Microsoft Word docx
|
|
|
- 棓 仰
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /, Vol. 7, No. 10 Reduced RKIP enhances nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT activity Li Yuan 1,2, Hong-Mei Yi 1,2, Hong Yi 1,2, Jia-Quan Qu 1,2, Jin-Feng Zhu 1,2, Li-Na Li 1,2, Ta Xiao 1,2, Zhen Zheng 1,2, Shan-Shan Lu 1,2, Zhi-Qiang Xiao 1,2 1 Research Center of Carcinogenesis and Targeted Therapy, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan , China 2 The Higher Educational Key Laboratory for Cancer Proteomics and Translational Medicine of Hunan Province, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan , China Correspondence to: Zhi-Qiang Xiao, zqxiao2001@hotmail.com Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, radioresistance, RKIP, ERK 1/2, AKT Received: October 06, 2015 Accepted: January 15, 2016 Published: February 05, 2016 ABSTRACT Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) functions as a chemo-immunotherapeutic sensitizer of cancers, but regulation of RKIP on tumor radiosensitivity remains largely unexplored. In this study, we investigate the role and mechanism of RKIP in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) radioresistance. The results showed that RKIP was frequently downregulated in the radioresistant NPC tissues compared with radiosensitive NPC tissues, and its reduction correlated with NPC radioresistance and poor patient survival, and was an independent prognostic factor. In vitro radioresponse assay showed that RKIP overexpression decreased while RKIP knockdown increased NPC cell radioresistance. In the NPC xenografts, RKIP overexpression decreased while RKIP knockdown increased tumor radioresistance. Mechanistically, RKIP reduction promoted NPC cell radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT activity, and AKT may be a downstream transducer of ERK signaling. Moreover, the levels of phospho-erk 1/2 and phospho-akt were increased in the radioresistant NPC tissues compared with radiosensitive ones, and negatively associated with RKIP expression, indicating that RKIP-regulated NPC radioresponse is mediated by ERK and AKT signaling in the clinical samples. Our data demonstrate that RKIP is a critical determinant of NPC radioresponse, and its reduction enhances NPC radioresistance through increasing ERK and AKT signaling activity, highlighting the therapeutic potential of RKIP-ERK-AKT signaling axis in NPC radiosensitization. INTRODUCTION Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is prominent in a number of Southeast Asian regions, and poses a very serious health problem in these areas [1]. Radiotherapy is a preferred and widely used modality for treatment of NPC, and most NPC patients can be cured if the disease is diagnosed and treated at an early stage. However, about 30% of NPC patients develop local recurrence and distant metastasis after radiotherapy duo to radioresistance, which is a major cause of treatment failure in many cases [2, 3]. Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) is a small evolutionary conserved protein that was first identified as a physiological inhibitor of Raf kinase, antagonizing Raf-1/MEK/ERK pathway [4]. Actually, RKIP has been implicated in multiple intracellular signaling pathways [5 8] that regulate various biological processes [9]. RKIP is well known for its metastasis suppression function [10], being its loss or reduced expression associated with metastasis and prognosis in many types of cancers [11 15]. Studies have showed that reduced RKIP correlates with the chemoresistance of cervical cancer [16], lung adenocarcinoma [17], gastric cancer [18] and prostate and breast cancer [19], and upregulation of RKIP expression increases the sensitivity of cancer cells to chemotherapy [16 20]. Moreover, RKIP expression level also correlates with immunotherapeutic response, and induction of RKIP expression results in the sensitization of resistant cancer cells to immunotherapy [20 23]. However, the role of RKIP in tumor radioresistance was rarely reported 11463
2 [24, 25]. In our previous comparative proteomic study, RKIP was identified as one of reduced proteins in the NPC tissues as compared to normal nasopharyngeal mucosal tissues [26]. Recently, we demonstrated that RKIP is a potential metastatic suppressor of NPC [27]. However, the role and signaling mechanism of RKIP in NPC radioresistance remain unclear. Ionizing radiation not only causes DNA doublestrand breaks (DSBs) of cancer cells, inducing cell apoptosis, but also generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to activation of multiple prosurvival and anti-apoptotic signaling pathways, such as MEK-ERK and PI3K-AKT pathways, which play a role in the cell survival from toxic stresses and the regulation of cell growth [28, 29]. As RKIP is an endogenous inhibitor of Raf-MEK-ERK pathway [4], RKIP downregulation will result in imbalance between activation and inhibition of MEK-ERK in the irradiated cells. The previous study also suggested that ROS stimulates cell proliferation in the palmitic acid-treated hepatocytes by activating ERK-AKT signaling pathway, in which AKT is a downstream transducer of ERK signaling [30]. Based on these reasons, we hypothesize that RKIP reduction increases NPC radioresistance by decreasing its inhibition on ERK and AKT signaling. In this study, we first detected RKIP expression in the radiosensitive and radioresistant NPC tissues, and evaluated its correlation with the radioresistance and clinical outcomes of NPC patients. Secondly, with a combination of loss-of-function and gain-of-function approaches, we analyzed the function of RKIP in NPC radioresponse, and assessed if reduced RKIP confers NPC cells radioresistance in vitro and in vivo. Finally, we determined whether RKIP-regulated NPC cell radioresponse is mediated through ERK and AKT signaling. Here, we report that RKIP reduction is associated with NPC radioresistance and poor patient prognosis, and reduced RKIP promotes NPC radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT signaling activity. RESULTS RKIP reduction is associated with NPC radioresistance and poor patient prognosis Immunohistochemistry was performed in a cohort of NPC tissues including 74 radioresistant and 75 radiosensitive NPCs and 30 normal nasopharyngeal mucosal (NNM) tissues. We observed that RKIP expression was dramatically reduced in the NPCs relative to NNM, and in the radioresistant NPCs relative to radiosensitive NPCs (Figure 1A, Table 1). The relationships between RKIP expression and clinicopathologic variables are summarized in Table 2. As shown in this table, the expression levels of RKIP were negatively correlated with NPC radioresistance (r = 0.489, P < 0.001), and tumors with low RKIP expression were frequently radioresistant. Moreover, the expression levels of RKIP were correlated with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. Since radioresistance is a major cause that leads to the poor outcomes of NPC patients, we analyzed the ability of RKIP to predict disease free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) of the patients. Survival analysis revealed that low RKIP level in NPCs correlated with the markedly reduced DFS and OS of the patients (Figure 1B). A univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis showed that RKIP expression level and clinical TNM stage significantly affected the DFS and OS of NPC patients (Table 3). A multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis confirmed that low RKIP expression was an independent predictor for the reduced DFS and OS of NPC patients (Table 3). These results indicate the importance of RKIP expression level in the clinical NPC radioresistance. RKIP reduction increases NPC cell radioresistance in vitro To determine the effect of RKIP on NPC cell radioresistance in vitro, we established CNE2-IR cell lines with stable RKIP overexpression, CNE2 cell lines with stable RKIP knockdown and their corresponding control cell lines (Figure 2A), and then cell radiosensitivity was determined. A clonogenic survival assay showed that RKIP overexpression decreased CNE2-IR cell radioresistance [AUC 1.33 (RKIP OE) vs (empty vector); P < 0.05; RPF = 0.71], whereas RKIP knockdown increased CNE2 cell radioresistance [AUC 1.35 (PKIP KD) vs (empty vector); P < 0.05; RPF = 1.35] (Figure 2B). Furthermore, the effect of RKIP on the cell proliferation in response to irradiation was examined by CCK-8 assay. As shown in the Figure 2C, RKIP overexpression inhibited while RKIP knockdown enhanced NPC cell proliferation after 4Gy irradiation. The apoptosis resulting from irradiation is, to a considerable degree, understood as radiosensitivity [31]. Therefore, we analyzed the effect of RKIP on the irradiation-induced apoptosis of NPC cells. Hoechst staining showed that RKIP overexpression increased irradiation-induced apoptosis of CNE2-IR cells [35.72 ± 5.70% (RKIP OE) vs ± 2.10% (empty vector); P < 0.01], whereas RKIP knockdown decreased irradiation-induced apoptosis of CNE2 cells [27.54 ± 3.71% (RKIP KD) vs ± 6.41% (empty vector); P < 0.01] (Figure 3A). Flow cytometry analysis also showed that RKIP overexpression increased irradiationinduced apoptosis of CNE2-IR cells [23.57 ± 2.43% (RKIP OE) vs ± 4.15% (empty vector); P < 0.01], whereas RKIP knockdown decreased irradiation-induced apoptosis of CNE2 cells [26.82 ± 2.47% (RKIP KD) vs
3 31.67 ± 2.65% (empty vector); P < 0.01] (Figure 3B). Taken together, these results demonstrate that RKIP reduction promotes NPC cell radioresistance in vitro. RKIP reduction increases NPC cell radioresistance in vivo To determine the effect of RKIP on NPC radioresistance in vivo, we generated subcutaneous tumors in nude mice using NPC cells with RKIP expression changes, and then tumor radioresponse was assessed after receiving total 8Gy irradiation. The results showed that radioresistance of tumors generated by RKIP overexpression CNE2-IR cells was significantly lower than that of tumors generated by control CNE2- IR cells, whereas radioresistance of tumors generated by RKIP knockdown CNE2 cells was significantly higher than that of tumors generated by control CNE2 cells as demonstrated by tumor growth and weight measurement (Figure 4A). TUNEL assay showed that RKIP knockdown decreased while RKIP overexpression increased the number of apoptotic cells in the xenograft tumors [10.55 ± 4.71% (RKIP KD) vs ± 3.70% (empty vector); P < 0.01] [21.67 ± 3.41% (RKIP OE) vs ± 3.10% (empty vector); P < 0.01] (Figure 4B). Immunohistochemical staining showed that RKIP knockdown decreased while RKIP overexpression increased the number of γh2ax positive cells, i.e. cells with DNA damage in the xenograft tumors [6.58 ± 0.92% (RKIP KD) vs ± 1.77% (empty vector); P < 0.01] [12.66 ± 1.36% (RKIP OE) vs ± 1.56% (empty vector); P < 0.01] (Figure 4C). Moreover, RKIP knockdown increased while RKIP overexpression decreased the number of Ki-67 positive cells, i.e. proliferation cells in the xenograft tumors [47.35 ± 7.6% (RKIP KD) vs ± 3.57% (empty Figure 1: RKIP reduction is correlated with NPC radioresistance and poor patient survival. (A) a representative result of RKIP, phospho-erk 1/2 and phospho-akt immunohistochemical staining in normal nasopharyngeal mucosa (NNM), and radiosensitive and radioresistant NPC tissues. Original magnification, 200. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for NPC patients according to the expression levels of RKIP. NPC patients with low RKIP expression have a significantly worse disease-free survival (left) and overall survival (right) than those with high RKIP expression
4 Table 1: The expression levels of RKIP, phospho-akt and pospho-erk 1/2 in the NNM and NPCs with different radioresponse RKIP Protein NNM (n, %) Radiosensitive NPC (n, %) Radioresistant NPC (n, %) Low (0 3) 5 (16.67) 28 (37.84) 64 (85.33) High (4 6) 25 (83.33) 46 (62.16) 11 (14.67) Phospho-AKT Low (0 3) 30 (100.00) 44 (59.46) 23 (30.67) High (4 6) 0 (0.00) 30 (40.54) 52 (69.33) Phospho-ERK 1/2 Low (0 3) 29 (96.67) 42 (56.76) 26 (34.67) High (4 6) 1 (3.33) 32 (43.24) 49 (65.33) NNM, normal nasopharyngeal mucosa; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma. P < 0.01 by χ 2 test, NNM vs. NPC; Radiosensitive NPC vs. Radioresistant NPC. Table 2: Correlation between RKIP expression and clinicopathological characteristics in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (n = 149, χ 2 test) Gender Variables N RKIP low high P Male Female Age (y) < Primary tumor (T) stage T T Lymph node (N) metastasis N N Clinical TNM stage I II III IV Radiation response Sensitivity Resistance
