根据渤海水文 气象和冰情特点 以国家海洋环境 预报中心的渤海海冰预报模式和 海洋模式为基础 开发了一个冰 海洋耦合模式 在该耦合 模式中 冰和海洋之间的动量和热量交换是双向的 冰厚和冰密集度的变化不仅由冰表面和冰底的热收支决定 还由开阔水的表面热收支决定 侧重阐述了耦合模式的动力和热力学过程的耦合 并 对模式中一些热力参数进行了讨论
苏 洁 吴辉碇 刘钦政 张蕴斐 白 珊 在国内外冰 海洋耦合模式研究基础上 根据渤海水文 气象和冰情特点 以国家海洋环境 预报中心的渤海海冰预报模式和 海洋模式为基础 开发了一个冰 海洋耦合模式 在该耦合 模式中 冰和海洋之间的动量和热量交换是双向的 冰厚和冰密集度的变化不仅由冰表面和冰底的热收支决定 还由开阔水的表面热收支决定 侧重阐述了耦合模式的动力和热力学过程的耦合 并 对模式中一些热力参数进行了讨论
标题
 648 江 苏 农 业 学 报 (Jiangsu J. of Agr. Sci. ),2013,29(3):648 ~ 653 h ttp: / / w w w. jsn y x b.c o m 王 摇 丹, 孙 摇 蕾, 孙 家 正, 等. 桑 葚 冻 结 过 程 中 的 温 度 变 化 特 性 [J]. 江 苏 农 业 学 报,2013,29(3):648 鄄 653. doi:10. 3969
648 江 苏 农 业 学 报 (Jiangsu J. of Agr. Sci. ),2013,29(3):648 ~ 653 h ttp: / / w w w. jsn y x b.c o m 王 摇 丹, 孙 摇 蕾, 孙 家 正, 等. 桑 葚 冻 结 过 程 中 的 温 度 变 化 特 性 [J]. 江 苏 农 业 学 报,2013,29(3):648 鄄 653. doi:10. 3969
5-25袁宏钧.indd
 第 24 卷 第 5 期 2015 年 5 月 碘 131 doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2015, 24(5):643 647. Chinese Journal of
第 24 卷 第 5 期 2015 年 5 月 碘 131 doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2015, 24(5):643 647. Chinese Journal of
0 000 00 70 7 80 000 % 90 00 7 80 0 7 000 000 7 9 0 0 7 7 8 Gorgoroon 000 8 8 7 8 9 99 7 7 008 9 E. H. Blair and J. A. Robertson The Philippine Island
 0 7 Journal of Peking University Philosophy and Social Sciences Vol. No. Jul. 0 郭 卫 东 0087 K 0 A 000-99 0 0-0- 8 8 7 79 8 00 00 0 9 00 00 000 00 000 00 000 0 9 00 97 7 00 Nassau 7 000 0 08 000 00 Trumball
0 7 Journal of Peking University Philosophy and Social Sciences Vol. No. Jul. 0 郭 卫 东 0087 K 0 A 000-99 0 0-0- 8 8 7 79 8 00 00 0 9 00 00 000 00 000 00 000 0 9 00 97 7 00 Nassau 7 000 0 08 000 00 Trumball
Microsoft Word - 3——郑运霞_news_.doc
 46 6 Vol.46, No.6 2015 11 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Nov., 2015 1013 * ( 200030), 100m 2010 13 :,,, 16% :,, 258m 35m, 123s 13s, 1 3 ; ; ; ; P444 doi: 10.11693/hyhz20150700186, (, 2005; Kepert, 2010;
46 6 Vol.46, No.6 2015 11 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Nov., 2015 1013 * ( 200030), 100m 2010 13 :,,, 16% :,, 258m 35m, 123s 13s, 1 3 ; ; ; ; P444 doi: 10.11693/hyhz20150700186, (, 2005; Kepert, 2010;
标题
 澳 门 博 彩 业 近 年 发 展 及 研 究 综 述 刘 爽 摘 要 : 博 彩 业 是 澳 门 的 支 柱 产 业, 其 持 续 发 展 很 大 程 度 上 关 系 到 澳 门 特 区 的 经 济 繁 荣 与 社 会 稳 定 本 文 从 博 彩 产 业 研 究 博 彩 机 产 业 研 究 问 题 赌 博 与 负 责 任 博 彩 投 注 者 行 为 研 究 博 彩 业 员 工 与 人 力 资 源
澳 门 博 彩 业 近 年 发 展 及 研 究 综 述 刘 爽 摘 要 : 博 彩 业 是 澳 门 的 支 柱 产 业, 其 持 续 发 展 很 大 程 度 上 关 系 到 澳 门 特 区 的 经 济 繁 荣 与 社 会 稳 定 本 文 从 博 彩 产 业 研 究 博 彩 机 产 业 研 究 问 题 赌 博 与 负 责 任 博 彩 投 注 者 行 为 研 究 博 彩 业 员 工 与 人 力 资 源
984 (Chinese J Geophys ) 49 tropical regions leading to the formation of the Asian summer monsoon over India the BOB and the SCS The extension of the
 49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol 49 No 4 Jul 2006 2006 49 (4) :983 992 Liang X Y Liu Y M Wu G X Roles of tropical and subtropical land- sea distribution and the Qinghai- Xizang Plateau in
49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol 49 No 4 Jul 2006 2006 49 (4) :983 992 Liang X Y Liu Y M Wu G X Roles of tropical and subtropical land- sea distribution and the Qinghai- Xizang Plateau in
14 17.,., Fig. 1 Bougeur gravity map of research region 2 Fig. 2 Magnetic map of research region
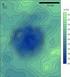 1 7 1 Vol. 17 No. 1 2002 3 (13 23) PROGRESS IN GEOPHYSICS March 2002 (,,100101) [ ],, 39.,,. [ ] ; ; [] P738 [] A [ ]100422903 (2002) 0120013211 0,,.,,, NE [1 ],.., ( NE, EW,NE ),.,.,,. 1 20 20 km ( 10