5 Table 3: Univariate and multivariate analyses of prognostic factors for overall and disease-free survival using Cox proportional hazards regression model (N = 149) Gender Variable Disease free survival (DFS) Overall survival (OS) Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis P HR (95% CI) P HR (95% CI) P HR (95% CI) P HR (95% CI) Male vs. Female ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Age(y) < 47 vs ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Primary tumor(t) stage T1 2 vs.t ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) lymph node(n) metastasis N0 vs.n ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Clinica TNM stage I II vs. III IV ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) RKIP expression level Low vs. High ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) vector); P < 0.01] [32.30 ± 4.42% (RKIP OE) vs ± 5.27% (empty vector); P < 0.01] (Figure 4D). Taken together, these results demonstrate that RKIP reduction promotes NPC cell radioresistance in vivo. RKIP-regulated NPC cell radioresponse is mediated by ERK and AKT signaling To explore the signaling mechanism of RKIP in NPC radioresistance, we investigated whether RKIP-regulated NPC cell radioresponse is mediated by ERK and AKT signaling. Western blotting showed that the phosphorylated level of ERK 1/2 and AKT significantly increased in the RKIP knockdown CNE2 cells, whereas significantly decreased in the RKIP overexpression CNE2-IR cells as compared to their corresponding control cells after 4Gy irradiation (Figure 5A). Moreover, the expression levels of phospho-erk 1/2 and phospho- AKT was reduced in the tumors generated by RKIP overexpression CNE2-IR cells, whereas increased in the tumors generated by RKIP knockdown CNE2 cells relative to tumors generated by their corresponding control cells after 8Gy irradiation (Figure 5B and 5C). The results indicate that RKIP inhibits the activation of ERK-1/2 and AKT signaling in the irradiated NPC cells and tumors. Interestingly, treatment of RKIP knockdown CNE2 cells with MEK inhibitor U0126 (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) decreased phospho-akt level, whereas transfection of ERK-2 expression plasmid into RKIP overexpression CNE2-IR cells significantly increased phospho-akt level after 4Gy irradiation, suggesting that AKT is a downstream transducer of ERK signaling in the RKIP-regulating signaling pathways of irradiated NPC cells (Figure 6A). Next, we determined whether RKIP reduction increases NPC radioresistance via ERK and PI3K signaling. A clone survival assay showed that treatment of RKIP knockdown CNE2 cells with U0126 (Promega) or AKT inhibitor LY (CST, Beverly, MA, USA) significantly abrogated cell radioresistance induced by RKIP knockdown [AUC 1.18 (U0126) vs (vehicle), P < 0.05; RPF = 0.85] [1.10 AUC (LY294002) vs (vehicle), P < 0.05; RPF = 0.79] (Figure 6B); transfection of AKT1 DNAzyme into RKIP knockdown CNE2 cells also significantly abolished cell radioresistance induced by RKIP knockdown [AUC 1.04 (AKT1 DNAzyme) vs (vehicle), P < 0.05; RPF = 0.75] (Figure 6B); transfection of ERK-2 or AKT1 expression plasmid into RKIP overexpression CNE2-IR cells restored cell radioresistance reduced by RKIP overexpression [AUC 1.73 (ERK-2 OE) vs (empty vector), P < 0.05; RPF = 1.34] [AUC 1.54 (AKT1 OE) vs (empty vector), P < 0.05; RPF = 1.16] (Figure 6C). Collectively, these data demonstrate that RKIP-regulated NPC cell radioresponse is mediated through ERK and AKT signaling, and RKIP reduction promotes NPC cell radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT activity. In the cohort of NPC tissues, we observed that the levels of phospho-erk 1/2 and phospho-akt were significantly higher in the radioresistant NPCs than those in the radiosensitive NPCs (Figure 1A, Table 1). Correlation analyses revealed that RKIP level was negatively associated with phospho-erk-1/2 level (r = 0.51, P < 0.001) and phospho-akt level (r = 0.33, 11467
6 Figure 2: RKIP reduction increases NPC cell radioresistance in vitro. (A) a representative result of Western blotting shows the levels of RKIP expression in the RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells, RKIP KD CNE2 cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells. (B) a clonogenic survival assay shows that radioresponse of RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells, RKIP KD CNE2 cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells. (top) cells were irradiated with a range of 1 8Gy radiation doses, and colonies that formed after incubation of 12 days were stained with crystal violet and photographed; (bottom) dose survival curves were created by fitting surviving fractions to the linear quadratic equation. (C) CCK-8 assay shows that proliferation of RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells, RKIP KD CNE2 cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after 4Gy irradiation. Three experiments were done; Means, SDs, and statistical significance are denoted; *P < OE, overexpression; KD, knockdown; EV, empty vector
7 P < 0.001), and phospho-erk 1/2 level was positively associated with phospho-akt level (r = 0.54, P < 0.001) (Figure 6D). The results indicate that RKIP reduction enhances the radioresistance of NPC patients probably by activating ERK and AKT signaling. DISCUSSION In this study, we found that RKIP was frequently downregulated in the radioresistant NPC tissues, and its reduction correlated with NPC radioresistance and poor patient survival, outlining a potential biomarker for NPC radiosensitization and patient prognosis. To gain insight into RKIP effect on NPC radioresponse, we performed in vitro and in vivo radioresponse assays with a combination of loss-of-function and gain-of-function approaches, and demonstrate that reduced RKIP enhances radioresistance in the NPC cells and xenograft tumors. Next, we investigated the signaling mechanism of RKIP-regulated NPC radioresponse. We observed that RKIP knockdown increased while RKIP overexpression decreased the phosphorylated level of ERK 1/2 and AKT in the NPC cells and xenograft tumors after irradiation, indicating that RKIP decreases the activation of ERK and AKT signaling in the irradiated NPC cells in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, our result also suggests that AKT is a downstream transducer of ERK signaling in the RKIP-regulating signaling pathways. To confirm that ERK and AKT signaling mediates RKIP-regulated NPC radioresponse, we used pharmacological and genetic approaches to change the activity or expression of ERK and AKT in the NPC cells, and then detected cell radioresponse. The results showed that MEK inhibitor U0126, PI3K inhibitor Figure 3: RKIP reduction inhibits irradiation-induced NPC cell apoptosis. (A) (left) RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells, RKIP KD CNE2 cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells were irradiated with 6Gy irradiation, incubated for 72 hours, and stained with Hoechst and photographed; (right) a histogram shows the apoptotic rate of these cells. (B) (left) RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells, RKIP KD CNE2 cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells were irradiated with 6Gy irradiation, incubated for 72 hours, subjected to analysis of apoptosis using flow cytometry, and a representative result of cell apoptosis is showed; (right) a histogram shows the apoptotic rate of these cells. Three experiments were done; Means, SDs, and statistical significance are denoted; *P < OE, overexpression; KD, knockdown; EV, empty vector
8 LY or AKT1 DNAzyme significantly abrogated cell radioresistance induced by RKIP knockdown in the radiosensitive NPC cells, and transfection of ERK-2 or AKT1 expression plasmid restored cell radioresistance reduced by RKIP overexpression in the radioresistant NPC cells. In the clinical NPC samples, the levels of phospho-erk 1/2 and phospho-akt were significantly higher in the radioresistant NPCs than those in the radiosensitive NPCs, and negatively associated with RKIP levels. Taken together, our results demonstrate that RKIP-regulated NPC cell radioresponse is mediated through ERK and AKT signaling, and RKIP reduction promotes NPC cell radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT activity. Futhermore, we observed that RKIP reduction conferred a clear proliferation advantage and apoptotic resistance to NPC cells in response to irradiation: RKIP knockdown increased while RKIP overexpression decreased cell proliferation; RKIP knockdown increased while RKIP overexpression decreased cell apoptosis. These data suggest that RKIP functions as proliferation inhibitor and anti-apoptotic factor in the irradiated NPC cells, which is consistent with RKIP-inhibiting ERK and AKT activity. Most of radioresistant NPCs with low RKIP expression along with data from the in vitro and in vivo radioresponse study indicate that RKIP is needed for ionizing radiation to kill NPC cells, and induction of RKIP expression can be an effective adjuvant for radiotherapy of NPCs with RKIP reduction. In fact, Rituximab has been shown to upregulate RKIP and sensitize non-hodgkin s lymphoma cells to chemotherapeutic-induced apoptosis [32], and nitric oxide [33] and proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 [23] have been reported to increase tumor cell sensitivity to chemo-immunotherapeutics via inducing RKIP expression and then inhibiting anti-apoptotic pathways. Furthermore, our in vitro and in vivo data showed that RKIP dwonregulation increased NPC radioresistance by enhancing ERK and AKT signaling activity, suggesting ERK and AKT as possible targets for personalized therapeutic intervention in NPCs with reduced RKIP. In summary, we demonstrate that RKIP is critical for radioresponse of NPC cells both in vitro and in vivo, and its reduction correlates with NPC radioresistance and poor patient prognosis, and RKIP reduction promotes NPC radioresistance via increasing ERK and AKT activity. These Figure 4: RKIP reduction increases NPC cell radioresistance in vivo. (A) the growth and weight of tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after 8Gy irradiation. (left) 3 weeks after irradiation, the mice were killed, and the tumors were photographed; (middle) the growth curves of the tumors after irradiation (n = 5 each group) at the sacrifice with respect to the first measurements; (right) the average weights of the tumors after irradiation (n = 5 each group) at the sacrifice. (B) (left) a representative image of TUNEL detection of apoptotic cells in the tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after irradiation; (right) a histogram shows percentages of apoptotic cells in the tumors (n = 5 each group). (C) (left) a representative image of immunohistochemical staining of γh2ax in the tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after irradiation; (right) a histogram shows percentages of γ-h2ax positive cells in the tumors (n = 5 each group). (D) (left) a representative image of immunohistochemical staining of Ki-67 in the tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after irradiation; (right) a histogram shows percentages of Ki-67 positive cells in the tumors (n = 5 each group). Means, SDs, and statistical significance are denoted; *P < Original magnification, 400. OE, overexpression; KD, knockdown; EV, empty vector
9 Figure 5: RKIP inhibits activity of ERK-1/2 and AKT signaling in the irradiated NPC cells and xenograft tumors. (A) (left) a representative result of Western blotting shows the levels of phospho-erk 1/2, phospho-akt and RKIP in the RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after 4Gy irradiation; (right) a histogram shows the levels of phospho-erk 1/2, phospho-akt and RKIP in these cells. (B) (top) a representative result of Western blotting shows the levels of phospho-erk 1/2, phospho-akt and RKIP in the tumors generated by RKIP KD CNE2 cells, RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells and their corresponding EV-transfected cells after 8Gy irradiation; (bottom) a histogram shows the expression levels of phospho-erk-1/2, phosphor-akt and RKIP in the xenograft tumors. Means, SDs, and statistical significance are denoted; *P < OE, overexpression; KD, knockdown; EV, empty vector
10 Figure 6: RKIP-regulated NPC cell radioresponse is mediated through ERK and AKT signaling. (A) (left) a representative result of Western blotting shows the levels of the phospho-erk-1/2, phospho-akt and RKIP in the RKIP KD CNE2 treated with a range of 5 20 μmol/l MEK inhibitor U0126; (right) a representative result of Western blotting shows the levels of phospho-erk-1/2, phospho-akt and RKIP in the RKIP OE CNE2-IR cells transfected with 4 μg/ml ERK-2 expression vector (OE). (B) a clonogenic survival assay shows that inhibition of ERK and AKT signaling significantly abrogated CNE2 KD cell radioresistance induced by RKIP knockdown. Cells treated with 10 μmol/l U0126, 10 μmol/l LY or 2 μmol/l AKT-1 DNAzyme were irradiated with a range of 1 8Gy radiation doses, and dose survival curves were created by fitting surviving fractions to the linear quadratic equation. (C) a clonogenic survival assay shows that activation of ERK and AKT signaling restored CNE2-IR OE cell radioresistance reduced by RKIP overexpression. Cells transfected with 4 μmol/l of ERK-2 or AKT-1 expression plasmid were irradiated with a range of 1 8Gy radiation doses, and dose survival curves were created by fitting surviving fractions to the linear quadratic equation. (C) Spearman rank correlation analysis shows that RKIP level was negatively associated with phospho-erk 1/2 level (a) and phospho-akt level (b), and phospho-erk 1/2 level was positively associated with phospho-akt level in 149 cases of NPCs. OE, overexpression; KD, knockdown
11 findings provide strong evidences for RKIP-ERK-AKT signaling axis as a radiosensitizing target in NPCs with reduced RKIP. MATERIALS AND METHODS Cell lines Radioresistant human NPC cell line CNE2-IR and radiosensitive cell line CNE2 cells were previously established by us [34], and cultured with RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Radioresistant CNE2-IR cells were derived from parental CNE2 cells by treating the cells with four rounds of sublethal ionizing radiation [34]. Radiosensitive CNE2, used as a control, were treated with the same procedure except sham irradiated. Experiments were performed with the CNE2-IR cells within 4 to 10 passages after the termination of irradiation, and their radioresistance was tested by a clonogenic survival assay before use. Patients and tissue samples One hundred and forty-nine NPC patients without distant metastasis (M0 stage) at the time of diagnosis who were treated by radical radiotherapy alone in the First Hospital of Chengzhou City (Chengzhou, China) between Jan 2007 and Dec 2009 were recruited in this study. Using a modified linear accelerator, radiotherapy was administered for treatment of NPC patients at 2Gy per fraction per day, 5 days per week, for a total dose of 70Gy. NPC tissue biopsies were obtained at the time of diagnosis before any therapy, fixed in 4% formalin and embedded in paraffin. 30 cases of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded normal nasopharyngeal mucosa tissues from the non-cancer patients in the same period were also collected, and used for controls. On the basis of the 1978 WHO classification [35], all tumors were histopathologically diagnosed as poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinomas (WHO type III). The clinical stage of the patients was classified and reclassified according to the 2008 NPC staging system of China [36]. The radiotherapy response was evaluated clinically for primary lesions based on nasopharyngeal fiberscope and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or CT (computed tomography) one month after the initiation of radiotherapy according to the following criteria. Radioresistant NPC patients were defined as ones with persistent disease (incomplete regression of primary tumor and/or neck lymphonodes) at > 3 months or with local recurrent disease at the nasopharynx and/or neck lymphonodes at 12 months after completion of radiotherapy. Radiosensitive NPC patients were defined as ones without the local residual lesions (complete regression) at > 3 months and without local recurrent disease at >12 months after completion of radiotherapy. Based on the above criteria, one hundred and forty-nine NPC patients were composed of seventy-four radioresistant and seventy-five radiosensitive ones. The patients were followed up strictly in outpatient clinics: every 3 month for the first year and then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and finally annually. The patients were followed up for a maximum period of eighty months and a median of fifty-eight months. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the interval from the initiation of primary radiotherapy to the date of cancer-related death or when censured at the latest date if patients were still alive. Disease-free survival (DFS) was defined as the time from the completion of primary radiotherapy to the date of pathological diagnosis or clinical evidence of local failure and/or distant metastasis. The clinicopathological parameters of the patients used in the present study are shown in Supplementary Table S1. Establishment of NPC cell lines with overexpression or knockdown of RKIP Recombinant plasmid pcdna3.1(+)-flag-rkip and lentiviral pgv248-puro-rkip shrna were previously described [27]. To generate NPC cell lines with RKIP overexpression, pcdna3.1(+)-flag-rkip and control plasmid pcdna3.1(+) were transfected into radioresistant CNE2-IR cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer s instruction, respectively. To generate NPC cell lines with RKIP knockdown, lentiviral pgv248-puro-rkip shrna and control lentiviral pgv248-puro-control shrna were used to infect radiosensitive CNE2 cells according to the manufacturer s instruction, respectively. Cells were selected using neomycin or puromycin for 2 weeks, and NPC cell lines with stable overexpression or knockdown of RKIP and control cell lines were obtained. Clonogenic survival assay A clonogenic survival assay was performed as previously described by us [34]. Briefly, cells were exposed to a range of radiation doses (1 8Gy), and 12 days after irradiation surviving colonies were stained with 0.5% crystal violet and counted. The survival fraction was calculated as the numbers of colonies divided by the numbers of cells seeded times plating efficiency. Radiation dose-response curves were created by fitting the data to the linear quadratic equation S = e αd βd^2 using GraphPad Prism 5.0, where S is the surviving fraction, α and β are inactivation constants, and D is the dose in Gy. The area under the curves (AUC) that represent the mean inactivation dose (MID) was calculated using GraphPad Prism 5.0. The radiation protection factor (RPF) was calculated by dividing the MID of the test cells by the MID of control cells
12 Cell proliferation assay Cells were seeded into 96-well plates ( cells/well). After incubation for 24 hours, the cells were irradiated with 4Gy. Cell viability at various time intervals was assessed by cell-counting kit-8 assay (CCK-8) (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer s instruction. The absorbance of each well was monitored by a spectrophotometer at 450 nm (A450). Three independent experiments were done in triplicate. Cell apoptosis assay Flow cytometry analysis and Hoechst staining of apoptotic cells 72 hours after 6Gy irradiation were performed as previously described by us [37]. In vivo tumor radioresponse assay Nude male mice that were 4 weeks old were obtained from the Laboratory Animal Center of Central South University (Changsha, China) and were maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions. For in vivo tumor radioresponse assay, mice (n = 5 each group) were subcutaneously injected with cells/mouse into the right flanks. When the tumor volumes reached approximately 50 mm 3, using a modified linear accelerator, a total dose of 8Gy ionizing radiation was delivered to the tumor at 2Gy per fraction per day in the 4 consecutive days. 3 weeks after completing irradiation, the mice were killed by cervical dislocation, and their tumors were excised, weighted, and cut in half, with one half fixed and embedded in paraffin for TUNEL and immunohistochemical staining, and the remaining half flash frozen in liquid nitrogen for Western blotting. Tumor volume (in mm 3 ) was measured by caliper measurements performed every 4 days and calculated by using the modified ellipse formula (volume = length width 2 /2). Western blotting Proteins were exacted from cells and tissues using RIPA buffer. An equal amount of protein in each sample was subjected to SDS-PAGE separation, followed by blotting onto a PVDF membrane (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). Blots were blocked with 5% nonfat dry milk or 3% BSA for 2 hours at room temperature and then incubated with anti-rkip antibody (#13006, CST), phospho-erk 1/2 (Thr183/Tyr185) (#4671, CST), or phospho-akt (Ser473) (#4060, CST) antibody overnight at 4C, followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 hour at room temperature. The signal was visualized with an enhanced chemiluminescence detection reagent (Pierce, Minneapolis, MN, USA). β-actin was detected simultaneously using monoclonal mouse anti-β-actin antibody (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA) as a loading control. Immunohistochemical staining Immunohistochemical staining of RKIP, phospho- ERK 1/2, phospho-akt, gh2ax (phospho-s139), a marker for DNA double-strand breaks [38], and Ki-67, a marker for cell proliferation, were performed on the formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue sections. Briefly, after antigen retrieval tissue sections were incubated with anti-rkip, anti-phospho-erk 1/2 (Thr183/Tyr185), anti-phospho-akt (Ser473), anti-gh2ax (ab2893, Abcom, Cambridge, MA, USA) or anti-ki-67 antibody (ab15580, Abcom) overnight at 4 C, and then were incubated with biotinylated secondary antibody followed by avidin-biotin peroxidase complex (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark). Finally, tissue sections were incubated with 3, 3 -diaminobenzidine (Sigma) and counterstained with hematoxylin. In negative controls, primary antibodies were omitted. Immunohistochemical staining was assessed and scored by two independent pathologists. Discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Staining intensity was categorized: absent staining as 0, weak as 1, moderate as 2, and strong as 3. The percentage of stained cells was categorized as no staining = 0, < 30% of stained cells = 1, 30~60% = 2, and > 60% = 3. The staining score (ranging from 0 6) for each tissue was calculated by adding the area score and the intensity score. A combined staining score of 3 was considered to be low expression; and a score of > 3 was considered to be high expression. Quantitative evaluation of DNA damaged or proliferation cells was done by examining the sections in ten random microscopic fields and counting the number of gh2ax or Ki-67 positive nuclei among 1000 carcinoma cells under the light microscope. The rate of DNA damaged or proliferation cells was expressed as positive cells per 100 cancer cells. In situ detection of apoptotic cells Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase(tdt)- mediated dutp nick end labeling (TUNEL) was performed to detect apoptotic cells of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue sections of xenograft tumors after irradiation with In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) according to the manufacturer s instruction. Quantitative evaluation of apoptotic cells was done by examining the sections in ten random microscopic fields and counting the number of TUNEL-positive cancer cells among 1000 carcinoma cells under the light microscope. The apoptotic index was 11474
13 expressed as positive cells per 100 cancer cells. Transient transfection of AKT1 DNAzyme, AKT1 or ERK-2 expression plasmid into NPC cells Cells were cultured with RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS one day before transfection. The transfection of 2 μmol/l DNAzyme targeting AKT1 (the sequence: 5 -TGGTCCACAGGCTAGCTACAACGA CCTGCGGCC-3 ) [39], 4 μg/ml recombinant plasmid preceiver-m13-akt1 (EX-A0022-M13; GeneCopoeia, Rockville, MD, USA) or recombinant plasmid preceiver- M13-ERK-2 (EX-A0354; GeneCopoeia) into NPC cells was performed using oligofectamine reagent (Life technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) or Lipofectamine hours after transfection, cells were subjected to further analysis. Statistical analysis All experiments were carried out at least 3 times. Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS 20.0 software. For comparisons between two groups, a Student t test or chi-square test was used. Survival curves were obtained by using Kaplan Meier method, and comparisons were made by using log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were conducted on all parameters by using Cox proportional hazards regression model. The Spearman rank correlation coefficient was used to determine the correlation between two parameters. P values less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. Ethics statement This study was approved by the ethics committee of the First Hospital of Chengzhou City, China. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in the study. All animal experiments were undertaken in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of Central South University, with the approval of the Scientific Investigation Board of Central South University. GRANT SUPPORT This work was supported by the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China ( ), the National Key Technology R & D Program of China (2013BAI01B07), the National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB910502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( , ), and Collaborative Innovation Center for Chemistry and Molecular Medicine of Hunan Province, China. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest. REFERENCES 1. Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2004; 5: Suarez C, Rodrigo JP, Rinaldo A, Langendijk JA, Shaha AR, Ferlito A. Current treatment options for recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; Lee AW, Poon Y, Foo W, Law SC, Cheung FK, Chan DK, Tung SY, Thaw M, Ho JH. Retrospective analysis of 5037 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during : overall survival and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992; 23: Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P, McFerran B, Kaiser C, Fee F, Katsanakis KD, Rose DW, Mischak H, Sedivy JM, Kolch W. Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature. 1999; 401: Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D, Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D, McFerran B, Wyche J, Kolch W, Sedivy JM. Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaBinducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol. 2001; 21: Goel R, Baldassare JJ. Killing two birds with one RKIP. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 15: Al-Mulla F, Bitar MS, Al-Maghrebi M, Behbehani AI, Al-Ali W, Rath O, Doyle B, Tan KY, Pitt A, Kolch W. Raf kinase inhibitor protein RKIP enhances signaling by glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Cancer Res. 2011; 71: Yousuf S, Duan M, Moen EL, Cross-Knorr S, Brilliant K, Bonavida B, LaValle T, Yeung KC, Al-Mulla F, Chin E, Chatterjee D. Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) blocks signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in breast and prostate cancer. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e Keller ET, Fu Z, Brennan M. The role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) in health and disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004; 68: Granovsky AE, Rosner MR. Raf kinase inhibitory protein: a signal transduction modulator and metastasis suppressor. Cell Res. 2008, 18: Keller ET, Fu Z, Yeung K, Brennan M. Raf kinase inhibitor protein: a prostate cancer metastasis suppressor gene. Cancer Lett. 2004; 207: Fu Z, Kitagawa Y, Shen R, Shah R, Mehra R, Rhodes D, Keller PJ, Mizokami A, Dunn R, Chinnaiyan AM, Yao Z, Keller ET. Metastasis suppressor gene Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a novel prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Prostate 2006; 66: Hagan S, Al-Mulla F, Mallon E, Oien K, Ferrier R, Gusterson B, García JJ, Kolch W. Reduction of Raf
14 kinase inhibitor protein expression correlates with breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11: Li HZ, Wang Y, Gao Y, Shao J, Zhao XL, Deng WM, Liu YX, Yang J, Yao Z. Effects of raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on metastasis and progression of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2008; 6: Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Behbehani AI, Bitar MS, George SS, Going JJ, García JJ, Scott L, Fyfe N, Murray GI, Kolch W. Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression in a survival analysis of colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24: Martinho O, Pinto F, Granja S, Miranda-Gonçalves V, Moreira MA, Ribeiro LF, di Loreto C, Rosner MR, Longatto-Filho A, Reis RM. RKIP inhibition in cervical cancer is associated with higher tumor aggressive behavior and resistance to cisplatin therapy. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e Li J, Wang Y, Song Y, Fu Z, Yu W. mir-27a regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting RKIP in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2014; 13: Liu H, Li P, Li B, Sun P, Zhang J, Wang B, Jia B. RKIP promotes cisplatin-induced gastric cancer cell death through NF-κB/Snail pathway. Tumour Biol. 2015; 36: Chatterjee D, Bai Y, Wang Z, Beach S, Mott S, Roy R, Braastad C, Sun Y, Mukhopadhyay A, Aggarwal BB, Darnowski J, Pantazis P, Wyche J, et al. RKIP sensitizes prostate and breast cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279: Bonavida B. RKIP-mediated chemo-immunosensitization of resistant cancer cells via disruption of the NF-κB/Snail/ YY1/RKIP resistance-driver loop. Crit Rev Oncog. 2014; 19: Baritaki S, Katsman A, Chatterjee D, Yeung KC, Spandidos DA, Bonavida B. Regulation of tumor cell sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by the metastatic suppressor Raf kinase inhibitor protein via Yin Yang 1 inhibition and death receptor 5 up-regulation. J Immunol. 2007; 179: Baritaki S, Militello L, Malaponte G, Spandidos DA, Salcedo M, Bonavida B. The anti-cd20 mab LFB-R603 interrupts the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/RKIP/PTEN resistance loop in B-NHL cells: role in sensitization to TRAIL apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 2011; 38: Baritaki S, Yeung K, Palladino M, Berenson J, Bonavida B. Pivotal roles of snail inhibition and RKIP induction by the proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 in tumor cell chemoimmunosensitization. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: Woods Ignatoski KM, Grewal NK, Markwart SM, Vellaichamy A, Chinnaiyan AM, Yeung K, Ray ME, Keller ET. Loss of Raf kinase inhibitory protein induces radioresistance in prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 72: Ruan L, Wang GL, Yi H, Chen Y, Tang CE, Zhang PF, Li MY, Li C, Peng F, Li JL, Chen ZC, Xiao ZQ. Raf kinase inhibitor protein correlates with sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiotherapy. J Cell Biochem. 2010; 110: Chen Y, Ouyang GL, Yi H, Li MY, Zhang PF, Li C, Li JL, Liu YF, Chen ZC, Xiao ZQ. Identification of RKIP as an invasion suppressor protein in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by proteomic analysis. J Proteome Res. 2008; 7: He QY, Yi HM, Yi H, Xiao T, Qu JQ, Yuan L, Zhu JF, Li JY, Wang YY, Li LN, Feng J, Lu SS, Xiao ZQ. Reduction of RKIP expression promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating Stat3 signaling ; 6: doi: /oncotarget Valerie K, Yacoub A, Hagan MP, Curiel DT, Fisher PB, Grant S, Dent P. Radiation-induced cell signaling: inside-out and outside-in. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007; 6: Dent P, Yacoub A, Contessa J, Caron R, Amorino G, Valerie K, Hagan MP, Grant S, Schmidt-Ullrich R. Stress and radiation-induced activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways. Radiat Res. 2003; 159: Wang X, Liu JZ, Hu JX, Wu H, Li YL, Chen HL, Bai H, Hai CX. ROS-activated p38 MAPK/ERK-Akt cascade plays a central role in palmitic acid-stimulated hepatocyteproliferation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011; 51: Gudkov AV, Komarova EA. The role of p53 in determining sensitivity to radiotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003; 3: Jazirehi AR, Vega MI, Chatterjee D, Goodglick L, Bonavida B Inhibition of the Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling pathway, Bcl-xL down-regulation, and chemosensitization of non- Hodgkin s lymphoma B cells by Rituximab. Cancer Res. 2004; 64: Bonavida B, Baritaki S, Huerta-Yepez S, Vega MI, Chatterjee D, Yeung K. Novel therapeutic applications of nitric oxide donors in cancer: roles in chemo- and immunosensitization to apoptosis and inhibition of metastases Nitric Oxide. 2008; 19: Feng XP, Yi H, Li MY, Li XH, Yi B, Zhang PF, Li C, Peng F, Tang CE, Li JL, Chen ZC, Xiao ZQ. Identification of biomarkers for predicting nasopharyngeal carcinoma response to radiotherapy by proteomics. Cancer Res. 2010; 70: Shanmugaratnam K, Sobin LH. The World Health Organization histological classification of tumours of the upper respiratory tract and ear. A commentary on the second edition. Cancer. 1993; 71: Pan J, Xu Y, Qiu S, Zong J, Guo Q, Zhang Y, Lin S, Lu JJ. A Comparison between the Chinese 2008 and the 7th edition AJCC staging systems for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2015; 38: Zeng GQ, Yi H, Li XH, Shi HY, Li C, Li MY, Zhang PF, Feng XP, Wan XX, Qu JQ, Xu Y, Sun Y, Chen ZC, et al. Identification of the proteins related to p53-mediated radioresponse in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by proteomic analysis. J Proteomics. 2011; 74:2723 3
15 38. Ivashkevich A, Redon CE, Nakamura AJ, Martin RF, Martin OA. Use of the gamma-h2ax assay to monitor DNA damage and repair in translational cancer research. Cancer Lett. 2012; 327: Yang L, Xiao L, Ma X, Tang M, Weng X, Chen X, Sun L, Cao Y. Effect of DNAzymes targeting Akt1 on cell proliferation and apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009; 8:
标题
 环 球 中 医 药 2016 年 5 月 第 9 卷 第 5 期 摇 Global Traditional Chinese Medicine, May 2016,Vol 郾 9, No 郾 5 摇 557 两 种 电 针 对 脊 髓 损 伤 14 天 后 大 鼠 运 动 功 能 神 经 元 及 MEK2 p 鄄 ERK1 表 达 的 影 响 论 著 宋 良 玉 摇 吕 威 摇 景 泉 凯 摇 莫 雨
环 球 中 医 药 2016 年 5 月 第 9 卷 第 5 期 摇 Global Traditional Chinese Medicine, May 2016,Vol 郾 9, No 郾 5 摇 557 两 种 电 针 对 脊 髓 损 伤 14 天 后 大 鼠 运 动 功 能 神 经 元 及 MEK2 p 鄄 ERK1 表 达 的 影 响 论 著 宋 良 玉 摇 吕 威 摇 景 泉 凯 摇 莫 雨
分 级 和 气 管 是 否 受 侵 是 影 响 预 后 的 独 立 危 险 因 素 关 键 词 状 腺 肿 瘤 ; 癌, 乳 头 状 ; 预 后 Clinical outcomes of 600 papillary thyroid carcinoma patients ZHANG Zong-min,
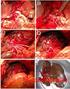 移 性 鳞 癌 患 者 的 临 床 资 料, 比 较 不 同 治 疗 手 段 的 效 果 50 例 患 者 男 性 44 例, 女 性 6 例, 年 龄 29~73 岁, 中 位 年 龄 52.5 岁 ; 临 床 分 期 :N2c 占 64% (32/50),N3 占 36% (18/50) 30 例 患 者 行 双 颈 淋 巴 结 清 扫 术 50 例 患 者 均 行 放 疗, 剂 量 为 50~66
移 性 鳞 癌 患 者 的 临 床 资 料, 比 较 不 同 治 疗 手 段 的 效 果 50 例 患 者 男 性 44 例, 女 性 6 例, 年 龄 29~73 岁, 中 位 年 龄 52.5 岁 ; 临 床 分 期 :N2c 占 64% (32/50),N3 占 36% (18/50) 30 例 患 者 行 双 颈 淋 巴 结 清 扫 术 50 例 患 者 均 行 放 疗, 剂 量 为 50~66
<4D6963726F736F667420576F7264202D20B2CCA3BA4542B2A1B6BE52746120496747BFB9CCE5D3EBB1C7D1CAB0A9B7D6C6DAB5C4B9D8CFB52E646F63>
 EB 病 毒 Rta/IgG 抗 体 与 鼻 咽 癌 分 期 的 关 系 蔡 永 林, 郑 裕 明, 成 积 儒, 李 军, 莫 永 坤, 钟 青 燕 ( 广 西 梧 州 市 红 十 字 会 医 院, 梧 州 市 肿 瘤 防 治 研 究 所, 广 西 梧 州 543002) 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 EB 病 毒 Rta/IgG 抗 体 与 鼻 咽 癌 临 床 分 期 的 关 系 方 法 用 酶
EB 病 毒 Rta/IgG 抗 体 与 鼻 咽 癌 分 期 的 关 系 蔡 永 林, 郑 裕 明, 成 积 儒, 李 军, 莫 永 坤, 钟 青 燕 ( 广 西 梧 州 市 红 十 字 会 医 院, 梧 州 市 肿 瘤 防 治 研 究 所, 广 西 梧 州 543002) 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 EB 病 毒 Rta/IgG 抗 体 与 鼻 咽 癌 临 床 分 期 的 关 系 方 法 用 酶
864 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 6 期 2016 年 6 月 of apoptosis related factors, decrease the incidence of adverse reactions, which is of great
 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 6 期 2016 年 6 月 863 曲 妥 珠 单 抗 联 合 多 西 紫 杉 醇 治 疗 Her-2 阳 性 乳 腺 癌 的 临 床 研 究 * 周 永 安, 刘 训 碧 黄 石 市 中 心 医 院 ( 普 爱 院 区 ) 乳 腺 肿 瘤 外 科, 湖 北 黄 石 435000 摘 要 : 目 的 探 析 注 射 用 曲
现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 6 期 2016 年 6 月 863 曲 妥 珠 单 抗 联 合 多 西 紫 杉 醇 治 疗 Her-2 阳 性 乳 腺 癌 的 临 床 研 究 * 周 永 安, 刘 训 碧 黄 石 市 中 心 医 院 ( 普 爱 院 区 ) 乳 腺 肿 瘤 外 科, 湖 北 黄 石 435000 摘 要 : 目 的 探 析 注 射 用 曲
Microsoft PowerPoint - ryz_030708_pwo.ppt
 Long Term Recovery of Seven PWO Crystals Ren-yuan Zhu California Institute of Technology CMS ECAL Week, CERN Introduction 20 endcap and 5 barrel PWO crystals went through (1) thermal annealing at 200 o
Long Term Recovery of Seven PWO Crystals Ren-yuan Zhu California Institute of Technology CMS ECAL Week, CERN Introduction 20 endcap and 5 barrel PWO crystals went through (1) thermal annealing at 200 o
聖馬爾定醫院正子中心健保開單診療指引(guideline)
 聖 馬 爾 定 醫 院 正 子 中 心 健 保 開 單 診 療 指 引 (guideline) 2011.10.27 全 身 癌 症 掃 描 檢 查 (2010 年 6 月 1 日 起 健 保 開 始 對 下 列 正 子 掃 描 之 適 應 症 給 付 ): 1. 乳 癌 淋 巴 癌 之 分 期 治 療 及 懷 疑 復 發 或 再 分 期 2. 大 腸 癌 直 腸 癌 食 道 癌 頭 頸 部 癌 (
聖 馬 爾 定 醫 院 正 子 中 心 健 保 開 單 診 療 指 引 (guideline) 2011.10.27 全 身 癌 症 掃 描 檢 查 (2010 年 6 月 1 日 起 健 保 開 始 對 下 列 正 子 掃 描 之 適 應 症 給 付 ): 1. 乳 癌 淋 巴 癌 之 分 期 治 療 及 懷 疑 復 發 或 再 分 期 2. 大 腸 癌 直 腸 癌 食 道 癌 頭 頸 部 癌 (
- I -
 2005 Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage on the Intervertebral Disc in Vertebroplasty () 2005 4 - I - - II - Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage
2005 Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage on the Intervertebral Disc in Vertebroplasty () 2005 4 - I - - II - Experimental Study about the Effects of the Bone Cement leakage
21 13 D / 2 10 ig ig 10 d 1. 0 g kg /2 2 β- 5 g kg g kg mg kg - 1 ig ig 24 h 5% 1 2% CMC-Na 2. 5 ml 30
 21 13 1 2 1* 2 1. 430065 2. 445000 20 10 5 g kg - 1 5 mg kg - 1 ig 10 d ig HE 1 TFF1 TFF1 P < 0. 01 P < 0. 01 P < 0. 01 P < 0. 05 R285. 5 doi 10. 13422 /j. cnki. syfjx. 2015130100 A 1005-9903 2015 13-0100-05
21 13 1 2 1* 2 1. 430065 2. 445000 20 10 5 g kg - 1 5 mg kg - 1 ig 10 d ig HE 1 TFF1 TFF1 P < 0. 01 P < 0. 01 P < 0. 01 P < 0. 05 R285. 5 doi 10. 13422 /j. cnki. syfjx. 2015130100 A 1005-9903 2015 13-0100-05
医学科研方法
 医 学 科 研 方 法 主 讲 苏 秀 兰 细 胞 生 物 学 教 授 第 一 讲 绪 论 一 概 念 : 在 医 学 科 学 研 究 活 动 中, 运 用 科 学 的 实 践 和 理 论 思 维 的 技 巧, 充 分 发 挥 自 己 的 智 慧, 去 寻 找 观 念 世 界 与 现 实 世 界 之 间 的 联 系 或 规 律, 从 而 发 现 新 现 象, 提 出 新 理 论 的 手 段 二 医
医 学 科 研 方 法 主 讲 苏 秀 兰 细 胞 生 物 学 教 授 第 一 讲 绪 论 一 概 念 : 在 医 学 科 学 研 究 活 动 中, 运 用 科 学 的 实 践 和 理 论 思 维 的 技 巧, 充 分 发 挥 自 己 的 智 慧, 去 寻 找 观 念 世 界 与 现 实 世 界 之 间 的 联 系 或 规 律, 从 而 发 现 新 现 象, 提 出 新 理 论 的 手 段 二 医
相 关 报 道 近 年 来 临 床 上 运 用 多 种 针 灸 疗 法 治 疗 肥 胖 及 其 引 起 的 并 发 症, 如 高 脂 血 症 糖 尿 病 高 血 压 及 痛 经 等, 均 获 得 满 意 疗 效. caused by sedentary lifestyle and genetic f
 在 线 投 稿 : http://www.baishideng.com/wcjd/ch/index.aspx 帮 助 平 台 : http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i5.815 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2016 年 2 月 18 日 ; 24(5): 815-820 ISSN 1009-3079 (print)
在 线 投 稿 : http://www.baishideng.com/wcjd/ch/index.aspx 帮 助 平 台 : http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i5.815 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2016 年 2 月 18 日 ; 24(5): 815-820 ISSN 1009-3079 (print)
5-25袁宏钧.indd
 第 24 卷 第 5 期 2015 年 5 月 碘 131 doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2015, 24(5):643 647. Chinese Journal of
第 24 卷 第 5 期 2015 年 5 月 碘 131 doi:10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.05.005 Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 2015, 24(5):643 647. Chinese Journal of
: TNM TNM 2
 : 10389822 : 1 : TNM TNM 2 p27 kip1 MMP-7 MMP-9 Cyclin E TGF-β1 p53 114 1999 2004 SCI >1.4 6 p27 kip1 MMP-7 MMP-9 Cyclin E TGF-β1 p53 1995-1999 114 114 Kaplan-Meier Log-rank 6 p27 kip1 MMP-7 PearsonX 2
: 10389822 : 1 : TNM TNM 2 p27 kip1 MMP-7 MMP-9 Cyclin E TGF-β1 p53 114 1999 2004 SCI >1.4 6 p27 kip1 MMP-7 MMP-9 Cyclin E TGF-β1 p53 1995-1999 114 114 Kaplan-Meier Log-rank 6 p27 kip1 MMP-7 PearsonX 2
by mild (22.7%). Inhaled corticosteroids, systemic corticosteroids, and antibiotics were applied to 94.8% (292 cases), 74.7% (230 cases), and 90.9% (2
 论 著 临 床 研 究 doi: 0.7499/j.issn.008-8830.204.2.007 郑 州 市 城 区 儿 童 哮 喘 的 流 行 病 学 调 查 及 发 病 相 关 因 素 分 析 赵 坤 宋 桂 华 古 华 倩 2 刘 爽 3 张 岩 郭 彦 荣 (. 河 南 中 医 学 院 第 一 附 属 医 院 儿 科 医 院, 河 南 郑 州 450000; 2. 杭 州 市 余 杭 区
论 著 临 床 研 究 doi: 0.7499/j.issn.008-8830.204.2.007 郑 州 市 城 区 儿 童 哮 喘 的 流 行 病 学 调 查 及 发 病 相 关 因 素 分 析 赵 坤 宋 桂 华 古 华 倩 2 刘 爽 3 张 岩 郭 彦 荣 (. 河 南 中 医 学 院 第 一 附 属 医 院 儿 科 医 院, 河 南 郑 州 450000; 2. 杭 州 市 余 杭 区
%
 38 1 2014 1 Vol. 38No. 1 January 2014 51 Population Research 2010 2010 2010 65 100028 Changing Lineal Families with Three Generations An Analysis of the 2010 Census Data Wang Yuesheng Abstract In contemporary
38 1 2014 1 Vol. 38No. 1 January 2014 51 Population Research 2010 2010 2010 65 100028 Changing Lineal Families with Three Generations An Analysis of the 2010 Census Data Wang Yuesheng Abstract In contemporary
405 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 是 临 床 较 为 常 见 的 心 血 管 疾 病, 病 情 危 急, 病 死 率 高 [1] 随 着 经 皮 冠 状 动 脉 介 入 治 疗 (percutaneous coronary intervention,pci) 技 术 在 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 急 诊
![405 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 是 临 床 较 为 常 见 的 心 血 管 疾 病, 病 情 危 急, 病 死 率 高 [1] 随 着 经 皮 冠 状 动 脉 介 入 治 疗 (percutaneous coronary intervention,pci) 技 术 在 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 急 诊 405 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 是 临 床 较 为 常 见 的 心 血 管 疾 病, 病 情 危 急, 病 死 率 高 [1] 随 着 经 皮 冠 状 动 脉 介 入 治 疗 (percutaneous coronary intervention,pci) 技 术 在 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 急 诊](/thumbs/42/23094402.jpg) 404 冠 心 舒 通 胶 囊 预 防 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 PCI 术 后 再 狭 窄 的 临 床 研 究 李 静, 王 建 榜, 王 西 辉 西 安 医 学 院 第 二 附 属 医 院 心 内 科, 陕 西 西 安 710038 摘 要 : 目 的 研 究 冠 心 舒 通 胶 囊 预 防 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 经 皮 冠 状 动 脉 介 入 治 疗 (PCI) 术 后 再 狭 窄 的 临 床
404 冠 心 舒 通 胶 囊 预 防 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 PCI 术 后 再 狭 窄 的 临 床 研 究 李 静, 王 建 榜, 王 西 辉 西 安 医 学 院 第 二 附 属 医 院 心 内 科, 陕 西 西 安 710038 摘 要 : 目 的 研 究 冠 心 舒 通 胶 囊 预 防 急 性 心 肌 梗 死 经 皮 冠 状 动 脉 介 入 治 疗 (PCI) 术 后 再 狭 窄 的 临 床
mm 400 mm 15 mm EOF mm/10a Fig. 1 Distributions
 7 2 2011 3 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol. 7 No. 2 March 2011 1673-1719 (2011) 02-0097-07 1961 2007 77 5 5 6 2 3 8 11 1980 1980 1990 2015 8 11 P426.6 A 7.86% 4 50 0.35 5 6 19 7 8 9 1 1906 2005
7 2 2011 3 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol. 7 No. 2 March 2011 1673-1719 (2011) 02-0097-07 1961 2007 77 5 5 6 2 3 8 11 1980 1980 1990 2015 8 11 P426.6 A 7.86% 4 50 0.35 5 6 19 7 8 9 1 1906 2005
( s y s t e m ) ( s t r e s s ) (stress model) ( s y s t e m ) [ ] [ 5 ] C o x [ 3 ] 1 [ 1, 2 ] [ 6-8 ] [ 9 ] Tw Fam Med Res 2003 Vol.1 No.1 23
![( s y s t e m ) ( s t r e s s ) (stress model) ( s y s t e m ) [ ] [ 5 ] C o x [ 3 ] 1 [ 1, 2 ] [ 6-8 ] [ 9 ] Tw Fam Med Res 2003 Vol.1 No.1 23 ( s y s t e m ) ( s t r e s s ) (stress model) ( s y s t e m ) [ ] [ 5 ] C o x [ 3 ] 1 [ 1, 2 ] [ 6-8 ] [ 9 ] Tw Fam Med Res 2003 Vol.1 No.1 23](/thumbs/88/115745072.jpg) 1, 4 1, 2 3 1 4 1, 2 1977 E n g e l 1999 5 1 ( 1 ) ( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 5 ) 2003 1 2 2-32 stress model, stress analysis [ 1 ] ( p s y c h o g e n e s i s ) (holism) (biomedical model) ( r e d u c t i o
1, 4 1, 2 3 1 4 1, 2 1977 E n g e l 1999 5 1 ( 1 ) ( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 5 ) 2003 1 2 2-32 stress model, stress analysis [ 1 ] ( p s y c h o g e n e s i s ) (holism) (biomedical model) ( r e d u c t i o
中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 46 卷 第 9 期 2015 年 5 月 1339 非 酒 精 性 脂 肪 性 肝 病 (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,nafld) 是 一 种 与 胰 岛 素 抵 抗 遗
 1338 中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 46 卷 第 9 期 2015 年 5 月 九 味 肝 泰 胶 囊 对 高 脂 饮 食 诱 导 大 鼠 非 酒 精 性 脂 肪 肝 的 治 疗 作 用 陈 菲 1 2,, 艾 国 3, 盛 柳 青 1, 麻 佳 蕾 1, 黄 正 明 1. 金 华 职 业 技 术 学 院 医 学 院, 浙 江 金 华
1338 中 草 药 Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 第 46 卷 第 9 期 2015 年 5 月 九 味 肝 泰 胶 囊 对 高 脂 饮 食 诱 导 大 鼠 非 酒 精 性 脂 肪 肝 的 治 疗 作 用 陈 菲 1 2,, 艾 国 3, 盛 柳 青 1, 麻 佳 蕾 1, 黄 正 明 1. 金 华 职 业 技 术 学 院 医 学 院, 浙 江 金 华
Microsoft Word - 360145.doc
 项 目 批 准 号 81273814 归 口 管 理 部 门 申 请 代 码 收 件 日 期 H2716 360145 y 国 家 自 然 科 学 基 金 委 员 会 资 助 项 目 计 划 书 资 助 类 别 : 面 上 项 目 亚 类 说 明 : 非 连 续 资 助 类 项 目 附 注 说 明 : 项 目 名 称 : 益 气 养 肺 法 拮 抗 bfgf 对 肺 癌 微 环 境 介 导 化 疗
项 目 批 准 号 81273814 归 口 管 理 部 门 申 请 代 码 收 件 日 期 H2716 360145 y 国 家 自 然 科 学 基 金 委 员 会 资 助 项 目 计 划 书 资 助 类 别 : 面 上 项 目 亚 类 说 明 : 非 连 续 资 助 类 项 目 附 注 说 明 : 项 目 名 称 : 益 气 养 肺 法 拮 抗 bfgf 对 肺 癌 微 环 境 介 导 化 疗
TGF-β AngⅡ B SD ~ 220g SPF. SCXK No SYXK ~ 25 40% ~ 70% OR37G-C