1 7 1 Vol. 17 No. 1 2002 3 (13 23) PROGRESS IN GEOPHYSICS March 2002 (,,100101) [ ],, 39.,,. [ ] ; ; [] P738 [] A [ ]100422903 (2002) 0120013211 0,,.,,, NE [1 ],.., ( NE, EW,NE ),.,.,,. 1 20 20 km ( 10
200 31 5 SWAN 0. 01 0. 01 6 min TITAN Thunder Identification Tracking Analysis SWAN TITAN and Nowcasting 19 TREC Tracking Radar Echo by Correlaction T
 31 1 2013 3 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 31 No. 1 March 2013. SWAN J. 2013 31 1 199-205. doi 10. 11755 /j. issn. 1006-7639 2013-01 - 0199 SWAN 730020 2011 7 7 SWAN SWAN 2012 2 SWAN 1006-7639 2013-01
31 1 2013 3 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 31 No. 1 March 2013. SWAN J. 2013 31 1 199-205. doi 10. 11755 /j. issn. 1006-7639 2013-01 - 0199 SWAN 730020 2011 7 7 SWAN SWAN 2012 2 SWAN 1006-7639 2013-01
a b
 38 3 2014 5 Vol. 38 No. 3 May 2014 55 Population Research + + 3 100038 A Study on Implementation of Residence Permit System Based on Three Local Cases of Shanghai Chengdu and Zhengzhou Wang Yang Abstract
38 3 2014 5 Vol. 38 No. 3 May 2014 55 Population Research + + 3 100038 A Study on Implementation of Residence Permit System Based on Three Local Cases of Shanghai Chengdu and Zhengzhou Wang Yang Abstract
~ 4 mm h 8 60 min 1 10 min N min 8. 7% min 2 9 Tab. 1 1 Test result of modified
 30 1 2013 1 Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development Vol. 30 No. 1 Jan. 2013 doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1002-0268. 2013. 01. 004 1 2 2 2 2 1. 400074 2. 400067 240 U416. 217 A 1002-0268
30 1 2013 1 Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development Vol. 30 No. 1 Jan. 2013 doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1002-0268. 2013. 01. 004 1 2 2 2 2 1. 400074 2. 400067 240 U416. 217 A 1002-0268
Jul Journal of Chinese Women's Studies No. 4 Ser. No. 148 * CFPS 2010 C A Where does the Ti
 2018 7 Jul. 2018 4 148 Journal of Chinese Women's Studies No. 4 Ser. No. 148 * 210023 CFPS 2010 C913. 68 A 1004-2563 2018 04-0019-14 Where does the Time Go Gender Differences in Time Use over the Life
2018 7 Jul. 2018 4 148 Journal of Chinese Women's Studies No. 4 Ser. No. 148 * 210023 CFPS 2010 C913. 68 A 1004-2563 2018 04-0019-14 Where does the Time Go Gender Differences in Time Use over the Life
~ ~ ~
 36 4 2015 385 ~ 397 The Chinese Journal for the History of Science and Technology Vol. 36 No. 4 2015 1951 ~ 1956 100049 100190 1951 ~ 1966 1951 ~ 1956 N092 P62-092 A 1673-1441 2015 04-0385-13 1951 ~ 1966
36 4 2015 385 ~ 397 The Chinese Journal for the History of Science and Technology Vol. 36 No. 4 2015 1951 ~ 1956 100049 100190 1951 ~ 1966 1951 ~ 1956 N092 P62-092 A 1673-1441 2015 04-0385-13 1951 ~ 1966
three regions or three strata 3 Seneca 4 ~ 65 Quaestiones naturales 4 Themon 1349 ~ 1361 Questions on the Four Books of Aristotle's Meteorolo
 33 3 2014 259 271 Studies in the History of Natural Sciences Vol. 33 No. 3 2014 100190 N092 P1-092 A 1000-1224 2014 03-0259-13 exhalation vapour smoke 1 2 2014-02-18 2014-09-21 1977 260 33 1 three regions
33 3 2014 259 271 Studies in the History of Natural Sciences Vol. 33 No. 3 2014 100190 N092 P1-092 A 1000-1224 2014 03-0259-13 exhalation vapour smoke 1 2 2014-02-18 2014-09-21 1977 260 33 1 three regions