 2017 7 43 4 Journal of Southwest Minzu University Natural Science Edition Jul. 2017 Vol. 43 No. 4 doi10. 11920 /xnmdzk. 2017. 04. 008 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 1. 610212 2. 6100413. 610031 AngⅡ TGF-β. SD 60 180 ~
2017 7 43 4 Journal of Southwest Minzu University Natural Science Edition Jul. 2017 Vol. 43 No. 4 doi10. 11920 /xnmdzk. 2017. 04. 008 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 1. 610212 2. 6100413. 610031 AngⅡ TGF-β. SD 60 180 ~
< F63756D656E D2D796E2D31C6DABFAF2D31D6D0D2BDD2A9CFD6B4FABBAF2D C4EA2DB5DA36C6DA2DB7E2C3E6CDC6BDE9A3A D36A3A92E6D6469>
 1. 530023 2. 530001 3. 530001 DCP 100 DCP 47 53 3 HOMA -IR HOMA - IR P
1. 530023 2. 530001 3. 530001 DCP 100 DCP 47 53 3 HOMA -IR HOMA - IR P
, GC/MS ph GC/MS I
 S00017052 O O , GC/MS ph GC/MS I Abstract Drug abuse is a serious issue throughout the world. Amphetamine-type stimulants (ATS) are substances frequently used by drug abusers. There are significant needs
S00017052 O O , GC/MS ph GC/MS I Abstract Drug abuse is a serious issue throughout the world. Amphetamine-type stimulants (ATS) are substances frequently used by drug abusers. There are significant needs
211 better than those in the control group, with significant difference between two groups (P < 0.05). The ocular hypertension of patients in the cont
 210 毛 果 芸 香 碱 联 合 拉 坦 前 列 素 治 疗 原 发 性 急 性 闭 角 型 青 光 眼 的 疗 效 观 察 符 元 党 1, 郑 振 优 2, 林 再 雄 2, 周 吉 良 1. 昌 江 黎 族 自 治 县 中 西 医 结 合 医 院, 海 南 昌 江 572700 2. 海 南 医 学 院 附 属 医 院 眼 科, 海 南 海 口 570100 1 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨
210 毛 果 芸 香 碱 联 合 拉 坦 前 列 素 治 疗 原 发 性 急 性 闭 角 型 青 光 眼 的 疗 效 观 察 符 元 党 1, 郑 振 优 2, 林 再 雄 2, 周 吉 良 1. 昌 江 黎 族 自 治 县 中 西 医 结 合 医 院, 海 南 昌 江 572700 2. 海 南 医 学 院 附 属 医 院 眼 科, 海 南 海 口 570100 1 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨
< F63756D656E D2D796E2DB9A4D7F72D31C6DABFAF2D31D6D0D2BDD2A9CFD6B4FABBAF2D C4EA2DB5DA34C6DAB8BDBCD32D30302DB7E2C3E6CDC6BDE941A3A D34A3A92E6D6469>
 2013 绎 Vol.15 No.4 阴 元元 450002 Ki-6772 Wistar 6 5 mg kg -1 30 0.8 mg kg -1 7.5 15.0 22.5 g kg -1 1 30 Ki-67 TUNEL Ki-67 P
2013 绎 Vol.15 No.4 阴 元元 450002 Ki-6772 Wistar 6 5 mg kg -1 30 0.8 mg kg -1 7.5 15.0 22.5 g kg -1 1 30 Ki-67 TUNEL Ki-67 P
07 353-408
 編 號 :CCMP96-RD-006 以 德 菲 法 探 討 中 醫 臨 床 證 型 診 斷 基 準 - 六 淫 證 型 蘇 奕 彰 中 國 醫 藥 大 學 摘 要 德 菲 法 (Delphi Method) 是 廣 泛 被 使 用 的 研 究 方 法, 尤 其 適 用 於 新 的 研 究 領 域 (new research area) 及 探 索 性 研 究 (exploratory studies),
編 號 :CCMP96-RD-006 以 德 菲 法 探 討 中 醫 臨 床 證 型 診 斷 基 準 - 六 淫 證 型 蘇 奕 彰 中 國 醫 藥 大 學 摘 要 德 菲 法 (Delphi Method) 是 廣 泛 被 使 用 的 研 究 方 法, 尤 其 適 用 於 新 的 研 究 領 域 (new research area) 及 探 索 性 研 究 (exploratory studies),
1269 malondialdehyde (MDA) were significantly decreased, while oxygen partial pressure (PaO 2 ), ph value, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione
 1268 维 生 素 A 联 合 牛 肺 表 面 活 性 物 质 治 疗 新 生 儿 呼 吸 窘 迫 综 合 征 的 临 床 研 究 朱 琼 1, 陈 小 利 2, 叶 华 2 1. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 儿 科, 重 庆 401520 2. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 内 儿 科, 重 庆 401520
1268 维 生 素 A 联 合 牛 肺 表 面 活 性 物 质 治 疗 新 生 儿 呼 吸 窘 迫 综 合 征 的 临 床 研 究 朱 琼 1, 陈 小 利 2, 叶 华 2 1. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 儿 科, 重 庆 401520 2. 重 庆 市 合 川 区 妇 幼 保 健 计 划 生 育 服 务 中 心 内 儿 科, 重 庆 401520
<4D6963726F736F667420576F7264202D20ECFAD0C0D0C0C2DBCEC4CCE1BDBB6F7665722E646F63>
 硕 士 专 业 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗 方 法 比 较 的 分 析 研 究 研 究 生 姓 名 指 导 教 师 姓 名 禚 欣 欣 康 定 华 专 业 名 称 皮 肤 性 病 学 研 究 方 向 皮 肤 肿 瘤 与 皮 肤 病 理 论 文 提 交 日 期 2013 年 4 月 I 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗
硕 士 专 业 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗 方 法 比 较 的 分 析 研 究 研 究 生 姓 名 指 导 教 师 姓 名 禚 欣 欣 康 定 华 专 业 名 称 皮 肤 性 病 学 研 究 方 向 皮 肤 肿 瘤 与 皮 肤 病 理 论 文 提 交 日 期 2013 年 4 月 I 鲍 温 病 临 床 病 理 特 征 和 几 种 治 疗
2 JCAM. June,2012,Vol. 28,NO. 6 膝 关 节 创 伤 性 滑 膜 炎 是 急 性 创 伤 或 慢 性 劳 损 所 致 的 关 节 滑 膜 的 无 菌 性 炎 症, 发 病 率 达 2% ~ 3% [1], 为 骨 伤 科 临 床 的 常 见 病 多 发 病 近 年 来
![2 JCAM. June,2012,Vol. 28,NO. 6 膝 关 节 创 伤 性 滑 膜 炎 是 急 性 创 伤 或 慢 性 劳 损 所 致 的 关 节 滑 膜 的 无 菌 性 炎 症, 发 病 率 达 2% ~ 3% [1], 为 骨 伤 科 临 床 的 常 见 病 多 发 病 近 年 来 2 JCAM. June,2012,Vol. 28,NO. 6 膝 关 节 创 伤 性 滑 膜 炎 是 急 性 创 伤 或 慢 性 劳 损 所 致 的 关 节 滑 膜 的 无 菌 性 炎 症, 发 病 率 达 2% ~ 3% [1], 为 骨 伤 科 临 床 的 常 见 病 多 发 病 近 年 来](/thumbs/42/22962570.jpg) 针 灸 临 床 杂 志 2012 年 第 28 卷 第 6 期 1 临 床 研 究 针 刀 治 疗 膝 关 节 创 伤 性 滑 膜 炎 的 临 床 研 究 向 伟 明 1, 丁 思 明 1, 张 秀 芬 2, 权 五 成 2, 唐 吉 莲 1, 杨 友 金 1, 黄 涣 强 1, 颜 勋 1, 曾 晓 宇 1, 朱 传 芳 1 1, 张 雄 ( 1. 重 庆 市 梁 平 县 第 二 人 民 医 院,
针 灸 临 床 杂 志 2012 年 第 28 卷 第 6 期 1 临 床 研 究 针 刀 治 疗 膝 关 节 创 伤 性 滑 膜 炎 的 临 床 研 究 向 伟 明 1, 丁 思 明 1, 张 秀 芬 2, 权 五 成 2, 唐 吉 莲 1, 杨 友 金 1, 黄 涣 强 1, 颜 勋 1, 曾 晓 宇 1, 朱 传 芳 1 1, 张 雄 ( 1. 重 庆 市 梁 平 县 第 二 人 民 医 院,
 2000.11 2000.11 2000 11 Abstract: Background: The development of autoantibodies in the sera of patients with cancers has been described, but the mechanism is still not clear. Objective: The aim of this
2000.11 2000.11 2000 11 Abstract: Background: The development of autoantibodies in the sera of patients with cancers has been described, but the mechanism is still not clear. Objective: The aim of this
1556 地 理 科 学 进 展 30 卷 他 关 于 农 村 住 房 结 构 与 抗 震 性 能 的 研 究, 则 多 是 从 工 程 抗 灾 的 角 度, 研 究 某 种 构 造 类 型 的 房 屋, 力 图 找 到 传 统 房 屋 的 结 构 失 误 和 新 建 房 屋 中 存 在 的 问 [
 第 30 卷 第 12 期 2011 年 12 月 地 理 科 学 进 展 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.30, No.12 Dec., 2012 中 国 农 村 地 区 住 房 结 构 的 区 域 差 异 及 其 影 响 因 素 1, 2, 李 方 一 3 1,, 高 晓 路 2 2, 王 英 杰 (1. 中 国 科 学 院 区 域 可 持 续 发 展 分 析 与 模 拟 重
第 30 卷 第 12 期 2011 年 12 月 地 理 科 学 进 展 PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY Vol.30, No.12 Dec., 2012 中 国 农 村 地 区 住 房 结 构 的 区 域 差 异 及 其 影 响 因 素 1, 2, 李 方 一 3 1,, 高 晓 路 2 2, 王 英 杰 (1. 中 国 科 学 院 区 域 可 持 续 发 展 分 析 与 模 拟 重
ment group was more effective than that of the control group OR = % CI = Conclusion The clinical efficacy of Chinese medic
 33 243 HAART Meta * 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 3 3 1. 530001 2. 538000 3. 530011 highly active anti-retroviral therapy HAART Pubmed HAART randomized controlled trials RCT Jadad RevMan5. 3 Meta 5 RCT 761 Meta HAART
33 243 HAART Meta * 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 3 3 1. 530001 2. 538000 3. 530011 highly active anti-retroviral therapy HAART Pubmed HAART randomized controlled trials RCT Jadad RevMan5. 3 Meta 5 RCT 761 Meta HAART
壹 緒 論 由 於 作 者 任 教 於 大 專 軍 事 校 院, 依 校 規 規 定 學 生 於 第 八 學 期 必 須 通 過 3000 公 尺 跑 步 測 驗 限 定 14 分 鐘 的 及 格 標 準 始 得 畢 業 ; 因 此 探 討 提 升 中 長 距 離 與 長 距 離 跑 步 能 力 的
 四 週 800 公 尺 間 歇 跑 步 訓 練 教 學 方 案 對 不 同 跑 步 能 力 者 的 訓 練 成 效 蔡 玉 敏 1 陳 智 仁 2, 3 * 陳 明 坤 1 中 華 民 國 空 軍 官 校 總 教 官 室 2 桃 園 創 新 技 術 學 院 體 育 保 健 室 3 國 立 中 興 大 學 體 育 室 摘 要 目 的 : 探 討 800 公 尺 間 歇 跑 步 訓 練 教 學 對 不
四 週 800 公 尺 間 歇 跑 步 訓 練 教 學 方 案 對 不 同 跑 步 能 力 者 的 訓 練 成 效 蔡 玉 敏 1 陳 智 仁 2, 3 * 陳 明 坤 1 中 華 民 國 空 軍 官 校 總 教 官 室 2 桃 園 創 新 技 術 學 院 體 育 保 健 室 3 國 立 中 興 大 學 體 育 室 摘 要 目 的 : 探 討 800 公 尺 間 歇 跑 步 訓 練 教 學 對 不
畜牧 动物医学 蚕 蜂
 中国农学通报 2015,31(20):181-185 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 老河口市砂梨花期的物候特点分析 邓 环 1 马德栗 1 徐洪海 2 洪国平 1 2 武汉区域气候中心 武汉 430074 老河口气象局 湖北老河口 441800 1 摘 要 为掌握湖北省老河口市砂梨花期的物候规律 利用老河口市 20 年的砂梨裂蕾期 初花期 和盛花期 4
中国农学通报 2015,31(20):181-185 Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 老河口市砂梨花期的物候特点分析 邓 环 1 马德栗 1 徐洪海 2 洪国平 1 2 武汉区域气候中心 武汉 430074 老河口气象局 湖北老河口 441800 1 摘 要 为掌握湖北省老河口市砂梨花期的物候规律 利用老河口市 20 年的砂梨裂蕾期 初花期 和盛花期 4
United Nations ~ ~ % 2010
 42 3 2018 5 Vol. 42 No. 3 May 2018 38 Population Research 2014 60 3% ~ 4% 10% 60 +
42 3 2018 5 Vol. 42 No. 3 May 2018 38 Population Research 2014 60 3% ~ 4% 10% 60 +
357 P <. 5. TCD findings revealed that the contralateral vertebral artery systolic blood flow velocities in patients with phase Ⅰ Ⅱ and Ⅲ steal groups
 356 TCD 212 3 215 4 TCD 45 TCD 8 Ⅰ 21 Ⅱ 11 Ⅲ 5 4 45 6 2 Ⅰ 12 9 Ⅱ 3 7 1 Ⅲ 3 2 r =. 78 P
356 TCD 212 3 215 4 TCD 45 TCD 8 Ⅰ 21 Ⅱ 11 Ⅲ 5 4 45 6 2 Ⅰ 12 9 Ⅱ 3 7 1 Ⅲ 3 2 r =. 78 P
03 年 8 月 Vol.5 No.8 支 气 管 哮 喘 ( 简 称 哮 喘 ) 是 儿 童 时 期 最 常 见 的 慢 性 呼 吸 道 疾 病 之 一 近 年 来, 随 着 人 类 文 明 的 发 展 社 会 化 进 程 的 加 快 经 济 水 平 的 提 高 和 科 技 的 进 步, 环 境
 03 年 8 月 Vol.5 No.8 DOI:0.7499/j.issn.008-8830.03.08.003 论 著 临 床 研 究 成 都 地 区 0~4 岁 城 乡 儿 童 哮 喘 流 行 病 学 调 查 对 比 分 析 李 敏 张 琼 时 维 娟 李 兰 李 艳 庞 英 姚 兵 蒋 虹 (. 四 川 省 医 学 科 学 院 / 四 川 省 人 民 医 院 儿 科, 四 川 成 都 6007;.
03 年 8 月 Vol.5 No.8 DOI:0.7499/j.issn.008-8830.03.08.003 论 著 临 床 研 究 成 都 地 区 0~4 岁 城 乡 儿 童 哮 喘 流 行 病 学 调 查 对 比 分 析 李 敏 张 琼 时 维 娟 李 兰 李 艳 庞 英 姚 兵 蒋 虹 (. 四 川 省 医 学 科 学 院 / 四 川 省 人 民 医 院 儿 科, 四 川 成 都 6007;.
600 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 5 期 2016 年 5 月 were significantly decreased, but the levels of IL-12 in two groups were significantly increa
 现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 5 期 2016 年 5 月 599 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合 细 辛 脑 注 射 液 治 疗 小 儿 毛 细 支 气 管 炎 的 临 床 研 究 唐 辉 英, 佘 定 平, 马 颐 娇 深 圳 市 儿 童 医 院 呼 吸 科, 广 东 深 圳 518026 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合
现 代 药 物 与 临 床 Drugs & Clinic 第 31 卷 第 5 期 2016 年 5 月 599 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合 细 辛 脑 注 射 液 治 疗 小 儿 毛 细 支 气 管 炎 的 临 床 研 究 唐 辉 英, 佘 定 平, 马 颐 娇 深 圳 市 儿 童 医 院 呼 吸 科, 广 东 深 圳 518026 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 喘 可 治 注 射 液 联 合
要, 理 想 糾 紛 解 決 方 式 以 公 會 協 助 處 理 與 委 託 保 險 公 司 幫 忙 和 解 ; (2) 研 究 發 現 糾 紛 案 件 中,40-50 歲 之 男 性 以 針 灸 或 推 拿 為 主 要 治 療 方 式 碩 士 與 博 士 年 資 15-20 年 每 診 人 數 越
 編 號 :CCMP98-RD-022 中 醫 醫 療 糾 紛 與 醫 師 責 任 保 險 之 評 估 研 究 陳 俞 沛 台 灣 中 醫 診 斷 學 會 研 究 目 的 : 摘 要 近 年 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 的 中 醫 界, 醫 療 糾 紛 發 生 率 與 發 生 頻 率 也 逐 漸 提 高, 為 影 響 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 與 維 持 良 好 醫 療 品 質 的 一 大 隱 憂 醫 師
編 號 :CCMP98-RD-022 中 醫 醫 療 糾 紛 與 醫 師 責 任 保 險 之 評 估 研 究 陳 俞 沛 台 灣 中 醫 診 斷 學 會 研 究 目 的 : 摘 要 近 年 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 的 中 醫 界, 醫 療 糾 紛 發 生 率 與 發 生 頻 率 也 逐 漸 提 高, 為 影 響 醫 病 關 係 和 諧 與 維 持 良 好 醫 療 品 質 的 一 大 隱 憂 醫 師
OncidiumGower Ramsey ) 2 1(CK1) 2(CK2) 1(T1) 2(T2) ( ) CK1 43 (A 44.2 ) CK2 66 (A 48.5 ) T1 40 (
 35 1 2006 48 35-46 OncidiumGower Ramsey ) 2 1(CK1) 2(CK2) 1(T1) 2(T2) (93 5 28 95 1 9 ) 94 1-2 5-6 8-10 94 7 CK1 43 (A 44.2 ) CK2 66 (A 48.5 ) T1 40 (A 47.5 ) T2 73 (A 46.6 ) 3 CK2 T1 T2 CK1 2006 8 16
35 1 2006 48 35-46 OncidiumGower Ramsey ) 2 1(CK1) 2(CK2) 1(T1) 2(T2) (93 5 28 95 1 9 ) 94 1-2 5-6 8-10 94 7 CK1 43 (A 44.2 ) CK2 66 (A 48.5 ) T1 40 (A 47.5 ) T2 73 (A 46.6 ) 3 CK2 T1 T2 CK1 2006 8 16
84 針 藥 併 施 治 療 偏 頭 痛 次 發 作 症 狀 為 左 顳 側 頭 脹 痛, 多 為 夜 間 發 作 影 響 睡 眠 或 工 作, 頻 率 為 一 天 發 作 一 次, 持 續 一 至 二 小 時, 疼 痛 指 數 7 分 (0 分 為 不 痛, 最 痛 為 滿 分 10 分 ), 需
 J Chin Med 26(1): 83-91, 2015 DOI: 10.3966/101764462015062601008 83 針 藥 併 施 治 療 偏 頭 痛 經 驗 - 病 例 報 告 1, 眞 # 1, #, * 1, 2 1, 2 1 高 雄 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 中 醫 科 系, 高 雄, 台 灣 2 長 庚 大 學 中 醫 系, 桃 園, 台 灣 103 12 26 104
J Chin Med 26(1): 83-91, 2015 DOI: 10.3966/101764462015062601008 83 針 藥 併 施 治 療 偏 頭 痛 經 驗 - 病 例 報 告 1, 眞 # 1, #, * 1, 2 1, 2 1 高 雄 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 中 醫 科 系, 高 雄, 台 灣 2 長 庚 大 學 中 醫 系, 桃 園, 台 灣 103 12 26 104
% GIS / / Fig. 1 Characteristics of flood disaster variation in suburbs of Shang
 20 6 2011 12 JOURNAL OF NATURAL DISASTERS Vol. 20 No. 6 Dec. 2011 1004-4574 2011 06-0094 - 05 200062 1949-1990 1949 1977 0. 8 0. 03345 0. 01243 30 100 P426. 616 A Risk analysis of flood disaster in Shanghai
20 6 2011 12 JOURNAL OF NATURAL DISASTERS Vol. 20 No. 6 Dec. 2011 1004-4574 2011 06-0094 - 05 200062 1949-1990 1949 1977 0. 8 0. 03345 0. 01243 30 100 P426. 616 A Risk analysis of flood disaster in Shanghai
untitled
 R2 10315 20042008 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE THEORY & TREATMENT TO RELIEVE PAIN OF BREAST CANCER PATIENTS 2007 5 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
R2 10315 20042008 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE THEORY & TREATMENT TO RELIEVE PAIN OF BREAST CANCER PATIENTS 2007 5 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 MCF-7 VEGF spss 20 5 ~ 6 h Cck-8 6 h r 2 = Cck-8 6 h 450 nm v Cck-8 v = h 450 nm 3 A = A - A A r 2 Cck -8 Mcf-7 1
 42 1 Vol 42 No 1 2018 1 Journal of Jiangxi Normal University Natural Science Jan 2018 1000-5862 2018 01-0100-06 MCF-7 VEGF 1 2 1 1 1 1* 1 570228 2 70102 Mcf -7 Cck-8 TUNEL- DAPI Cck-8 Cck-8 TUNEL-DAPI
42 1 Vol 42 No 1 2018 1 Journal of Jiangxi Normal University Natural Science Jan 2018 1000-5862 2018 01-0100-06 MCF-7 VEGF 1 2 1 1 1 1* 1 570228 2 70102 Mcf -7 Cck-8 TUNEL- DAPI Cck-8 Cck-8 TUNEL-DAPI
Microsoft Word - _6-15_--CCMP93-CT-107.doc
 Yearbook of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 23(6),303-320,2005 中 醫 藥 年 報 第 23 期 第 6 冊 編 號 :CCMP93-CT-107 補 中 益 氣 湯 抑 制 多 種 惡 性 細 胞 腫 瘤 生 長 機 轉 的 體 外 細 胞 與 肺 氣 虛 老 鼠 模 型 之 先 驅 研 究 沈 建 忠 長 庚 大 學 中 醫 系 摘 要
Yearbook of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 23(6),303-320,2005 中 醫 藥 年 報 第 23 期 第 6 冊 編 號 :CCMP93-CT-107 補 中 益 氣 湯 抑 制 多 種 惡 性 細 胞 腫 瘤 生 長 機 轉 的 體 外 細 胞 與 肺 氣 虛 老 鼠 模 型 之 先 驅 研 究 沈 建 忠 長 庚 大 學 中 醫 系 摘 要
18 A B S 17.44±1() ±6.26( ) 54.23±5.5( ) 6.42±1.51() m 30m t α =.05 ( )AB 1 5 (p>.05)( )AB 1 5 (p<.05)( )A (p>.05)( )B (p<.05)( )A B
 The Effect of Different Training Method on Quick Coordination ability in High School Female Soccer Players 18 A B S 17.44±1() 161.39±6.26( ) 54.23±5.5( ) 6.42±1.51() 15 60-90 30m 30m t α =.05 ( )AB 1 5
The Effect of Different Training Method on Quick Coordination ability in High School Female Soccer Players 18 A B S 17.44±1() 161.39±6.26( ) 54.23±5.5( ) 6.42±1.51() 15 60-90 30m 30m t α =.05 ( )AB 1 5
: ( ),,
 Case Discussion: ( ), RN, ScD, MPH : 24,,,,,,, ( ) ) ( ), : ( ),, randomized controlled trial (RCT). minimization program,,,, : : ; Apgar score > 7 ;, : ; ; ; ; (BT180/min; 2, 83,50 (60.2%).,
Case Discussion: ( ), RN, ScD, MPH : 24,,,,,,, ( ) ) ( ), : ( ),, randomized controlled trial (RCT). minimization program,,,, : : ; Apgar score > 7 ;, : ; ; ; ; (BT180/min; 2, 83,50 (60.2%).,
國家圖書館典藏電子全文
 A Study on the Job Stress and the Ways of Coping for the Director of Elementary School in the Middle Area of Taiwan Abstract This study aims at probing the subject current status as related to stress and
A Study on the Job Stress and the Ways of Coping for the Director of Elementary School in the Middle Area of Taiwan Abstract This study aims at probing the subject current status as related to stress and
 : 23 S00017242 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------3 -------------------------------------------------------------------7
: 23 S00017242 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------3 -------------------------------------------------------------------7
JOURNAL OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING AND ENGINEERING VIBRATION Vol. 31 No. 5 Oct /35 TU3521 P315.
 31 5 2011 10 JOURNAL OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING AND ENGINEERING VIBRATION Vol. 31 No. 5 Oct. 2011 1000-1301 2011 05-0075 - 09 510405 1 /35 TU3521 P315. 8 A Earthquake simulation shaking table test and analysis
31 5 2011 10 JOURNAL OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING AND ENGINEERING VIBRATION Vol. 31 No. 5 Oct. 2011 1000-1301 2011 05-0075 - 09 510405 1 /35 TU3521 P315. 8 A Earthquake simulation shaking table test and analysis
度 身 體 活 動 量 ; 芬 蘭 幼 兒 呈 現 中 度 身 體 活 動 量 之 比 例 高 於 臺 灣 幼 兒 (5) 幼 兒 在 投 入 度 方 面 亦 達 顯 著 差 異 (χ²=185.35, p <.001), 芬 蘭 與 臺 灣 幼 兒 多 半 表 現 出 中 度 投 入 與 高 度
 臺 灣 與 芬 蘭 幼 兒 園 室 內 自 由 遊 戲 內 涵 之 探 討 林 昭 溶 毛 萬 儀 經 國 管 理 暨 健 康 學 院 幼 兒 保 育 系 副 教 授 joyce@ems.cku.edu.tw 吳 敏 而 國 家 教 育 研 究 院 研 究 員 rozwu@mail.naer.edu.tw wanyi@ems.cku.edu.tw 摘 要 自 由 遊 戲 被 視 為 是 幼 兒 的
臺 灣 與 芬 蘭 幼 兒 園 室 內 自 由 遊 戲 內 涵 之 探 討 林 昭 溶 毛 萬 儀 經 國 管 理 暨 健 康 學 院 幼 兒 保 育 系 副 教 授 joyce@ems.cku.edu.tw 吳 敏 而 國 家 教 育 研 究 院 研 究 員 rozwu@mail.naer.edu.tw wanyi@ems.cku.edu.tw 摘 要 自 由 遊 戲 被 視 為 是 幼 兒 的
... (1)....(3)..(5)... (22) (22)......(22)... (22)... (23)....(33)... (33)....(34)....(47)....(51).....(52)......(61)......(62)
 97017608 OO ... (1)....(3)..(5)... (22).......(22)......(22)... (22)... (23)....(33)... (33)....(34)....(47)....(51).....(52)......(61)......(62) C 2002 2 2003 12 146 64.27 110 36 Logistic 2003 12 2004
97017608 OO ... (1)....(3)..(5)... (22).......(22)......(22)... (22)... (23)....(33)... (33)....(34)....(47)....(51).....(52)......(61)......(62) C 2002 2 2003 12 146 64.27 110 36 Logistic 2003 12 2004
instillation therapy combined with Western medicine can reduce the levels of ALT, TBA, ALP, TBIL, DBIL and GGT, and improve the anti-cmv-igm negative
 在 线 投 稿 : http://www.baishideng.com/wcjd/ch/index.aspx 帮 助 平 台 : http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v23.i28.4568 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2015 年 10 月 8 日 ; 23(28): 4568-4573 ISSN 1009-3079
在 线 投 稿 : http://www.baishideng.com/wcjd/ch/index.aspx 帮 助 平 台 : http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v23.i28.4568 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2015 年 10 月 8 日 ; 23(28): 4568-4573 ISSN 1009-3079
< F63756D656E D2D796E2D31C6DABFAF2D31D6D0D2BDD2A9CFD6B4FABBAF2D C4EA2DB5DA38C6DA2D30362DC3F1D7E5D2BDD2A92E6D6469>
 绎 1 2 1. 8300112 援 830000 CNKI 1979-20121989-2013 PubMed/MEDLINE Jadad Cochrane RevMan 5.2.0 Meta 4 360 Meta OS WMD 95%-0.48-0.81-0.160.04-0.150.22 RR 95% 1.671.292.151.220.354.20 doi: 10.11842/wst.2014.08.030
绎 1 2 1. 8300112 援 830000 CNKI 1979-20121989-2013 PubMed/MEDLINE Jadad Cochrane RevMan 5.2.0 Meta 4 360 Meta OS WMD 95%-0.48-0.81-0.160.04-0.150.22 RR 95% 1.671.292.151.220.354.20 doi: 10.11842/wst.2014.08.030
戊 酸 雌 二 醇 片 联 合 宫 颈 注 射 利 多 卡 因 用 于 绝 经 后 妇 女 取 环 的 临 床 效 果 评 价 陆 琴 芬, 等 371 Keywords groups, no removal difficulties and failure, was statistically s
 370 临 床 与 病 理 杂 志 J Clin Pathol Res 2015, 35(3) http://www.lcbl.net doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.03.009 View this article at: http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.03.009 戊 酸 雌 二 醇 片 联
370 临 床 与 病 理 杂 志 J Clin Pathol Res 2015, 35(3) http://www.lcbl.net doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.03.009 View this article at: http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.03.009 戊 酸 雌 二 醇 片 联
ALT) (alanine aminotransferase (aspartate RAD aminotransferaseast) (alkaline phosphatase) γ - (gamma [3] glutamyltransferase) : (D) (R) D / R 1 / 3 D
![ALT) (alanine aminotransferase (aspartate RAD aminotransferaseast) (alkaline phosphatase) γ - (gamma [3] glutamyltransferase) : (D) (R) D / R 1 / 3 D ALT) (alanine aminotransferase (aspartate RAD aminotransferaseast) (alkaline phosphatase) γ - (gamma [3] glutamyltransferase) : (D) (R) D / R 1 / 3 D](/thumbs/49/25341128.jpg) 2015 8 15 4 The Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine Aug. 2015 Vol.15 No.4 ( 518038) [ ] (ALT) (AST) () γ- () 2 351 3 18 AST ALT AST (P 0.05) ALT (P >0.05) (P
2015 8 15 4 The Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine Aug. 2015 Vol.15 No.4 ( 518038) [ ] (ALT) (AST) () γ- () 2 351 3 18 AST ALT AST (P 0.05) ALT (P >0.05) (P
1 ABSTRACT 3 5 13 14 14 15 15 16 17 18 18 18 18-21 28 33 34 46 47 53 54 2
 : - S99017212 O O 1 1 ABSTRACT 3 5 13 14 14 15 15 16 17 18 18 18 18-21 28 33 34 46 47 53 54 2 - A L Aeq CNE 463 3-5 L Aeq L Aeq CNE WHO/ISH 1999 [49] 18.6kPa / 12.0kPa EpiInfo6.04 SPSS10.0 Logistic 10
: - S99017212 O O 1 1 ABSTRACT 3 5 13 14 14 15 15 16 17 18 18 18 18-21 28 33 34 46 47 53 54 2 - A L Aeq CNE 463 3-5 L Aeq L Aeq CNE WHO/ISH 1999 [49] 18.6kPa / 12.0kPa EpiInfo6.04 SPSS10.0 Logistic 10
為 減 少 腫 瘤 治 療 時 間, 提 高 治 療 過 程 的 舒 適 度, 降 低 因 身 體 蠕 動 而 造 成 劑 量 給 予 的 不 確 定 性, 提 升 治 療 的 精 確 度, 增 加 腫 瘤 局 部 控 制 率, 避 免 正 常 組 織 接 受 到 不 必 要 的 劑 量, 降 低
 中 華 民 國 生 物 醫 學 工 程 學 會 腫 瘤 醫 學 影 像 暨 治 療 儀 器 新 知 研 討 會 主 辦 單 位 : 澄 清 綜 合 醫 院 中 港 分 院 / 中 華 民 國 生 物 醫 學 工 程 學 會 會 議 日 期 :101 年 12 月 22 日 ( 星 期 六 ) 會 議 地 點 : 澄 清 醫 院 中 港 分 院 17 樓 國 際 會 議 廳 ( 台 中 市 中 港 路
中 華 民 國 生 物 醫 學 工 程 學 會 腫 瘤 醫 學 影 像 暨 治 療 儀 器 新 知 研 討 會 主 辦 單 位 : 澄 清 綜 合 醫 院 中 港 分 院 / 中 華 民 國 生 物 醫 學 工 程 學 會 會 議 日 期 :101 年 12 月 22 日 ( 星 期 六 ) 會 議 地 點 : 澄 清 醫 院 中 港 分 院 17 樓 國 際 會 議 廳 ( 台 中 市 中 港 路
标题
 853 对实验性大鼠甲状腺肿的影响 * 田先翔,王瑞,泮剑英,吴勇,鲁云,郑国华 ( 湖北中医药大学药学院,武汉摇 430065) 摘摇 要摇 目的摇 研究对实验性大鼠甲状腺肿模型的影响及其作用机制 方法摇 将 SD 大鼠随机分为 6 组:,,低 中 高剂量组, 除外,其余各组大鼠连续灌服 丙基硫氧嘧啶(20 mg kg d ) 造模 低 中 高剂量组同时灌服水溶液,剂量分别为 4. 4, 8. 8,17.
853 对实验性大鼠甲状腺肿的影响 * 田先翔,王瑞,泮剑英,吴勇,鲁云,郑国华 ( 湖北中医药大学药学院,武汉摇 430065) 摘摇 要摇 目的摇 研究对实验性大鼠甲状腺肿模型的影响及其作用机制 方法摇 将 SD 大鼠随机分为 6 组:,,低 中 高剂量组, 除外,其余各组大鼠连续灌服 丙基硫氧嘧啶(20 mg kg d ) 造模 低 中 高剂量组同时灌服水溶液,剂量分别为 4. 4, 8. 8,17.
天 主 教 輔 仁 大 學 社 會 學 系 學 士 論 文 小 別 勝 新 婚? 久 別 要 離 婚? 影 響 遠 距 家 庭 婚 姻 感 情 因 素 之 探 討 Separate marital relations are getting better or getting worse? -Exp
 天 主 教 輔 仁 大 學 社 會 學 系 學 士 論 文 小 別 勝 新 婚? 久 別 要 離 婚? 影 響 遠 距 家 庭 婚 姻 感 情 因 素 之 探 討 Separate marital relations are getting better or getting worse? -Explore the impact of emotional factors couples do not
天 主 教 輔 仁 大 學 社 會 學 系 學 士 論 文 小 別 勝 新 婚? 久 別 要 離 婚? 影 響 遠 距 家 庭 婚 姻 感 情 因 素 之 探 討 Separate marital relations are getting better or getting worse? -Explore the impact of emotional factors couples do not
- 14 - Drug Evaluation Research 第 36 卷 第 1 期 2013 年 2 月 料 ), 山 西 皇 城 相 府 药 业 有 限 公 司, 批 号 20111003 ( 人 口 服 推 荐 剂 量 为 每 日 3 次, 每 次 4 粒, 成 人 体 质 量 按 60
 Drug Evaluation Research 第 36 卷 第 1 期 2013 年 2 月 - 13 - 柴 青 消 癖 胶 囊 对 乳 腺 增 生 模 型 大 鼠 的 治 疗 作 用 研 究 * 刘 聪, 岳 永 花, 郝 旭 亮 山 西 省 中 医 药 研 究 院, 山 西 太 原 030012 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 柴 青 消 癖 胶 囊 对 乳 腺 增 生 模 型 大 鼠 的 治
Drug Evaluation Research 第 36 卷 第 1 期 2013 年 2 月 - 13 - 柴 青 消 癖 胶 囊 对 乳 腺 增 生 模 型 大 鼠 的 治 疗 作 用 研 究 * 刘 聪, 岳 永 花, 郝 旭 亮 山 西 省 中 医 药 研 究 院, 山 西 太 原 030012 摘 要 : 目 的 探 讨 柴 青 消 癖 胶 囊 对 乳 腺 增 生 模 型 大 鼠 的 治
卫生政策研究进展
 卫 生 政 策 研 究 进 展 Progress in Health Policy Research 慢 性 病 管 理 专 刊 2013 年 第 3 期 ( 总 第 46 期 ) 上 海 市 卫 生 发 展 研 究 中 心 2013 年 5 月 25 日 编 者 按 慢 性 病 已 经 成 为 21 世 纪 全 球 各 国 发 展 面 临 的 主 要 挑 战 之 一 在 我 国, 慢 性 病 是
卫 生 政 策 研 究 进 展 Progress in Health Policy Research 慢 性 病 管 理 专 刊 2013 年 第 3 期 ( 总 第 46 期 ) 上 海 市 卫 生 发 展 研 究 中 心 2013 年 5 月 25 日 编 者 按 慢 性 病 已 经 成 为 21 世 纪 全 球 各 国 发 展 面 临 的 主 要 挑 战 之 一 在 我 国, 慢 性 病 是
米 诺 地 尔 酊 联 合 复 方 甘 草 酸 苷 治 疗 斑 秃 疗 效 评 价 及 对 血 清 TNF-α TGF-β1 和 IL-12 的 影 响 陈 玉 华 1039 Keywords group was significantly lower than the research group
 1038 临 床 与 病 理 杂 志 J Clin Pathol Res 2015, 35(6) http://www.lcbl.net doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.06.032 View this article at: http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.06.032 米 诺 地 尔 酊 联 合
1038 临 床 与 病 理 杂 志 J Clin Pathol Res 2015, 35(6) http://www.lcbl.net doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.06.032 View this article at: http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2015.06.032 米 诺 地 尔 酊 联 合
 國 立 屏 東 教 育 大 學 中 國 語 文 學 系 碩 士 班 碩 士 論 文 國 小 國 語 教 科 書 修 辭 格 分 析 以 南 一 版 為 例 指 導 教 授 : 柯 明 傑 博 士 研 究 生 : 鄺 綺 暖 撰 中 華 民 國 一 百 零 二 年 七 月 謝 辭 寫 作 論 文 的 日 子 終 於 畫 下 了 句 點, 三 年 前 懷 著 對 文 學 的 熱 愛, 報 考 了 中
國 立 屏 東 教 育 大 學 中 國 語 文 學 系 碩 士 班 碩 士 論 文 國 小 國 語 教 科 書 修 辭 格 分 析 以 南 一 版 為 例 指 導 教 授 : 柯 明 傑 博 士 研 究 生 : 鄺 綺 暖 撰 中 華 民 國 一 百 零 二 年 七 月 謝 辭 寫 作 論 文 的 日 子 終 於 畫 下 了 句 點, 三 年 前 懷 著 對 文 學 的 熱 愛, 報 考 了 中
國家圖書館典藏電子全文
 i ii Abstract The most important task in human resource management is to encourage and help employees to develop their potential so that they can fully contribute to the organization s goals. The main
i ii Abstract The most important task in human resource management is to encourage and help employees to develop their potential so that they can fully contribute to the organization s goals. The main
ADR ADR ADR : 2
 8 2000 10 2001 5 ADR ADR 415 ADR44 ADR 10.6% 2661 ADR105 ADR 3.9% P
8 2000 10 2001 5 ADR ADR 415 ADR44 ADR 10.6% 2661 ADR105 ADR 3.9% P
Vol. 22 No. 4 JOURNAL OF HARBIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Aug GPS,,, : km, 2. 51, , ; ; ; ; DOI: 10.
 22 4 2017 8 Vol. 22 No. 4 JOURNAL OF HARBIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Aug. 2017 150080 GPS,,, : 27. 36 km, 2. 51, 110. 43, ; ; ; ; DOI: 10. 15938 /j. jhust. 2017. 04. 015 U469. 13 A 1007-2683
22 4 2017 8 Vol. 22 No. 4 JOURNAL OF HARBIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Aug. 2017 150080 GPS,,, : 27. 36 km, 2. 51, 110. 43, ; ; ; ; DOI: 10. 15938 /j. jhust. 2017. 04. 015 U469. 13 A 1007-2683
240 生 异 性 相 吸 的 异 性 效 应 [6] 虽 然, 心 理 学 基 础 研 [7-8] 究 已 经 证 实 存 在 异 性 相 吸 异 性 相 吸 是 否 存 在 于 名 字 认 知 识 别 尚 无 报 道 本 实 验 选 取 不 同 性 别 的 名 字 作 为 刺 激 材 料, 通
![240 生 异 性 相 吸 的 异 性 效 应 [6] 虽 然, 心 理 学 基 础 研 [7-8] 究 已 经 证 实 存 在 异 性 相 吸 异 性 相 吸 是 否 存 在 于 名 字 认 知 识 别 尚 无 报 道 本 实 验 选 取 不 同 性 别 的 名 字 作 为 刺 激 材 料, 通 240 生 异 性 相 吸 的 异 性 效 应 [6] 虽 然, 心 理 学 基 础 研 [7-8] 究 已 经 证 实 存 在 异 性 相 吸 异 性 相 吸 是 否 存 在 于 名 字 认 知 识 别 尚 无 报 道 本 实 验 选 取 不 同 性 别 的 名 字 作 为 刺 激 材 料, 通](/thumbs/42/22943812.jpg) 2011 年 Journal of Capital Medical University 4月 第2 期 Apr 2011 Vol 32 No 2 基础研究 doi: 10 3969 / j issn 1006-7795 2011 02 015 人脑识别不同性别名字反应时的差异研究 高迎霄 陈昭燃 * 张明霞 ( 首都医科大学神经生物系高级脑功能中心) 摘要 目的 探讨男女对不同性别名字认知加工速度是否存在差异
2011 年 Journal of Capital Medical University 4月 第2 期 Apr 2011 Vol 32 No 2 基础研究 doi: 10 3969 / j issn 1006-7795 2011 02 015 人脑识别不同性别名字反应时的差异研究 高迎霄 陈昭燃 * 张明霞 ( 首都医科大学神经生物系高级脑功能中心) 摘要 目的 探讨男女对不同性别名字认知加工速度是否存在差异
<30302DB7E2C3E6CDC6BDE9A3A D34A3A92E6D6469>
 212 绎 Vol.14 No.5 ScienceDirect 阴 元元 元元 / 99978 5 doi: 1.3969/j.issn.1674-3849.212.5.3 2 1 29 72.7% 21 27.1% 24.26% 1 [1] 1 2 21 7.85 [2] 1 29 21% 662 26 9.38 211 3.8 27.2% 1 212-3-26 212-1-19 元 UL16/9-Y4/CMS/WYT1/ICMS
212 绎 Vol.14 No.5 ScienceDirect 阴 元元 元元 / 99978 5 doi: 1.3969/j.issn.1674-3849.212.5.3 2 1 29 72.7% 21 27.1% 24.26% 1 [1] 1 2 21 7.85 [2] 1 29 21% 662 26 9.38 211 3.8 27.2% 1 212-3-26 212-1-19 元 UL16/9-Y4/CMS/WYT1/ICMS
Microsoft Word - 20101483毕业论文+-+副本
 密 级 : 公 开 学 号 :20101483 硕 士 学 位 论 文 祛 斑 玉 容 方 对 色 素 沉 着 小 鼠 血 酪 氨 酸 酶 及 皮 肤 形 态 的 影 响 研 究 生 王 茜 指 导 教 师 学 科 专 业 所 在 学 院 毕 业 时 间 孙 亦 农 中 医 康 复 学 第 二 临 床 医 学 院 2013 年 6 月 Freckle of Yurong side of pigmentation
密 级 : 公 开 学 号 :20101483 硕 士 学 位 论 文 祛 斑 玉 容 方 对 色 素 沉 着 小 鼠 血 酪 氨 酸 酶 及 皮 肤 形 态 的 影 响 研 究 生 王 茜 指 导 教 师 学 科 专 业 所 在 学 院 毕 业 时 间 孙 亦 农 中 医 康 复 学 第 二 临 床 医 学 院 2013 年 6 月 Freckle of Yurong side of pigmentation
~ a 3 h NCEP ~ 24 3 ~ ~ 8 9 ~ km m ~ 500 m 500 ~ 800 m 800 ~ m a 200
 31 1 2013 3 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 31 No. 1 March 2013. J. 2013 31 1 62-69. doi 10. 11755 /j. issn. 1006-7639 2013-01 - 0062 211101 2000 ~ 2010 3 h 2. 5 2. 5 NCEP 2 5 ~ 7 02 11 05 ~ 08 2 ~ 8
31 1 2013 3 Journal of Arid Meteorology Vol. 31 No. 1 March 2013. J. 2013 31 1 62-69. doi 10. 11755 /j. issn. 1006-7639 2013-01 - 0062 211101 2000 ~ 2010 3 h 2. 5 2. 5 NCEP 2 5 ~ 7 02 11 05 ~ 08 2 ~ 8
名称未設定
 127 Insulin IR Glucose transport GLUT4 P P IRS PI3K P GLUT4 Akt/PKB GSK-3 P Inactive GSK-3 Active GS Active GS Inactive P Glycogen synthesis 128 129 IRS-1 PH PTB 1242 IRS-2 PH PTB NGDY NDQY 1338 IRS-3
127 Insulin IR Glucose transport GLUT4 P P IRS PI3K P GLUT4 Akt/PKB GSK-3 P Inactive GSK-3 Active GS Active GS Inactive P Glycogen synthesis 128 129 IRS-1 PH PTB 1242 IRS-2 PH PTB NGDY NDQY 1338 IRS-3
Microsoft Word - A200810-897.doc
 基 于 胜 任 特 征 模 型 的 结 构 化 面 试 信 度 和 效 度 验 证 张 玮 北 京 邮 电 大 学 经 济 管 理 学 院, 北 京 (100876) E-mail: weeo1984@sina.com 摘 要 : 提 高 结 构 化 面 试 信 度 和 效 度 是 面 试 技 术 研 究 的 核 心 内 容 近 年 来 国 内 有 少 数 学 者 探 讨 过 基 于 胜 任 特 征
基 于 胜 任 特 征 模 型 的 结 构 化 面 试 信 度 和 效 度 验 证 张 玮 北 京 邮 电 大 学 经 济 管 理 学 院, 北 京 (100876) E-mail: weeo1984@sina.com 摘 要 : 提 高 结 构 化 面 试 信 度 和 效 度 是 面 试 技 术 研 究 的 核 心 内 容 近 年 来 国 内 有 少 数 学 者 探 讨 过 基 于 胜 任 特 征
1.0 % 0.25 % 85μm % U416 Sulfate expansion deformation law and mechanism of cement stabilized macadam base of saline areas in Xinjiang Song
 1.0 % 0.25 % 85μm 0.97 0.136 % U416 Sulfate expansion deformation law and mechanism of cement stabilized macadam base of saline areas in Xinjiang Song Liang 1,2 Wang Xuan-cang 1 1 School of Highway, Chang
1.0 % 0.25 % 85μm 0.97 0.136 % U416 Sulfate expansion deformation law and mechanism of cement stabilized macadam base of saline areas in Xinjiang Song Liang 1,2 Wang Xuan-cang 1 1 School of Highway, Chang
(baking powder) 1 ( ) ( ) 1 10g g (two level design, D-optimal) 32 1/2 fraction Two Level Fractional Factorial Design D-Optimal D
 ( ) 4 1 1 1 145 1 110 1 (baking powder) 1 ( ) ( ) 1 10g 1 1 2.5g 1 1 1 1 60 10 (two level design, D-optimal) 32 1/2 fraction Two Level Fractional Factorial Design D-Optimal Design 1. 60 120 2. 3. 40 10
( ) 4 1 1 1 145 1 110 1 (baking powder) 1 ( ) ( ) 1 10g 1 1 2.5g 1 1 1 1 60 10 (two level design, D-optimal) 32 1/2 fraction Two Level Fractional Factorial Design D-Optimal Design 1. 60 120 2. 3. 40 10
66 臺 中 教 育 大 學 學 報 : 人 文 藝 術 類 Abstract This study aimed to analyze the implementing outcomes of ability grouping practice for freshman English at a u
 臺 中 教 育 大 學 學 報 : 人 文 藝 術 類 0 年,(),-0 65 私 立 科 技 大 學 四 技 大 一 新 生 英 文 能 力 分 級 教 學 成 效 分 析 An Analysis of the Implementing Outcomes of Ability Grouping of Freshman English in a University of Technology 溫
臺 中 教 育 大 學 學 報 : 人 文 藝 術 類 0 年,(),-0 65 私 立 科 技 大 學 四 技 大 一 新 生 英 文 能 力 分 級 教 學 成 效 分 析 An Analysis of the Implementing Outcomes of Ability Grouping of Freshman English in a University of Technology 溫
mm ~
 16 3 2011 6 Vol 16 No 3 JOURNAL OF HARBIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Jun 2011 1 2 3 1 150040 2 150040 3 450052 1 3 4 > 1 ~ 3 > > U414 A 1007-2683 2011 03-0121- 06 Shrinkage Characteristics of
16 3 2011 6 Vol 16 No 3 JOURNAL OF HARBIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Jun 2011 1 2 3 1 150040 2 150040 3 450052 1 3 4 > 1 ~ 3 > > U414 A 1007-2683 2011 03-0121- 06 Shrinkage Characteristics of
Microsoft PowerPoint _代工實例-1
 4302 動態光散射儀 (Dynamic Light Scattering) 代工實例與結果解析 生醫暨非破壞性分析團隊 2016.10 updated Which Size to Measure? Diameter Many techniques make the useful and convenient assumption that every particle is a sphere. The
4302 動態光散射儀 (Dynamic Light Scattering) 代工實例與結果解析 生醫暨非破壞性分析團隊 2016.10 updated Which Size to Measure? Diameter Many techniques make the useful and convenient assumption that every particle is a sphere. The
电 话 随 访 对 初 产 妇 产 褥 期 母 乳 喂 养 行 为 及 意 向 的 影 响 The effect of telephone follow-up on breastfeeding behaviors and intentions of new mothers during the po
 ( 医 学 部 ) 在 职 人 员 申 请 硕 士 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 : 电 话 随 访 对 初 产 妇 产 褥 期 母 乳 喂 养 行 为 及 意 向 的 影 响 学 院 ( 医 院 所 ): 北 京 大 学 护 理 学 院 学 科 专 业 : 护 理 学 申 请 人 姓 名 : 导 师 姓 名 职 称 : 陆 虹 副 教 授 完 成 时 间 : 二 O 一 O 年 五 月 电 话
( 医 学 部 ) 在 职 人 员 申 请 硕 士 学 位 论 文 论 文 题 目 : 电 话 随 访 对 初 产 妇 产 褥 期 母 乳 喂 养 行 为 及 意 向 的 影 响 学 院 ( 医 院 所 ): 北 京 大 学 护 理 学 院 学 科 专 业 : 护 理 学 申 请 人 姓 名 : 导 师 姓 名 职 称 : 陆 虹 副 教 授 完 成 时 间 : 二 O 一 O 年 五 月 电 话
Microsoft Word - 01李惠玲ok.doc
 康 寧 學 報 11:1-20(2009) 1 數 位 學 習 於 護 理 技 術 課 程 之 運 用 與 評 值 * 李 惠 玲 ** 高 清 華 *** 呂 莉 婷 摘 要 背 景 : 網 路 科 技 在 教 育 的 使 用 已 成 為 一 種 有 利 的 教 學 輔 助 工 具 網 路 教 學 的 特 性, 在 使 學 習 可 不 分 時 間 與 空 間 不 同 進 度 把 握 即 時 性 資
康 寧 學 報 11:1-20(2009) 1 數 位 學 習 於 護 理 技 術 課 程 之 運 用 與 評 值 * 李 惠 玲 ** 高 清 華 *** 呂 莉 婷 摘 要 背 景 : 網 路 科 技 在 教 育 的 使 用 已 成 為 一 種 有 利 的 教 學 輔 助 工 具 網 路 教 學 的 特 性, 在 使 學 習 可 不 分 時 間 與 空 間 不 同 進 度 把 握 即 時 性 資
% % % % % % ~
 1001-5558 2015 03-0021-16 2010 C91 A 2014 5 2010 N. W. Journal of Ethnology 2015 3 86 2015.No.3 Total No.86 2010 2010 2181.58 882.99 40.47% 1298.59 59.53% 2013 2232.78 847.29 37.95% 1385.49 62.05% 1990
1001-5558 2015 03-0021-16 2010 C91 A 2014 5 2010 N. W. Journal of Ethnology 2015 3 86 2015.No.3 Total No.86 2010 2010 2181.58 882.99 40.47% 1298.59 59.53% 2013 2232.78 847.29 37.95% 1385.49 62.05% 1990
08陈会广
 第 34 卷 第 10 期 2012 年 10 月 2012,34(10):1871-1880 Resources Science Vol.34,No.10 Oct.,2012 文 章 编 号 :1007-7588(2012)10-1871-10 房 地 产 市 场 及 其 细 分 的 调 控 重 点 区 域 划 分 理 论 与 实 证 以 中 国 35 个 大 中 城 市 为 例 陈 会 广 1,
第 34 卷 第 10 期 2012 年 10 月 2012,34(10):1871-1880 Resources Science Vol.34,No.10 Oct.,2012 文 章 编 号 :1007-7588(2012)10-1871-10 房 地 产 市 场 及 其 细 分 的 调 控 重 点 区 域 划 分 理 论 与 实 证 以 中 国 35 个 大 中 城 市 为 例 陈 会 广 1,
Leisure Participation Type Differences And Leisure Satisfaction Differences Between Various Body Mass Indices: A Correlation Study To Taiwan s College
 / / 40 3500 3064 1 Leisure Participation Type Differences And Leisure Satisfaction Differences Between Various Body Mass Indices: A Correlation Study To Taiwan s College Student Lien-Chung Lee / Chia-Te
/ / 40 3500 3064 1 Leisure Participation Type Differences And Leisure Satisfaction Differences Between Various Body Mass Indices: A Correlation Study To Taiwan s College Student Lien-Chung Lee / Chia-Te
 2 1: 1 7-27 ( 2001) Formosa n Entomol. 2 1 : 1 7-27 (2001) (Orgyia posticus) ( ) * (Orgyia posticus (Walker)) 10 15 20 25 30 35 12L : 12D 25 5 10-35 64.1 40.0 26.2 16.2 16.2 21.1 19.6 16.0 8.2 6.9 6.0
2 1: 1 7-27 ( 2001) Formosa n Entomol. 2 1 : 1 7-27 (2001) (Orgyia posticus) ( ) * (Orgyia posticus (Walker)) 10 15 20 25 30 35 12L : 12D 25 5 10-35 64.1 40.0 26.2 16.2 16.2 21.1 19.6 16.0 8.2 6.9 6.0
Dan Buettner / /
 39 1 2015 1 Vol. 39 No. 1 January 2015 74 Population Research 80 + /60 + 90 + 90 + 0 80 100028 Measuring and Comparing Population Longevity Level across the Regions of the World Lin Bao Abstract Appropriate
39 1 2015 1 Vol. 39 No. 1 January 2015 74 Population Research 80 + /60 + 90 + 90 + 0 80 100028 Measuring and Comparing Population Longevity Level across the Regions of the World Lin Bao Abstract Appropriate
固本解郁法?治
 81 J Chin Med 13(2): 81-88, 2002 固 本 解 鬱 法 論 治 中 風 後 抑 鬱 症 (poststroke depression) 對 照 研 究 劉 慶 憲 1,2 宋 永 建 3 1 浙 江 省 平 湖 市 中 醫 醫 院 神 經 內 科 浙 江, 平 湖, 中 國 2 上 海 第 二 醫 科 大 學 2002 屆 高 級 醫 師 班 3 上 海 第 二 醫 科
81 J Chin Med 13(2): 81-88, 2002 固 本 解 鬱 法 論 治 中 風 後 抑 鬱 症 (poststroke depression) 對 照 研 究 劉 慶 憲 1,2 宋 永 建 3 1 浙 江 省 平 湖 市 中 醫 醫 院 神 經 內 科 浙 江, 平 湖, 中 國 2 上 海 第 二 醫 科 大 學 2002 屆 高 級 醫 師 班 3 上 海 第 二 醫 科
3020 ISSN 1009-3079 (print) ISSN 2219-2859 (online) 研 发 前 沿,,.,,,. 方 法 : 86, 43. 7 d,,, 7 d 1, 4. (The Radiation Therapy Oncology, RTOG),,. 结 果 : 100%
 wcjd@wjgnet.com 2014 7 28 ; 22(21): 3019-3023 ISSN 1009-3079 (print) ISSN 2219-2859 (online) CLINICAL RESEARCH 回 生 口 服 液 对 急 性 放 射 性 食 管 炎 防 治 作 用 的 临 床 疗 效 Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG), the
wcjd@wjgnet.com 2014 7 28 ; 22(21): 3019-3023 ISSN 1009-3079 (print) ISSN 2219-2859 (online) CLINICAL RESEARCH 回 生 口 服 液 对 急 性 放 射 性 食 管 炎 防 治 作 用 的 临 床 疗 效 Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG), the
填 表 说 明 1. 本 表 所 填 数 据 截 至 时 间 为 2011 年 9 月 底 2. 本 表 请 用 A4 纸 双 面 打 印, 加 盖 学 校 公 章 后 上 报 3. 表 内 所 填 数 据 请 学 校 认 真 核 实, 确 保 准 确 无 误 4. 建 设 完 成 情 况 对 照
 填 表 说 明 1. 本 表 所 填 数 据 截 至 时 间 为 2011 年 9 月 底 2. 本 表 请 用 A4 纸 双 面 打 印, 加 盖 学 校 公 章 后 上 报 3. 表 内 所 填 数 据 请 学 校 认 真 核 实, 确 保 准 确 无 误 4. 建 设 完 成 情 况 对 照 表 等 相 关 表 格 栏 高 不 够 请 自 行 增 加 5. 表 格 中 填 写 的 相 关 量
填 表 说 明 1. 本 表 所 填 数 据 截 至 时 间 为 2011 年 9 月 底 2. 本 表 请 用 A4 纸 双 面 打 印, 加 盖 学 校 公 章 后 上 报 3. 表 内 所 填 数 据 请 学 校 认 真 核 实, 确 保 准 确 无 误 4. 建 设 完 成 情 况 对 照 表 等 相 关 表 格 栏 高 不 够 请 自 行 增 加 5. 表 格 中 填 写 的 相 关 量
Microsoft Word 葉一隆.doc
 60 3 Journal of Taiwan Agricultural Engineering 103 9 Vol. 60, No. 3, September 2014 ph ph Value Characteristics and Pomacea Canaliculata Culling Performance of Tea Seed Kernel and Sapindus Doses Wan-Chu
60 3 Journal of Taiwan Agricultural Engineering 103 9 Vol. 60, No. 3, September 2014 ph ph Value Characteristics and Pomacea Canaliculata Culling Performance of Tea Seed Kernel and Sapindus Doses Wan-Chu
~ 10 2 P Y i t = my i t W Y i t 1000 PY i t Y t i W Y i t t i m Y i t t i 15 ~ 49 1 Y Y Y 15 ~ j j t j t = j P i t i = 15 P n i t n Y
 * 35 4 2011 7 Vol. 35 No. 4 July 2011 3 Population Research 1950 ~ 1981 The Estimation Method and Its Application of Cohort Age - specific Fertility Rates Wang Gongzhou Hu Yaoling Abstract Based on the
* 35 4 2011 7 Vol. 35 No. 4 July 2011 3 Population Research 1950 ~ 1981 The Estimation Method and Its Application of Cohort Age - specific Fertility Rates Wang Gongzhou Hu Yaoling Abstract Based on the
4 51 1 Scoones 1998 20 60 70 2002 2001 20 90 World Bank DFID Sussex IDS 2012 2 2. 1 UNDP CARE DFID DFID DFID 1997 IDS 2009 1 5
 38 4 2014 7 Vol. 38 No. 4 July 2014 50 Population Research * 30 4 100872 Livelihood and Development Capacity of Families Obeying the Family Planning Policy in Rural China A Sustainable Livelihood Analytical
38 4 2014 7 Vol. 38 No. 4 July 2014 50 Population Research * 30 4 100872 Livelihood and Development Capacity of Families Obeying the Family Planning Policy in Rural China A Sustainable Livelihood Analytical
??? 1
 浙 江 省 肿 瘤 预 防 与 控 制 工 作 介 绍 Introduction to cancer control and prevention in Zhejiang Province 浙 江 省 疾 病 预 防 控 制 中 心 Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention 1 提 纲 (Outline) 流 行 病
浙 江 省 肿 瘤 预 防 与 控 制 工 作 介 绍 Introduction to cancer control and prevention in Zhejiang Province 浙 江 省 疾 病 预 防 控 制 中 心 Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention 1 提 纲 (Outline) 流 行 病
STEAM STEAM STEAM ( ) STEAM STEAM ( ) 1977 [13] [10] STEM STEM 2. [11] [14] ( )STEAM [15] [16] STEAM [12] ( ) STEAM STEAM [17] STEAM STEAM STEA
![STEAM STEAM STEAM ( ) STEAM STEAM ( ) 1977 [13] [10] STEM STEM 2. [11] [14] ( )STEAM [15] [16] STEAM [12] ( ) STEAM STEAM [17] STEAM STEAM STEA STEAM STEAM STEAM ( ) STEAM STEAM ( ) 1977 [13] [10] STEM STEM 2. [11] [14] ( )STEAM [15] [16] STEAM [12] ( ) STEAM STEAM [17] STEAM STEAM STEA](/thumbs/92/108190716.jpg) 2017 8 ( 292 ) DOI:10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2017.08.017 STEAM 1 1 2 3 4 (1. 130117; 2. + 130117; 3. 130022;4. 518100) [ ] 21 STEAM STEAM STEAM STEAM STEAM STEAM [ ] STEAM ; ; [ ] G434 [ ] A [ ] (1970 ) E-mail:ddzhou@nenu.edu.cn
2017 8 ( 292 ) DOI:10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2017.08.017 STEAM 1 1 2 3 4 (1. 130117; 2. + 130117; 3. 130022;4. 518100) [ ] 21 STEAM STEAM STEAM STEAM STEAM STEAM [ ] STEAM ; ; [ ] G434 [ ] A [ ] (1970 ) E-mail:ddzhou@nenu.edu.cn
[29] a N d N b 2 d sin θ N b ФФ a b Ф Ф θ θ a b Fig.1 Working principle demonstration of a phased-array antenna θ
![[29] a N d N b 2 d sin θ N b ФФ a b Ф Ф θ θ a b Fig.1 Working principle demonstration of a phased-array antenna θ [29] a N d N b 2 d sin θ N b ФФ a b Ф Ф θ θ a b Fig.1 Working principle demonstration of a phased-array antenna θ](/thumbs/93/113150193.jpg) 1/(cos cos ) 1 X X 20130576 863 2007AA061901 1988E mailliujun198802@126.com [29] a N d N b 2 d sin θ N b ФФ a b Ф Ф θ θ a b Fig.1 Working principle demonstration of a phased-array antenna θ B A B 1
1/(cos cos ) 1 X X 20130576 863 2007AA061901 1988E mailliujun198802@126.com [29] a N d N b 2 d sin θ N b ФФ a b Ф Ф θ θ a b Fig.1 Working principle demonstration of a phased-array antenna θ B A B 1
Microsoft Word - ED-774.docx
 journal.newcenturyscience.com/index.php/gjanp Global Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice,214,Vol.1,No.1 The practicality of an improved method of intravenous infusion exhaust specialized in operating
journal.newcenturyscience.com/index.php/gjanp Global Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice,214,Vol.1,No.1 The practicality of an improved method of intravenous infusion exhaust specialized in operating
(1) (2) (IVI) (2001) (IVI) 50% ~8% 1~30cm (IVI) Study on the Plant Succession of Slopeland Landslide Areas Following H
 (1) (2) 921 7-200120022006 2008 (IVI)(2001) (IVI) 50% 2008 7~8% 1~30cm (IVI) Study on the Plant Succession of Slopeland Landslide Areas Following Hydroseeding Process Chiao-Shu Feng Graduate Student, Department
(1) (2) 921 7-200120022006 2008 (IVI)(2001) (IVI) 50% 2008 7~8% 1~30cm (IVI) Study on the Plant Succession of Slopeland Landslide Areas Following Hydroseeding Process Chiao-Shu Feng Graduate Student, Department
2015医学版第六期
 第 4 卷 第 6 期 205 年 2 月 Journal of Lanzhou University(Medical Sciences) Vol.4 No.6 Dec. 205 文 章 编 号 :000-282 (205) 06-0054-05 金 昌 队 列 人 群 代 谢 综 合 征 率 及 组 分 分 析 彭 峥, 白 亚 娜, 王 凤 杰 2, 李 娟 生, 李 海 燕 2, 刘 燕 青,
第 4 卷 第 6 期 205 年 2 月 Journal of Lanzhou University(Medical Sciences) Vol.4 No.6 Dec. 205 文 章 编 号 :000-282 (205) 06-0054-05 金 昌 队 列 人 群 代 谢 综 合 征 率 及 组 分 分 析 彭 峥, 白 亚 娜, 王 凤 杰 2, 李 娟 生, 李 海 燕 2, 刘 燕 青,
左下肢多发软组织肿瘤二次术后复发伴梗阻性黄疸一例诊治
 Asian Case Reports in Oncology 亚 洲 肿 瘤 科 病 例 报 告, 2014, 3, 1-5 http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/acrpo.2014.31001 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.hanspub.org/journal/acrpo.html) Diagnosis and Treatment
Asian Case Reports in Oncology 亚 洲 肿 瘤 科 病 例 报 告, 2014, 3, 1-5 http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/acrpo.2014.31001 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.hanspub.org/journal/acrpo.html) Diagnosis and Treatment
~ ~
 * 40 4 2016 7 Vol. 40 No. 4 July 2016 35 Population Research 2014 1 2016 2016 9101. 0 40 49. 6% 2017 ~ 2021 1719. 5 160 ~ 470 100872 Accumulated Couples and Extra Births under the Universal Tw o-child
* 40 4 2016 7 Vol. 40 No. 4 July 2016 35 Population Research 2014 1 2016 2016 9101. 0 40 49. 6% 2017 ~ 2021 1719. 5 160 ~ 470 100872 Accumulated Couples and Extra Births under the Universal Tw o-child
徐 小 平, 等. 封 闭 式 负 压 引 流 技 术 治 疗 Fournier 坏 疽 的 临 床 疗 效 349 结 果 : 治 疗 后 7 14 d 观 察 组 FGSI 均 较 对 照 组 低 (P <0.05), 观 察 组 平 均 清 创 次 数 为 3.8 次, 明 显 少 于 对 照
 wcjd@wjgnet.com 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2015 年 1 月 18 日 ; 23(2): 348-352 ISSN 1009-3079 (print) ISSN 2219-2859 (online) 临 床 经 验 CLINICAL PRACTICE 封 闭 式 负 压 引 流 技 术 治 疗 Fournier 坏 疽 的 临 床 疗 效 徐 小 平, 蔡 晓 辉, 张 磊,
wcjd@wjgnet.com 世 界 华 人 消 化 杂 志 2015 年 1 月 18 日 ; 23(2): 348-352 ISSN 1009-3079 (print) ISSN 2219-2859 (online) 临 床 经 验 CLINICAL PRACTICE 封 闭 式 负 压 引 流 技 术 治 疗 Fournier 坏 疽 的 临 床 疗 效 徐 小 平, 蔡 晓 辉, 张 磊,
168 健 等 木醋对几种小浆果扦插繁殖的影响 第1期 the view of the comprehensive rooting quality, spraying wood vinegar can change rooting situation, and the optimal concent
 第 31 卷 第 1 期 2013 年 3 月 经 济 林 研 究 Nonwood Forest Research Vol. 31 No.1 Mar. 2013 木醋对几种小浆果扦插繁殖的影响 健 1,2 杨国亭 1 刘德江 2 (1. 东北林业大学 生态研究中心 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040 2. 佳木斯大学 生命科学学院 黑龙江 佳木斯 154007) 摘 要 为了解决小浆果扦插繁殖中生根率及成活率低等问题
第 31 卷 第 1 期 2013 年 3 月 经 济 林 研 究 Nonwood Forest Research Vol. 31 No.1 Mar. 2013 木醋对几种小浆果扦插繁殖的影响 健 1,2 杨国亭 1 刘德江 2 (1. 东北林业大学 生态研究中心 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040 2. 佳木斯大学 生命科学学院 黑龙江 佳木斯 154007) 摘 要 为了解决小浆果扦插繁殖中生根率及成活率低等问题
